Last reviewed: 21 Mar 2025
Last updated: 26 Mar 2024
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- nasal obstruction
- nasal discharge
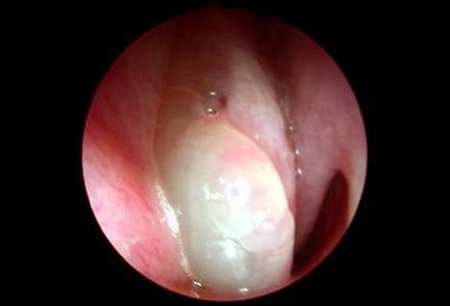
- polyps visible on examination or imaging
Risk factors
- asthma
- eosinophilic granulomatous polyangiitis (EGPA, also known as Churg-Strauss syndrome)
- allergic fungal rhinosinusitis (AFRS)
- aspirin sensitivity
- genetic predisposition
Diagnostic tests
Tests to consider
- CT sinuses
- biopsy
- nasal smear and culture
- CBC with differential
- antineutrophil cytoplasm antibodies (ANCA)
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- skin prick tests/serum allergen-specific IgE tests
- aspirin challenge
- olfaction studies
- quality-of-life measures
- nasal airway assessment
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Hesham A. Saleh, MBBCh, FRCS, FRCS (ORL-HNS)

Consultant Rhinologist
Charing Cross Hospital
Professor of Practice in Rhinology
Imperial College
London
UK
Disclosures
HAS declares that he has no competing interests.
Guy Scadding, FRCP, PhD
Consultant Allergist
Royal Brompton and Harefield NHS Trust
London
UK
Disclosures
GS has received lecture fees from ALK-Abello, Meda, and Glenmark Pharmaceuticals and sponsorship from GSK to attend a conference.
Acknowledgements
Dr Hesham A. Saleh and Dr Guy Scadding would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Richard J. D. Hewitt and Dr Romana Kuchai, previous contributors to this topic.
Disclosures
RJDH and RK declare that they have no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Sietze Reitsma, MD, PhD
Rhinologist
Amsterdam University Medical Centers
Amsterdam
Netherlands
Disclosures
SR declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer