Tests
1st tests to order
prenatal triple/quadruple test
Test
Triple screen includes AFP (alpha-fetoprotein), hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), and uE3 (unconjugated estriol), while the quadruple screen also includes inhibin A. These tests are routinely offered between 15 and 20 weeks' gestation.
A mathematical calculation involving the levels of these 3 or 4 substances and considerations of maternal age, weight, race, and diabetic status are used to determine risk. Both the triple and the quadruple screen can detect about 75% to 80% of pregnancies affected by spina bifida and nearly 95% of those with anencephaly.[72]
Result
elevated
prenatal ultrasound
Test
Fetal ultrasound is used to document size and location of the neural tube defect and to identify presence of hydrocephalus and other midline congenital anomalies. The so-called "lemon" sign refers to the shape of the fetal skull in transverse views on fetal head ultrasonography. It is present when there is hydrocephalus, and is due to frontal bones losing their normal convex contour and appearing flattened or inwardly scalloped.
The "banana" sign is seen on transverse views of the fetal head when Chiari malformation is present. It is due to the obliteration of the cisterna magna and loss of normal roundness of the cerebellar hemispheres.
Result
may show flattened or inwardly scalloped frontal bones (lemon sign); obliteration of cisterna magna and loss of normal roundness of cerebellar hemispheres may be seen (banana sign)
fetal MRI
Test
Considered a useful adjunct to ultrasound. Fast MRI of the fetus can be used to better define structural brain anomalies that may be associated with some neural tube defects. It may also provide additional information to guide neurosurgical management in select cases.[69][70]
Performed when prenatal fetal surgery is being considered or if there are unclear findings on ultrasonography.[75] The absence of a covering membrane is associated with scoliosis and high-risk bladder dysfunction.[79][80]
Result
identifies topography, contents of sacs, CNS and non-CNS findings
cranial ultrasound
Test
Used to estimate cortical mantle thickness and monitor progression of ventricle size in infants prior to shunt placement. Asymptomatic infants who have stable, mild, or moderate ventriculomegaly may be monitored safely for up to 5 months as long as cortical mantle thickness is at least 3.5 cm.
Result
cortical mantle thickness, ventricle size
spinal ultrasound
Test
Recommended in neonates with lumbosacral stigmata known to be associated with spinal dysraphism, such as midline or paramedian masses and/or neurocutaneous markings, pinpoint midline dimples, and paramedian deep dimples.[85]
Result
may show tethering, diastomyelia, hydromyelia, or syringomyelia
CT head
Test
Although cranial ultrasound is typically used to monitor for progression of hydrocephalus in newborns and infants, a CT scan may also be performed after shunt insertion to confirm ventriculoperitoneal catheter placement and evaluate ventricle size. Low-radiation techniques should be used, and repeated exposure should be avoided if alternate imaging modalities are available.
Result
evaluates ventricular size and tonsillar ectopia; confirms ventriculoperitoneal catheter placement
urine culture
Test
Urine culture should be obtained in all newborns with spina bifida. In the first 2 months of life, bacteriuria, even if asymptomatic, should be treated. This is because urinary tract infection can be difficult to diagnose in neonates, it can rapidly progress to sepsis, and there is a greater risk of cortical scarring in the neonatal period compared with older age groups.
Result
positive or negative
serum BUN and creatinine
Test
Elevated creatinine is evidence of upper tract compromise. Should be obtained once infant is more than 5 days old. Earlier studies reflect maternal levels.
Result
normal or elevated
renal ultrasound
Test
For a newborn, renal and bladder ultrasound should be obtained several days after the cele repair as a baseline investigation for neurogenic bladder.
Result
evaluates kidney size and configuration; estimates bladder capacity; determines presence of hydronephrosis
urodynamic study
Test
Regarded as the primary diagnostic study for neurogenic bladder. Typically obtained between 6 and 12 months of age. It is used to determine whether the patient has a high-risk versus low-risk bladder with regards to upper tract deterioration.
A leak-point pressure >40 cm of water, the presence of detrusor sphincter dyssynergia, and small bladder capacity due to detrusor hyperreflexia are associated with a high-risk bladder and considered an indication to initiate intermittent catheterization.
Result
determines detrusor leak-point pressure, presence of detrusor sphincter dyssynergia, as well as bladder capacity and compliance
voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG)
Test
VCUG is performed only if the renal ultrasound shows hydronephrosis, to identify whether vesicoureteral reflux is present and antibiotic prophylaxis is indicated. Most centers prefer to perform a urodynamic study at 4 to 6 weeks of age for this purpose. However, not all centers are able to perform urodynamic studies in neonates; some will just perform a renal and bladder ultrasound plus a VCUG to assess bladder function at this stage.
Result
may show vesicoureteral reflux
Tests to consider
prenatal amniocentesis or postnatal chromosomal analysis
Test
Testing for associated trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 is usually offered prenatally by amniocentesis. However, if not performed in the prenatal period, chromosome analysis may be necessary if the newborn exam documents other major congenital anomalies or if there are more than 3 minor congenital anomalies in addition to spina bifida.
Trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 are both associated with a poor outcome.
Result
may show trisomy 13 or trisomy 18
fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) testing
Test
Indicated (if not already done prenatally) if the newborn exam documents other major congenital anomalies or if there are more than 3 minor congenital anomalies in addition to the spina bifida.
Result
may show 22q deletion syndrome
MRI brain and spine
Test
MRI is indicated if Chiari symptoms are severe or if the neurologic exam is markedly asymmetric. Chiari malformation is the caudal displacement of the cerebellar tonsils and vermis, caudal medulla, and occasionally the fourth ventricle, into the cervical spinal canal. Some centers offer myelo series MRI. This is an abbreviated MRI sequence designed to screen for ventriculomegaly, Chiari, tethered cord, and syrinx as one limited study, consisting mainly of T1-weighted sagittal views of the entire spine and axial views of the head. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Brain MRI scan showing Chiari malformationFrom the collection of Dr Nienke P. Dosa; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Spine MRI scan showing tethered cordFrom the collection of Dr Nienke P. Dosa; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Spine MRI scan showing tethered cordFrom the collection of Dr Nienke P. Dosa; used with permission [Citation ends].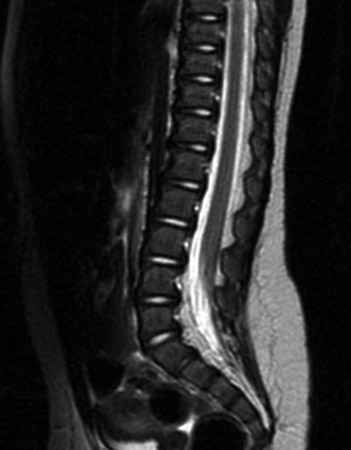
Imaging or interventions requiring sedation or general anesthesia should be avoided in young patients with low-risk asymptomatic lesions due to the risk of sedation/anesthesia to the developing child.[67]
Result
agenesis of corpus callosum, cerebellar tonsil ectopia, brainstem compression, ventriculomegaly, syrinx
hip ultrasound
Test
Hip ultrasound is obtained for infants with low lumbar and sacral motor-level defects (likely to be ambulatory) who have asymmetric hip abduction or positive Barlow or Ortolani sign (eliciting a clunk from the hip as it relocates).
Controversy exists as to whether imaging is needed for children with higher functional motor levels, because treatment is of little benefit and there is a high risk of re-dislocation in nonambulatory children.
Result
subluxation at hip in infants ≤3 months of age
hip x-ray
Test
For infants with sacral motor levels (likely to be ambulatory) >3 months of age, hip radiographs are preferred over ultrasound if hip exam is abnormal: asymmetric hip abduction or positive Barlow or Ortolani sign (eliciting a clunk from the hip as it relocates). Beyond 3 months of age, conventional x-ray studies are used to evaluate the hips. Imaging of hips is not recommended for children with higher lesion levels because treatment is of little benefit and there is a high risk of re-dislocation in nonambulatory children.[89]
Result
abnormal relationship between femoral head and acetabulum
fetal echocardiography
Test
Fetal echocardiography may be considered if prenatal ultrasound suggests a congenital cardiac malformation, or a genetic syndrome associated with cardiac defects is suspected.
Result
may be abnormal
polysomnography
Test
Polysomnography should be considered across the lifespan of the patient, to identify Chiari-related sleep-disordered breathing such as central sleep apnea and hypoventilation.
Result
may be abnormal
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer