History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
positive family history of PHP
Types Ia and Ic have an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. Due to the poor reproductive capacity of people who have types Ia or Ic, little information is available regarding how frequently the mutation is passed on.[26]
Type Ib is usually sporadic, although familial cases are reported.[27][28]
The inheritance of type II is unknown, but it has been hypothesized that it may be an acquired defect secondary to vitamin D deficiency.[6]
muscle cramp
Many patients with mild hypocalcemia are asymptomatic, but muscle cramp is the most common symptom encountered.
paresthesias
Affect the lips, fingers, or toes.
A common early symptom of hypocalcemia.
muscle twitches
A sign of severe hypocalcemia.
positive Chvostek sign
Elicited by tapping a finger on the facial nerve in front of the tragus of the ear with the mouth slightly opened.
Twitching of the ipsilateral facial muscles is considered positive and is a sign of hypersensitivity of the nerve fibers.
Occurs in hypocalcemia but is not specific.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Eliciting Chvostek signCooper MS, Gittoes NJL. BMJ. 2008 Jun 7;336(7656):1298-302 [Citation ends].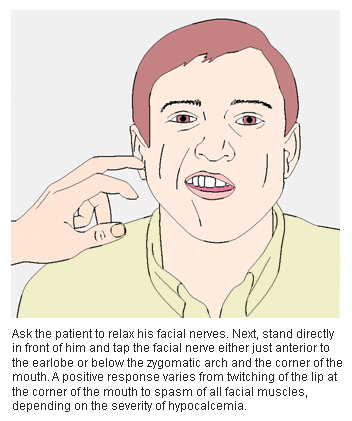
intellectual disability
A key feature of PHP.
Albright hereditary osteodystrophy
Features include short stature (height <10ᵗʰ percentile), stocky habitus, round face, brachymetacarpals, brachymetatarsals, BMI 95ᵗʰ percentile or greater, and dental abnormalities.
Dental abnormalities include enamel hypoplasia, absent or delayed tooth eruption, and short or blunted roots.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Child with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy showing a round face and a short nose with a flat nasal bridgeWilson LC, Trembath RC. J Med Genet. 1994 Oct;31(10):779-84 [Citation ends].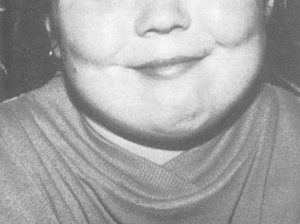 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hands of an adult with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy showing shortening of the IV metacarpal and distal phalanges, and knuckle dimples in the clenched fistsWilson LC, Trembath RC. J Med Genet. 1994 Oct;31(10):779-84 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Hands of an adult with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy showing shortening of the IV metacarpal and distal phalanges, and knuckle dimples in the clenched fistsWilson LC, Trembath RC. J Med Genet. 1994 Oct;31(10):779-84 [Citation ends].
uncommon
muscle spasm
A sign of severe hypocalcemia. If spasms affect laryngeal smooth muscle, the patient will develop life-threatening stridor.
tetany
A late sign of severe hypocalcemia.
positive Trousseau sign
Elicited by inflating a blood pressure cuff placed over the brachial artery to 20 mmHg above systolic for 5 minutes.
The distal ischemia produces tetany of the hand with flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joints and extension at the interphalangeal joints.
The more rapid the response, the lower the serum calcium.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Eliciting Trousseau signCooper MS, Gittoes NJL. BMJ. 2008 Jun 7;336(7656):1298-302 [Citation ends].
Other diagnostic factors
common
lethargy
A nonspecific symptom that may reflect either hypocalcemia or hypothyroidism.
anxiety
A nonspecific symptom that can occur in hypocalcemia.
uncommon
seizures
Occurs in severe hypocalcemia.
paroxysmal dyskinesias
PHP is a rare cause of paroxysmal dyskinesias (involuntary intermittent movement disorders).[30]
brittle nails
A subtle sign of hypocalcemia.
dry hair
A subtle sign of hypocalcemia.
subcutaneous calcification
Calcification of the pinna of the ear or subdermal calcification/ossification occur as a consequence of calcium phosphate deposition, produced by hyperphosphatemia.[45]
cataracts
A consequence of hyperphosphatemia, leading to calcium phosphate deposition in the eye.
features of hypothyroidism
The clinical features of hypothyroidism include weakness, lethargy, cold sensitivity, constipation, weight gain, depression, menstrual irregularity, myalgia, dry or coarse skin, eyelid edema, thick tongue, coarse hair, facial edema, and bradycardia.
features of other hormone resistance
Delayed puberty and infertility; commonly seen in patients with generalized hormone resistance due to resistance to the action of gonadotropins.
Chiari type 1 anomaly
Sporadic cases of this congenital hindbrain abnormality have been reported.[33]
history of cholesterol gallstones
Sporadic cases.[34]
features of psychosis
Sporadic cases.[35]
Risk factors
strong
positive family history of PHP
Types Ia and Ic have an autosomal dominant mode of inheritance. Due to the poor reproductive capacity of people who have types Ia and Ic, little information is available regarding how frequently the mutation is passed on.
Type Ib is usually sporadic, although familial cases are reported.[27][28]
The inheritance of type II is unknown, but it has been hypothesized that type II PHP may be an acquired defect secondary to vitamin D deficiency.[6]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer