History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
erythema migrans
Typical rash that occurs 1 to 2 weeks after a tick bite (range, 1 to 36 days).[2]
Central clearing is classic but not necessary for diagnosis.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema migransFrom the personal collection of Dr Cristian Speil; used with permission [Citation ends].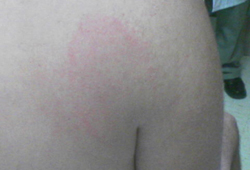 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema migransFrom the personal collection of Dr Cristian Speil; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema migransFrom the personal collection of Dr Cristian Speil; used with permission [Citation ends].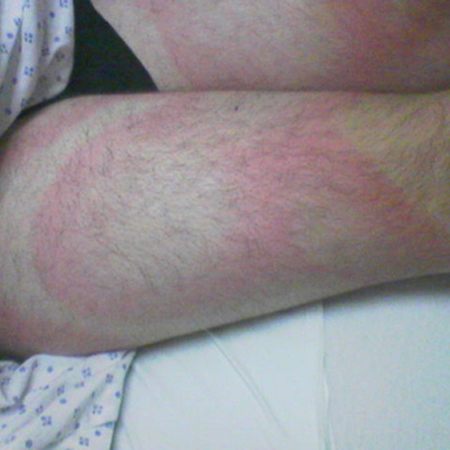 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Posterior right shoulder region of a patient with Lyme disease showing erythema migransCDC Image Library [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Posterior right shoulder region of a patient with Lyme disease showing erythema migransCDC Image Library [Citation ends].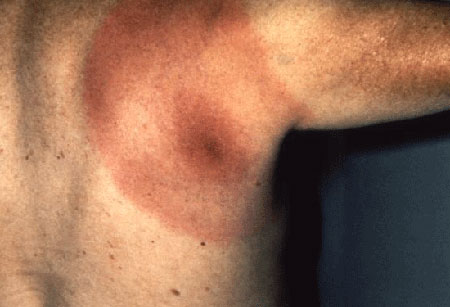 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lateral aspect of the left thigh of a patient who’d presented with what was diagnosed as Lyme disease showing the characteristic red, expanding rash (erythema migrans)CDC Image Library [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Lateral aspect of the left thigh of a patient who’d presented with what was diagnosed as Lyme disease showing the characteristic red, expanding rash (erythema migrans)CDC Image Library [Citation ends].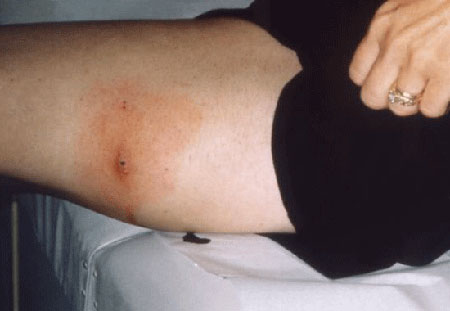
constitutional symptoms
Fever, headache, myalgias, fatigue, or arthralgias may occur after infection.
Nausea and vomiting are rare.
Other diagnostic factors
uncommon
facial palsy
Unilateral facial muscle weakness of the lower motor neuron type (cranial nerve VII) may occur.
Less commonly, Lyme disease causes bilateral facial nerve palsy.
arthritis or arthralgia
Mono- or polyarticular joint swelling and pain most commonly involve the knees.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: This Lyme disease patient presented with the signs and symptoms indicative of arthritic changes to his right knee due to a Borrelia burgdorferi bacterial infectionCDC Image Library [Citation ends].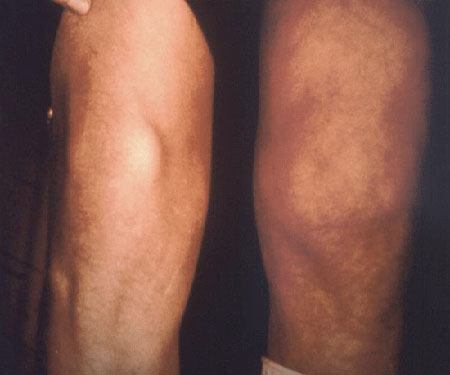
regional lymphadenopathy
Enlargement of draining regional lymph nodes may occur.
stiff neck
Occurs in cases of aseptic meningitis.
lymphocytoma cutis
Painless bluish-red nodule or plaque on the ear lobe, nipple, or scrotum, which has been reported only in Europe.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Borrelial lymphocytomaGzzz, CC BY-SA 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons; used with permission [Citation ends].
acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans
Red to bluish discoloration on the extensor surfaces of extremities, which ultimately becomes atrophic.
Occurs in Europe.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicansNguyen AL et al. Case Reports 2016; 2016: bcr2016216033; used with permission [Citation ends].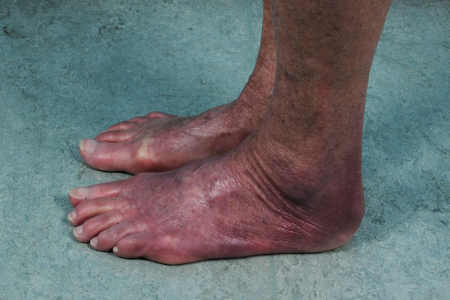
atrioventricular (AV) block or myopericarditis
Cardiovascular complications include carditis with AV block (second- or third-degree) and, less commonly, myopericarditis.
radiculoneuropathy
Neurologic manifestations include painful radiculoneuropathy.
encephalomyelitis, peripheral neuropathy, encephalopathy
Late neurologic complications usually manifest as encephalomyelitis, peripheral neuropathy, or encephalopathy.
Peripheral neuropathy presents as mild diffuse polyneuropathy in a glove and stocking distribution.
Risk factors
strong
exposure to infected ticks
outdoor activities
Occupational, recreational, and residential exposure to tick-infested woods, or fields near woods, in endemic areas is a risk factor.
In general, woods are more risky than fields near woods.
tick bite duration
Duration of feeding by a tick has to be longer than 48 hours for transmission of infection. History of a tick bite is more common in Europe than in the US.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer