Tests
1st tests to order
polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for Cryptosporidium species identification
Test
Option for initial testing for Cryptosporidium.[74]
Stool samples should be submitted fresh, without preservatives containing formalin, mercury, or polyvinyl alcohol.[79]
Detection of DNA by PCR-based methods may also be helpful for the detection of other lifecycle stages in specimen types other than stool (intestinal fluid, broncho-alveolar washings, antral washings, tissue samples, and biopsy specimens) from immunocompromised patients.
Availability of PCR testing varies.
Result
CryptosporidiumDNA detected
stained stool microscopy
Test
Option for initial testing for Cryptosporidium.[74]
For microscopy, stool samples may be submitted fresh or in 10% formalin. Stools in formalin need to be concentrated by ethyl acetate sedimentation before making a smear stained with acid-fast, fluorescent, or direct immunofluorescent stains.[80]
The diagnosis cannot be excluded by one negative stained microscopy test result, and several samples should be tested (three are recommended).[80][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Acid-fast-stained Cryptosporidium oocystsFrom the Cryptosporidium Reference Unit collection; used with permission [Citation ends].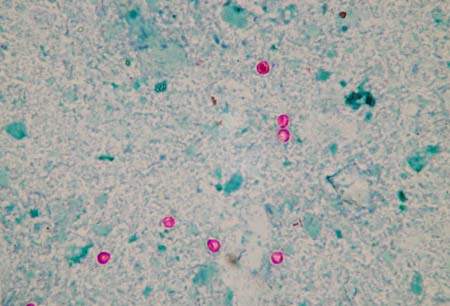 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Direct-immunofluorescent-stained Cryptosporidium oocystsFrom the Cryptosporidium Reference Unit collection; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Direct-immunofluorescent-stained Cryptosporidium oocystsFrom the Cryptosporidium Reference Unit collection; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
Cryptosporidium oocysts seen
Cryptosporidium antigen detection
Test
Option for initial testing for Cryptosporidium.[74]
Stool samples may be submitted fresh, in 5% or 10% formalin, or in sodium acetate-acetic acid formalin, but reference to the specific kit instructions should be made. Concentrated samples are unsuitable for testing with enzyme immunoassay or immunochromatographic tests.
Cryptosporidium antigen detection methods provide an alternative to labor-intensive highly skilled stained microscopy.
Enzyme immunoassays are reportedly superior to acid-fast microscopy and comparable to direct immunofluorescence microscopy in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Rapid immunochromatographic assays are comparable to acid-fast microscopy.
Combined kits for the detection of Cryptosporidium and Giardia, or of Cryptosporidium, Giardia, and Entamoeba histolytica, are available. The test kit performance should be monitored, as false positives have been reported.[80][81][82] CDC: laboratory identification of parasitic diseases of public health concern - cryptosporidiosis Opens in new window Positive reactions should be confirmed using a different test.
Result
positive for Cryptosporidium antigen
Tests to consider
ultrasound scan of the biliary tract
Test
Ultrasound scan of the biliary tract is indicated where biliary tract involvement is suspected in an immunocompromised patient.
Result
dilatation of the common bile duct and/or intrahepatic ducts, thickening of the gallbladder wall, pericholecystic fluid
CT scan of the biliary tract
Test
CT scan of the biliary tract is indicated where biliary tract involvement is suspected in an immunocompromised patient.
Result
dilatation of the common bile duct and/or intrahepatic ducts, thickening of the gallbladder wall, pericholecystic fluid
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Test
Confirmation of biliary cryptosporidiosis is possible using ERCP to obtain histologic biopsies and bile for laboratory testing.
Result
dilated common bile duct, papillitis, papillary stenosis, intrahepatic ductal strictures, dilated pancreatic duct; method of obtaining a sample for testing
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer