Differentials
Common
Viral gastroenteritis
History
characterized by foul-smelling watery diarrhea, fever, multiple episodes of vomiting, and abdominal pain; usually self-limited but significant volume depletion and malnutrition can occur
Exam
signs of volume depletion (i.e., depressed anterior fontanel in infants, sunken eyes, dry mucosal membranes, sticky saliva, loss of skin turgor, slow capillary refill) may be present; mild abdominal tenderness, hyperactive bowel sounds
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Bacterial gastroenteritis
History
history of contaminated water/food, diarrhea (may be bloody or mixed with mucus), abdominal pain, fever, and multiple episodes of vomiting
Exam
abdominal distension and tenderness, signs of volume depletion (i.e., depressed anterior fontanel in infants, sunken eyes, dry mucosal membranes, sticky saliva, loss of skin turgor, slow capillary refill) may be present
1st investigation
- stool culture:
positive for causative bacteria in some cases
More - stool microscopy:
presence of red blood cells and neutrophils
Other investigations
- stool serotyping/polymerase chain reaction (PCR):
positive for causative bacteria
More
Giardiasis
History
history of travel, contaminated water/food, IgA deficiency, foul-smelling watery/fatty stools, abdominal pain, bloating, or weight loss
Exam
usually unremarkable in acute disease but abdominal distension, pallor, edema, or growth retardation can occur in chronic disease
1st investigation
- stool microscopy:
presence of cysts and trophozoites
- stool antigen detection:
positive for cyst wall
More
Other investigations
- duodenal aspirates and biopsies:
presence of cysts and trophozoites
Migraine
History
headache (paroxysmal episodes that can be unilateral or bilateral), photophobia; these symptoms may be preceded by an aura
Exam
usually normal
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
- MRI head:
almost always normal, rules out intracranial lesion
More
Motion/travel sickness
History
history of passive movement (can be visual), dizziness, eructation, increased salivation, and malaise
Exam
often normal but pallor, diaphoresis, unsteadiness, and lack of coordination can be seen
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
Labyrinthitis
History
history of vertigo, dizziness, hearing loss, tinnitus, otalgia, and flu-like symptoms; irritation of the vestibular system can be secondary to trauma, central nervous system, ear infection, or vestibular neuritis
Exam
nystagmus or signs of infection in the ear
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
- audiogram:
sensorineural hearing loss
- MRI head:
normal or evidence of enhancement in the inner ear
More
Concussion (mild traumatic brain injury)
History
history of head trauma or participation in contact sport; symptoms include headache, altered mental status, confusion, amnesia, and behavioral changes; loss of consciousness does not always occur
Exam
altered mental and cognitive status, confusion, altered coordination, normal neurologic exam
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
- CT/MRI head:
normal
More
Meningitis
History
headache, nuchal rigidity, photophobia, fever, altered mental status, confusion, history of previous infection; with infants, irritability, lethargy, and poor feeding
Exam
bulging fontanel indicates increased intracranial pressure (infants); seizures, petechial or purpuric rash, nuchal rigidity (uncommon in children <2 years of age; absence does not exclude meningitis), and Kernig or Brudzinski signs can occur; some children may not exhibit meningeal signs
1st investigation
- cerebrospinal fluid cell count:
elevated WBC count
- cerebrospinal fluid protein:
elevated (bacterial); elevated or normal (viral)
- cerebrospinal fluid glucose:
may be low
- cerebrospinal fluid Gram stain:
may be positive (bacterial)
- cerebrospinal fluid culture:
may be positive
Other investigations
- blood culture:
may be positive
- CBC:
may be elevated WBC count, left shift, low platelets
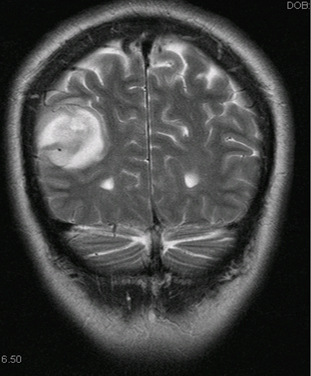
Brain tumor
History
irritability and lethargy in infants; headache or nausea/vomiting on waking, abnormal gait, seizures, and behavioral changes in older children
Exam
bulging fontanel and macrocephaly in infants; papilledema, focal neurologic signs, and cranial nerve paralysis in older children
1st investigation
- CT/MRI head:
presence of mass, empty sella, flattening of the globe; posterior fossa, leptomeningeal, or subarachnoid spread
More
Other investigations
Hydrocephalus
History
irritability and lethargy in infants; headache or nausea/vomiting on waking and behavioral changes in older children; associated with prematurity, meningocele, and genetic syndromes
Exam
bulging fontanel, macrocephaly, dilated scalp veins, frontal bossing, and spasticity in infants; papilledema and cranial nerve paralysis in older children; may result in brain injury if not treated
1st investigation
Other investigations
Pyloric stenosis
History
family history, more common in males, symptoms usually presents between 2 and 12 weeks of age, postprandial nonbilious projectile vomiting (usually contains ingested formula content), lack of weight gain or weight loss
Exam
undernourished infant, presence of mobile epigastric mass (rarely detected), visible peristalsis; signs of volume depletion may be present; jaundice may occur
1st investigation
- ultrasound abdomen:
pylorus muscle thickness >4 mm, pyloric canal length >17 mm
More
Other investigations
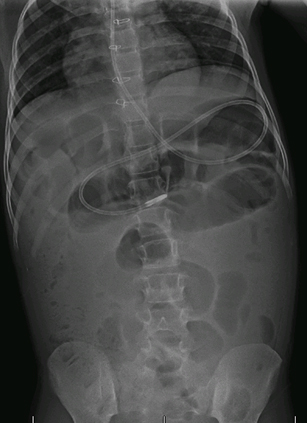
Intussusception
History
usual age 3-6 months (up to 5 years), abdominal pain alternating with periods of exhaustion, hematochezia (may be described as currant jelly stool)
Exam
abdominal distension and abdominal mass may be present; may cause intestinal necrosis, acute abdomen, or obstruction
1st investigation
- plain abdominal x-ray:
may be normal but "target sign", visible abdominal mass, or obstruction possible
More - ultrasound abdomen:
hypoechoic ring with hyperechoic center
Other investigations
- diagnostic/therapeutic air or contrast enema:
meniscus sign, coiled spring sign
More
Intestinal malrotation
History
onset <1 month age with bilious vomiting; more concerning symptoms include hematochezia, abdominal distension, and shock; for older children, presents as chronic vomiting and poor weight gain
Exam
exam initially normal but may demonstrate rapid progression to acute abdomen secondary to bowel necrosis; there is a high risk of midgut volvulus and intestinal necrosis
1st investigation
Other investigations
- CT abdomen (with oral and intravenous contrast):
no oral contrast beyond duodenum (volvulus); no contrast in the distal superior mesenteric artery (volvulus with ischemia); twirling of the superior mesenteric artery and vein (volvulus); transposition of superior mesenteric artery and vein (malrotation); a transition point in bowel caliber, right-sided duodenum; duodenum courses anterior or to right of superior mesenteric artery
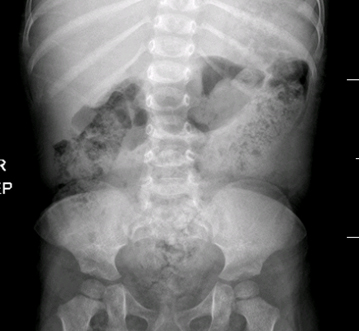
Small bowel atresia
History
history of polyhydramnios or Down syndrome with symptoms of feeding intolerance and vomiting appearing soon after birth
Exam
abdominal distension (absent in proximal atresia, severe with visible loops in distal compromise, tenderness indicates peritonitis, mass indicates meconium peritonitis), possible failure to pass meconium, signs of volume depletion may be present
1st investigation
- plain abdominal x-ray:
double bubble sign, proximal presence of gas with distal absence
Diabetic ketoacidosis
History
poorly controlled diabetes type 1 is typical; may be first manifestation of diabetes with polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, weight loss, drowsiness, lethargy, anorexia, and abdominal pain
Exam
altered mental status, acetone breath, tachycardia, hypotension, hyperventilation, and signs of volume depletion can be present; can cause severe complications or even death if untreated
1st investigation
- blood glucose level:
elevated
- urinalysis:
positive for glucose and ketones
- serum electrolytes:
sodium (low); potassium (elevated); chloride (low); magnesium (low); calcium (low); phosphate (normal or elevated)
- anion gap:
elevated anion gap
- ABG:
pH varies from 7.00 to 7.30, arterial bicarbonate ranges from <10 mEq/L to >15 mEq/L
- serum ketones:
positive
Other investigations
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
History
regurgitation is present in 50% of infants with no other symptoms; symptoms include feeding refusal, irritability, hematemesis, failure to thrive (infants), laryngitis (children), and heartburn/acid regurgitation (adolescents)
Exam
usually normal, pallor (due to anemia in severe cases)
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment but may vary widely by age; obtain a detailed history from from the patient, parent, or caregiver
Cyclic vomiting
History
family history of migraine, stereotypical episodes of vomiting for hours or days, episodes alternate with normal periods of health; lethargy, headache, and diarrhea may be present
Exam
usually normal, absence of red flags (e.g., weight loss, neurologic findings, papilledema, anemia, abdominal mass tenderness, positive fecal occult blood)
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Gastroparesis
History
may occur after a viral disease or be associated with systemic conditions; symptoms include postprandial vomiting of food contents 1-4 hours after meals, poor appetite, early satiety, and abdominal pain
Exam
usually normal but abdominal distension may be present
1st investigation
- gastric emptying scintigraphy:
gastric retention of >90%, 60%, and 10% at the end of 1, 2, and 4 hours, respectively; liquid phase contrast in infants and solid phase in children
Constipation
History
usual age less than 1 year or 2-4 years with fewer than 3 bowel movements per week, withholding maneuvers, toilet avoidance, straining, large stools, and fecal incontinence
Exam
abdominal distension, fecal mass palpated in the abdomen
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
More
Functional dyspepsia
History
children and adolescents with epigastric abdominal pain, indigestion, early satiety, and absence of red flags (e.g., weight loss, blood in stool or urine, fever, vomiting, abnormal growth)
Exam
usually normal
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
- fecal occult blood:
negative
- CBC:
normal
- complete metabolic profile:
normal
- ESR:
normal
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy:
normal
More
Testicular torsion
History
males with acute onset of testicular/scrotal pain and abdominal pain; nausea and vomiting occur in many patients
Exam
scrotal edema or erythema with scrotal tenderness to palpation
1st investigation
Other investigations
- scintigraphy:
decreased uptake of radioactive technetium-99m to the affected testicle
More
Urinary tract infection
History
fever, irritability, lethargy, poor feeding, and failure to thrive in infants and toddlers; dysuria, urinary frequency, and flank pain in children and adolescents
Exam
usually normal; suprapubic tenderness in infants; costovertebral tenderness seen with pyelonephritis in children and adolescents
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
positive leukocyte esterase and/or nitrites
- urine culture:
catheter: urine specimens obtained by catheter: >10,000 colony-forming units (cfu)/mL in a symptomatic child
More
Other investigations
Nephrolithiasis
History
positive family history, acute severe flank/abdominal pain, hematuria, dysuria, urgent nausea and vomiting
Exam
costovertebral angle tenderness
1st investigation
- urinalysis:
may be normal or positive for blood
- noncontrast CT abdomen:
calcification seen within urinary tract
More
Other investigations
- ultrasound renal:
calcification seen within urinary tract
More
Peptic ulcer disease
History
risk factors include Helicobacter pylori infection, chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, and stress; symptoms include irritability and feeding intolerance in infants and toddlers; dyspepsia, epigastric pain, hematemesis, and melena in children and adolescents
Exam
epigastric tenderness, pointing sign, and pallor in presence of anemia; can lead to bleeding, anemia, or stricture if diagnosis is missed
1st investigation
- fecal occult blood:
occult blood may be present
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy plus biopsy:
peptic ulcer; may also detect cause (e.g., Helicobacter pylori)
Other investigations
Acute appendicitis
History
abdominal pain, anorexia, and fever
Exam
right lower quadrant tenderness, Rovsing sign, psoas sign, obturator sign, and diminished bowel sounds
1st investigation
- CBC:
mild leukocytosis
- ultrasound abdomen:
aperistaltic or noncompressible structure in region of appendix with outer diameter >6 mm
Other investigations
- CT abdomen/pelvis:
abnormal appendix (diameter >6 mm) identified or calcified appendicolith seen in association with periappendiceal inflammation
Acute pancreatitis
History
midepigastric abdominal pain (may radiate to back), anorexia, and malaise
Exam
epigastric and periumbilical abdominal pain on palpation and signs of volume depletion may be present
1st investigation
Other investigations
- abdominal ultrasound:
assess for obstructive gallstone
Hepatitis A
History
often asymptomatic but fever, malaise, jaundice, and abdominal pain may be present
Exam
usually normal; jaundice, hepatomegaly, and right upper quadrant abdominal tenderness can be present but are more common in adolescents
1st investigation
- serum aminotransferases:
elevated
- serum bilirubin:
elevated
Lactose intolerance
History
frequent in Asian and African-American people; can be secondary to prematurity, gastroenteritis, or medications; family history, abdominal pain, flatulence, diarrhea, and symptoms after ingestion of dairy products
Exam
usually normal; may note abdominal distension after lactose ingestion and a perianal erythematous rash due to carbohydrate malabsorption
1st investigation
- fecal pH:
reduced
- lactose hydrogen breath test:
breath hydrogen >20 parts per million after lactose load and intolerance symptoms
Other investigations
- small bowel biopsy:
normal or reduced intestinal lactase and/or other disaccharidases
Food allergy
History
onset generally <1 year of age with cough, rash, diarrhea or constipation, hematochezia, and failure to thrive; symptoms often associated with wheat, milk, soy, egg, peanut, or shellfish ingestion
Exam
eczema, rhinitis, wheezing, pallor, and abdominal distension
1st investigation
- in vitro IgE-specific immunoassay:
depends on food allergen
Other investigations
- skin prick testing:
wheal diameter 3 mm greater than control
- atopy patch testing:
erythema and induration
Eosinophilic disease
History
dysphagia, choking with eating, food impaction, and atopy with eosinophilic esophagitis; diarrhea, hematochezia, and failure to thrive with eosinophilic gastroenteritis
Exam
usually normal but may note pallor, eczema, and abdominal distension
1st investigation
- CBC:
possible peripheral eosinophilia
- serum immunoglobulins:
IgE elevated
Other investigations
- esophagogastroduodenoscopy plus biopsy:
furrowing stricture, whitish papules, ≥15 eosinophils/high-power field (eosinophilic esophagitis); >20-25 eosinophils/high-power field (eosinophilic gastroenteritis)
Bulimia nervosa
History
recurrent episodes of binge eating with self-induced vomiting, uncontrolled food intake, concern about weight gain/ body image, depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and hematemesis
Exam
dental enamel erosion, pallor, signs of volume depletion may be present, and arrhythmia
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
- CBC:
anemia
- complete metabolic panel:
may show: hypokalemia, elevated creatinine, hypomagnesemia, elevated LFTs
- ECG:
may be abnormal
Toxic ingestion
History
witnessed or deliberate ingestion or medication error; symptoms vary from mild and nonspecific to severe and depend on toxin ingested; examples of ingestions in children ages ≤5 years are cosmetics, cleaning substances, analgesics, pesticides, cough and cold preparations, cardiovascular drugs, stimulants and street drugs, and essential oils
Exam
symptoms range from normal to altered mental status, hypoxemia, seizures, hypotension, arrhythmias, respiratory depression, and possible death
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
- ECG:
characteristic changes of causative agent, arrhythmias
- serum electrolytes:
can be abnormal
- ABG:
hypoxemia, metabolic acidosis, respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis
- comprehensive urine drug screen:
possible identification of toxin or drug
- serum drug levels:
drug level detected
More
Medication adverse effects
History
history of taking drug known to cause nausea and vomiting (e.g., chemotherapy, opioid analgesics, anticholinergic drugs such as antidepressants or antispasmodics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics)
Exam
nonspecific
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
Uncommon
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
History
common cause of vertigo in children with intermittent episodes of vertigo alternating with normal periods, disequilibrium, diaphoresis, and specific provoking positions
Exam
nystagmus during Dix-Hallpike maneuver with normal exam between episodes
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment with nystagmus during Dix-Hallpike maneuver
Other investigations
Pseudotumor cerebri (benign intracranial hypertension)
History
family history, visual field loss, diplopia, headache, tinnitus, obesity, and specific medication history (e.g., nalidixic acid, nitrofurantoin, indomethacin, isotretinoin, lithium, anabolic steroids)
Exam
papilledema, cranial nerve paralysis, and decreased visual function
1st investigation
- MRI head:
negative intracranial and intraorbital pathology, empty sella, flattening of the globe
Other investigations
- lumbar puncture:
elevated pressure: opening pressure >250 mm H₂O
More
Superior mesenteric artery syndrome
History
recent weight loss, prolonged bed rest, or spinal surgery with intermittent nausea/vomiting and abdominal pain following eating; symptoms improve in left lateral or prone position
Exam
thin body habitus and low weight; upper abdominal distension not always present
1st investigation
- upper gastrointestinal series:
stomach dilatation, cut-off sign, obstruction in the third portion of the duodenum with possible positional improvement
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
duodenal compression between aorta and superior mesenteric artery
More
Addison disease (primary adrenal insufficiency)
History
secondary to autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, or chronic use of corticosteroids; symptoms include lethargy, anorexia, weight loss, failure to thrive, and salt craving
Exam
hypotension and oral hyperpigmentation; may result in shock if left untreated
1st investigation
- serum electrolytes:
hyponatremia, hyperkalemia
- morning serum cortisol level:
cortisol <5 micrograms/dL
More
Other investigations
- adrenal stimulation testing:
serum cortisol <18 micrograms/dL
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
History
failure to thrive, weight loss, poor feeding, irregular menses, and precocious puberty
Exam
hypotension, hyperpigmentation, hirsutism, and ambiguous genitalia in neonates
1st investigation
- serum electrolytes:
hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, metabolic acidosis
- serum 17-hydroxyprogesterone:
elevated for age
Other investigations
Protein metabolism disorders
History
includes organic acidemias and urea cycle disorders; newborn or infant with possible family history, poor feeding, failure to thrive, and lethargy; metabolic crisis may be precipitated by illness or surgery
Exam
seizures, floppiness, and low muscular tone
1st investigation
- venous pH CO₂:
acidosis (aminoaciduria), alkalosis (urea cycle disorders)
Other investigations
- serum ammonia level:
elevated (aminoaciduria), markedly elevated (urea cycle disorders)
More - plasma amino acids/organic acids:
abnormal
Carbohydrate metabolism disorders
History
includes galactosemia and fructosemia; newborn or infant with poor feeding, vomiting after feeds, lethargy, and bleeding; may lead to liver dysfunction, sepsis, or brain damage
Exam
septic appearance, jaundice, and hepatomegaly
1st investigation
- LFTs:
elevated aminotransferases (galactosemia, fructosemia)
- urine sugars/reducing substances:
galactose (galactosemia), fructose (fructosemia)
Other investigations
- blood enzyme determination:
abnormal
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
History
occurs more frequently in adolescents and girls with symptoms usually occurring in the morning or with postural changes; nausea is commonly associated with orthostatic dizziness, anxiety, fainting/near-fainting episodes, abdominal pain, early satiety, bloating, and constipation
Exam
orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia, and skin color changes
1st investigation
- orthostatic vital signs (screening):
heart rate increase >20 bpm or systolic BP decrease >20 mmHg when standing
- tilt-table test (diagnosis):
orthostatic tachycardia with changing position
Other investigations
Hirschsprung disease
History
passage of meconium greater than 48 hours after birth with explosive diarrhea, bilious vomiting, and failure to thrive
Exam
abdominal distension and absence of stool in rectal vault with possible production of large volume watery stool on rectal exam
1st investigation
- contrast enema:
transition zone possible
More
Other investigations
- anorectal manometry:
absent rectoanal inhibitory reflex
- rectal biopsy:
absence of ganglion cells, increased acetylcholinesterase stain
Ovarian torsion
History
adolescent females with severe sharp lower abdominal pain and fever; vaginal bleeding uncommon
Exam
abdominal distension, abdominal/pelvic tenderness, palpable adnexal mass, and tachycardia
1st investigation
- ultrasound abdomen with Doppler:
solid, cystic, or complex adnexal mass with decreased blood flow to ovary
More
Other investigations
- CT abdomen:
may show fallopian tube thickening, smooth wall thickening of the twisted adnexal cystic mass, ascites, and uterine deviation toward the twisted side
More
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
History
children generally <5 years of age with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea; fever can be absent; seizures can be present
Exam
hypertension, pallor, petechiae, and peripheral edema
1st investigation
Other investigations
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
History
frequently diagnosed prenatally; symptoms depend on age but can include hematuria and failure to thrive in infants, and recurrent abdominal or back pain with cyclic vomiting in older children
Exam
abdominal mass in infants
1st investigation
- ultrasound renal:
hydronephrosis
Other investigations
- diuretic renogram:
lack of excretion in the affected side
Small bowel lymphoma
History
higher incidence in celiac disease and certain gastrointestinal infections (e.g., Campylobacter); abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fever, and bilious vomiting if obstruction present
Exam
pallor, abdominal distension, abdominal tenderness, presence of mass on palpation, organomegaly, ascites, clubbing, signs of obstruction or perforation
1st investigation
- CT abdomen:
presence of mass or obstruction
Other investigations
- upper gastrointestinal series plus small bowel follow-through:
mucosal fold thickening or obstruction
Rumination
History
usually in developmentally delayed children but may also occur with normal development; presence of postprandial effortless oral regurgitations (contents may be re-swallowed) with absence of heartburn or nausea, and weight loss
Exam
usually normal but dental erosions can be present
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Factitious disorder
History
perpetrator is frequently one parent, who may be involved in healthcare industry; presence of multiple unexplained symptoms, including nausea and vomiting, where symptoms do not improve despite medical management; may lead to severe iatrogenic surgery and even death if diagnosis missed
Exam
usually normal
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Cannabis hyperemesis syndrome
History
frequent to daily cannabis use, intermittent nausea and vomiting, compulsory bathing behaviors that improve symptoms, insomnia, polydipsia, and abdominal pain; does not respond to treatment with medications
Exam
usually normal
1st investigation
- urinary drug screen:
positive for cannabinoids
Other investigations
Otitis media
History
fever, sleep disturbance, headache, diarrhea, irritability in infants, otalgia in older children, poor appetite
Exam
bulging, erythematous, or opaque tympanic membrane; myringitis
1st investigation
- clinical exam:
usually diagnosed by clinical assessment
Other investigations
Pneumonia
History
symptoms depend on age but can include fever, lethargy, cough, dyspnea, chest pain, poor oral intake, and abdominal pain
Exam
respiratory distress (tachypnea, cyanosis, retractions, decreased breath sounds and crackles, low oxygen saturation); sepsis and respiratory failure can occur if diagnosis missed
1st investigation
- chest x-ray:
infiltration, consolidation, effusions, cavitation
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer