Tests
1st tests to order
pelvic ultrasound
Test
Transvaginal pelvic ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality to evaluate a clinically suspected ovarian mass, providing both qualitative and quantitative information valuable in management.[80][81] Combined transvaginal and transabdominal ultrasound may be useful for evaluating larger masses.[81]
Ultrasound with Doppler imaging can characterize the mass (e.g., cystic, solid, complex), and in most cases can triage the mass into benign or malignant categories.[81][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ovarian cyst with nodules on ultrasoundFrom the collection of Justin C. Chura, MD, Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, PA [Citation ends].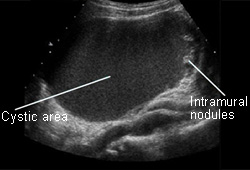 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ovarian cyst with normal Doppler flowFrom the collection of Justin C. Chura, MD, Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, PA [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ovarian cyst with normal Doppler flowFrom the collection of Justin C. Chura, MD, Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, PA [Citation ends].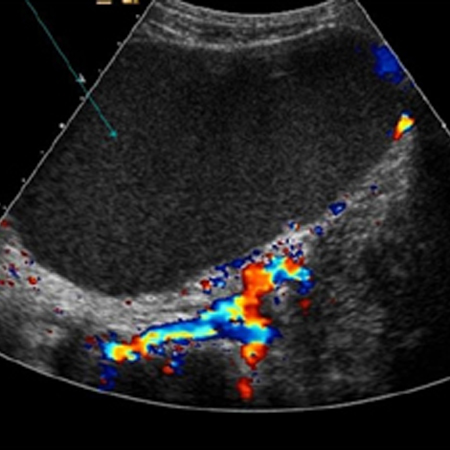 Suspicious masses on ultrasound are typically solid or complex (cystic and solid), septated, and multiloculated and demonstrate a high blood flow (increased Doppler flow).[82]
Suspicious masses on ultrasound are typically solid or complex (cystic and solid), septated, and multiloculated and demonstrate a high blood flow (increased Doppler flow).[82]
If suspicious findings are discovered on ultrasound, referral to a gynecologic oncologist is recommended.[79]
Result
presence of solid, complex, septated, multiloculated mass; high blood flow
CA-125
Test
Serum CA-125 levels are elevated in >80% of women with advanced-stage disease.[91] However, this biomarker is not diagnostic because CA-125 levels can be elevated as a result of nonmalignant conditions (e.g., endometriosis, uterine fibroids, pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, appendicitis, and ovarian cysts) and other malignant conditions (e.g., pancreatic, breast, lung, gastric, and colon cancers).[64] Furthermore, normal CA-125 levels are observed in approximately 50% of patients with early-stage ovarian cancer.[91]
Despite its limitations, it is common practice for clinicians to routinely check CA-125 levels as part of the preoperative evaluation of an adnexal mass.
An elevated CA-125 level is more predictive of malignancy in postmenopausal women than in premenopausal women.[92] In postmenopausal women, a CA-125 level greater than 65 units/mL is reported to have 98% specificity for diagnosing ovarian cancer. In premenopausal women CA-125 levels between 35 and 65 units/mL are associated with a 50% to 60% risk of cancer. Consultation with a gynecologic oncologist is recommended for postmenopausal women with an elevated CA-125, and for premenopausal women with a very elevated CA-125.[79]
CA-125 levels are most useful postoperatively once a histologic diagnosis of ovarian cancer has been confirmed, where it can be used to monitor treatment response and disease recurrence.[93][94] However, use of CA-125 alone for monitoring and detecting disease recurrence has not been found to improve survival.[95]
Sensitivity is high and specificity is low for this test.
Result
may be elevated (>35 units/mL)
histopathology
Test
Definitive diagnosis of ovarian cancer is based on histopathology.[88][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Microscopic view of ovarian cancerFrom the collection of Justin C. Chura, MD, Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, PA [Citation ends].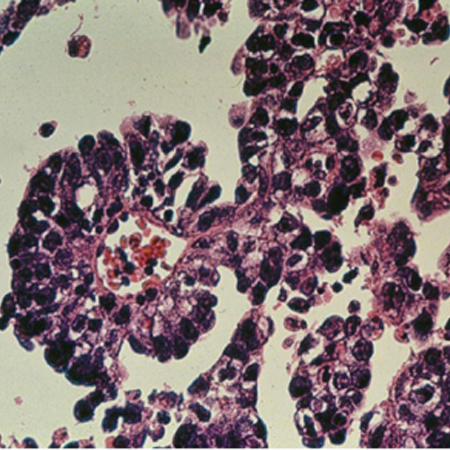 Usually, surgical removal of the affected ovary is necessary for histologic diagnosis. Surgery is also used for staging and tumor debulking (cytoreduction).
Usually, surgical removal of the affected ovary is necessary for histologic diagnosis. Surgery is also used for staging and tumor debulking (cytoreduction).
For premenopausal patients with a suspicious ovarian mass detected on transvaginal ultrasound, surgery is frequently deferred for 2 to 3 menstrual cycles to establish if the mass is functional or physiologic.
Biopsy and fine-needle aspiration (FNA) are not routinely recommended for definitive diagnosis as these procedures can disseminate tumor cells into the peritoneal cavity.[17] They are also prone to sampling error, and may be nondiagnostic. However, for patients unsuitable for surgery, or those with bulky (advanced) disease who are unlikely to achieve complete cytoreduction or optimal (residual disease <1 cm) cytoreduction with surgery, a definitive histologic diagnosis should be obtained by core biopsy (or FNA if biopsy is not possible) prior to initiating neoadjuvant chemotherapy.[17][90]
Result
infiltrative destructive growth best demonstrated by clusters of disorganized cells, usually with desmoplasia
Tests to consider
genetic testing
Test
Genetic risk evaluation, including counseling and genetic testing, is recommended for women with a blood relative with a known pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant in a cancer susceptibility gene, or a strong family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer (BRCA1, BRCA2, ATM, BRIP1, PALB2, RAD51C, RAD51D) or colorectal, endometrial, and/or ovarian cancer (Lynch syndrome variants: MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, PMS2, EPCAM).[14][15][75][76][77][78]
Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of ovarian cancer should undergo genetic risk evaluation and germline and somatic genetic testing (e.g., for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, and other ovarian cancer susceptibility genes) if not previously done.[74][77][88]
Germline testing for a specific pathogenic variant can be carried out, if known; tailored multigene panel testing is recommended if the variant is unknown, based on personal and family history.[14][62][74] BRCA1, BRCA2, and Lynch syndrome genes (MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, PMS2, EPCAM) are generally recommended in multigene panels for patients with ovarian cancer, with further genes added based on personal and family history.[74] Germline testing should be offered regardless of results from tumor testing.[74]
Result
may be positive
PET, PET-CT, or PET/MRI
MRI
Test
In circumstances where ultrasound cannot adequately characterize an ovarian mass, abdominal/pelvic MRI without and with gadolinium contrast may provide additional information (e.g., origin of a mass [uterine, ovarian, tubal]) and help determine if the mass is benign or malignant.[81]
Result
presence of vascular vegetations in cystic masses, and ascites, suggests malignancy
CT scan
Test
CT is less sensitive than ultrasound and MRI in evaluating pelvic organs; therefore, it is not considered part of the standard diagnostic workup for a pelvic or adnexal mass.[81]
CT imaging is mainly used for initial staging of ovarian cancer before initiation of treatment.[83]
CT imaging of the abdomen and pelvis can be used to detect the presence of upper abdominal metastatic disease if suspected on examination.[84][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ovarian masses and ascites on coronal CTFrom the collection of Justin C. Chura, MD, Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, PA [Citation ends].
Chest CT can be used to detect the presence of pleural or pulmonary metastatic disease, and pleural effusion, if suspected on examination.[83]
Result
presence of peritoneal thickening, enlarged lymph nodes, ascites, omental thickening, liver metastases, pleural metastases, pulmonary metastases, pleural effusion
biomarker tests
Test
In the US, several biomarker tests (OVA1, OVERA, and the risk of ovarian malignancy algorithm [ROMA]) have been approved for determining risk of ovarian cancer in women with an ovarian adnexal mass for which surgery is planned. These tests are not to be used as ovarian cancer screening tools (i.e., prior to detection of an adnexal mass) or as stand-alone diagnostic tests.[17]
Testing for other tumor biomarkers (e.g. inhibin, alpha-fetoprotein, beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, lactate dehydrogenase, carcinoembryonic antigen, and CA 19-9) may be useful in the preoperative workup and monitoring of less common ovarian cancers.[17]
Result
individual biomarker levels may be elevated; ovarian cancer risk is reported in the context of menopausal status
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer