Tests
1st tests to order
urinalysis and microscopy of urine sediment
Test
Dysmorphic red blood cells (RBCs), subnephrotic proteinuria, and active sediment points to the presence of GN.
This is reasonably sensitive and specific.
Result
hematuria, proteinuria, dysmorphic RBCs, leukocytes, and RBC casts
comprehensive metabolic profile
Test
Elevated creatinine (indicates severe or advanced disease). Normal creatinine does not exclude significant renal pathology.
Elevated liver enzymes may be seen if etiology is related to hepatitis C virus or hepatitis B virus.
Patients with nephrotic syndrome have hypoalbuminemia.
Result
normal or elevated creatinine, elevated liver enzymes, hypoalbuminemia
estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)
Test
Determined by mathematical equations such as the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) formula, the eGFR gives an indication of the severity and stage of chronic kidney disease. [ Glomerular Filtration Rate Estimate by CKD-EPI Equation Opens in new window ]
More accurate than serum creatinine alone.
Result
normal or reduced
complete blood count
Test
Anemia is a feature of several systemic diseases that are associated with GN.
Result
normocytic normochromic anemia
lipid profile
Test
Patients with nephrotic syndrome have hyperlipidemia.
Result
hyperlipidemia or normal
24-hour urine collection
Test
If proteinuria is detected on urinalysis, 24-hour urine collection should be performed as this is the preferred method for quantifying proteinuria in glomerulonephritis.[1]
Alternatively, spot urine protein:creatinine ratio (PCR) can be performed to estimate 24-hour urinary protein excretion.[1]
Result
protein excretion rate ≥3.5 g per 24 hours indicates nephrotic-range proteinuria
ultrasound of kidneys
Test
Thinning of the cortex and shrunken kidneys indicate a chronic process, thereby reducing the chances of treatment success.
Helps differentiate from other causes of acute kidney injury such as obstructive uropathy.
Result
small kidneys or normal
Tests to consider
spot urine protein:creatinine ratio (PCR)
Test
If proteinuria is detected on urinalysis, 24-hour urine collection should be performed as this is the preferred method for quantifying proteinuria in glomerulonephritis.[1]
Alternatively, spot urine PCR can be performed to estimate 24-hour urinary protein excretion.[1]
Result
PCR ≥3000 mg/g (≥300 mg/mmol) indicates nephrotic-range proteinuria
spot urine albumin:creatinine ratio (ACR)
Test
Not a first-line diagnostic for quantifying proteinuria in GN.[1]
Albumin may only account for around 65% of total urinary protein content.[1]
Result
normal to mildly increased albuminuria: <30 mg/g (<3.39 mg/mmol); moderately increased albuminuria: 30-300 mg/g (3.39 to 33.9 mg/mmol); severely increased albuminuria: >300 mg/g (>33.9 mg/mmol)
erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP)
Test
Nonspecific test; an elevated ESR or CRP indicates systemic inflammation, such as vasculitis.
Result
elevated or normal
complement levels
Test
Help narrow the differential diagnosis: for example, differentiate pauci-immune from some types of immune complex GN.
Result
low or normal C3 in some immune complex diseases
rheumatoid factor
Test
Positive result indicates rheumatoid arthritis or cryoglobulinemia.
Result
positive or normal
antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
Test
Positive result indicates possible pauci-immune glomerulonephritis.[40]
Result
positive or normal
antiglomerular basement membrane (GBM) antibody
Test
Positive result indicates anti-GBM disease or Goodpasture syndrome.
Result
positive or negative
antistreptolysin O antibody
Test
High or rising titers indicate poststreptococcal GN.
Result
high or rising titers, or normal
antihyaluronidase
Test
High or rising titers indicate poststreptococcal GN.
Result
high or rising titers, or normal
anti-DNase
Test
Positive result indicates poststreptococcal GN.
Result
positive or normal
anti-double-stranded DNA
Test
Positive result indicates systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).[41]
Result
positive or normal
antinuclear antibody
Test
High titers indicate SLE.
Result
high titers, or normal
cryoglobulins
Test
Positive result indicates cryoglobulinemia.
Result
positive or normal
hepatitis C virus and hepatitis B virus serology
Test
Positive result indicates acute or chronic hepatitis C virus/hepatitis B virus infection.
Result
positive or normal
HIV serology
Test
Presence of antibody indicates HIV infection. Note that the test is highly sensitive for detecting HIV but not GN.
Result
antibody to HIV, or normal
serum or urine protein electrophoresis
Test
Elevated gamma-globulin associated with several conditions including lymphoma, amyloidosis, and SLE. A monoclonal paraprotein indicates myeloma, immunoglobulin light chain (AL) amyloidosis, monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance, or monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance.
Result
monoclonal or polyclonal gammopathy or normal
serum free light chains
Test
Kappa/lambda ratio may be abnormal in multiple myeloma, amyloidosis, monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance, and monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance.
Result
normal or abnormal kappa/lambda ratio
drug screen
Test
May be useful if suspected drug or medication toxicity.
Result
positive or normal
kidney biopsy
Test
The definitive test for diagnosis of GN.[3] In some circumstances, treatment may proceed without a kidney biopsy confirmation of diagnosis (e.g., biopsy is contraindicated; biopsy result is unlikely to affect treatment or estimate of prognosis; to avoid delaying treatment in patients with rapidly progressive GN).[1][40][42]
Light microscopy, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy will reveal pattern of glomerular injury and severity.
Immunofluorescence and electron microscopy may show patterns of immune complex deposition.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Minimal change nephropathy: the glomerulus has a normal appearanceFrom: Mason PD, Musey CD. BMJ. 1994 Dec 10;309(6968):1557-63 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Crescentic glomerulonephritis with cellular crescent occupying large portion Bowman's capsule and compressing glomerular tuftFrom: Mason PD, Musey CD. BMJ. 1994 Dec 10;309(6968):1557-63 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Crescentic glomerulonephritis with cellular crescent occupying large portion Bowman's capsule and compressing glomerular tuftFrom: Mason PD, Musey CD. BMJ. 1994 Dec 10;309(6968):1557-63 [Citation ends].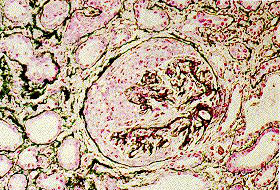 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Light microscopy of kidney biopsy showing typical lesions of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (arrows)Adapted from Nagi AH, Alexander F, Lannigan R. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Dec;24(9):846-50 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Light microscopy of kidney biopsy showing typical lesions of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (arrows)Adapted from Nagi AH, Alexander F, Lannigan R. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Dec;24(9):846-50 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Membranous nephropathy showing fine granular immunofluorescent staining of IgG along basement membraneMason PD, Musey CD. BMJ. 1994 Dec 10;309(6968):1557-63 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Membranous nephropathy showing fine granular immunofluorescent staining of IgG along basement membraneMason PD, Musey CD. BMJ. 1994 Dec 10;309(6968):1557-63 [Citation ends].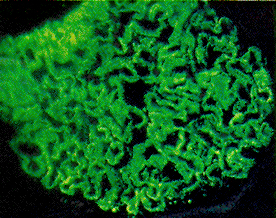 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Membranous nephropathy shows slightly prominent capillary walls that appear more rigid than normal; however, deposits cannot be directly visualized (light microscopy; periodic acid Schiff stain)Fogo AB, Lusco MA, Najafian B, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;66(3):e15-7 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Membranous nephropathy shows slightly prominent capillary walls that appear more rigid than normal; however, deposits cannot be directly visualized (light microscopy; periodic acid Schiff stain)Fogo AB, Lusco MA, Najafian B, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;66(3):e15-7 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Membranous nephropathy with thickened capillary walls with the appearance of numerous pinpoint “holes” in tangential sections, indicating deposits that did not stain (light microscopy; Jones silver stain)Fogo AB, Lusco MA, Najafian B, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;66(3):e15-7 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Membranous nephropathy with thickened capillary walls with the appearance of numerous pinpoint “holes” in tangential sections, indicating deposits that did not stain (light microscopy; Jones silver stain)Fogo AB, Lusco MA, Najafian B, et al. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;66(3):e15-7 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis showing (left) thickened capillary loops with diffuse cellular proliferation, giving characteristic "lobular" appearance (light microscopy; stains: hematoxylin and eosin) and (right) coarse patchy granular immunofluorescent staining of IgM along capillary loopsFrom: Mason PD, Musey CD. BMJ. 1994 Dec 10;309(6968):1557-63 [Citation ends].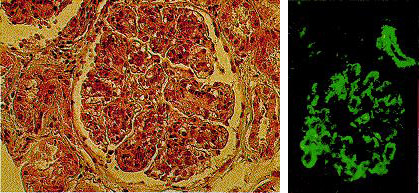
Result
characteristic findings on light, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy
antiphospholipase A2 receptor antibodies
Test
A positive result is seen in patients with membranous GN.
Result
positive or normal
computed tomographic scan of chest and abdomen
Test
May be important to exclude malignancy in older patients.
Result
normal or positive for malignancy
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer