Last reviewed: 16 Mar 2025
Last updated: 16 Apr 2024
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- digoxin exposure
- gastrointestinal symptoms
- central nervous system symptoms
- visual symptoms
Risk factors
- age >55 years
- decreased renal clearance
- hyperkalemia (>5.0 mEq/L)
- hypokalemia (<3.0 to 3.5 mEq/L)
- concomitant use of specific drugs
- hypomagnesemia
- hypercalcemia
- hypothyroidism
Diagnostic tests
1st tests to order
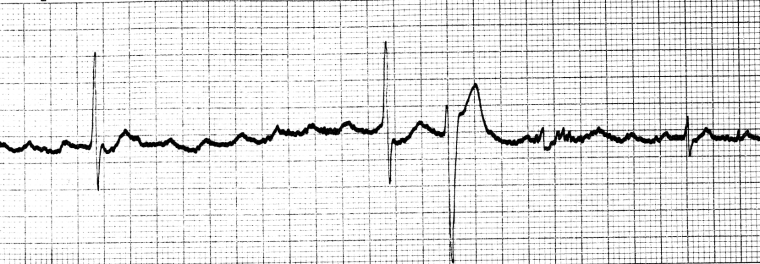
- ECG
- digoxin serum concentration
- serum potassium level
- serum magnesium level
- serum creatinine and BUN
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Scott Phillips, MD
Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine
Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology
University of Colorado
Denver
CO
Associate Medical Director
Washington Poison Center
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
SP declares that he has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Scott Phillips would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Oladapo A. Odujube and Dr Robert S. Hoffman, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
OAO and RSH declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Edward W. Boyer, MD
University of Massachusetts Medical School
Worcester
MA
Disclosures
EWB declares that he has no competing interests.
Ruben Thanacoody, MD, FRCP(Edin)
Consultant Physician and Clinical Toxicologist
National Poisons Information Service (Newcastle)
Newcastle-upon-Tyne
UK
Disclosures
RT declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer