Tests
1st tests to order
ABG
Test
Should be measured in seriously ill patients who present with a chief complaint of shortness of breath or who have tachypnea or Kussmaul respirations, particularly in cases of suspected poisoning.
Identifies acid-base disturbances, amplifies the information available from the basic clinical chemistries, and identifies deterioration in oxygenation that might not yet be clinically apparent.
Result
initially respiratory alkalosis; later concomitant metabolic acidosis (more prominent in children as they have less capacity to compensate with hyperventilation than adults), potentially with wide anion gap
serum electrolyte panel
Test
Multiple electrolyte abnormalities may occur.
Result
hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and/or hypomagnesemia may be present
serum salicylate level
Test
Salicylate levels should be followed every 2-4 hours until they peak.[18]
Many exposures are subacute or chronic, and salicylate levels, if positive, are primarily useful in helping to increase probability of the diagnosis.
Treatment decisions are driven by clinical presentation rather than salicylate level, but salicylate levels can help to determine whether the patient is still absorbing salicylate and so assist in decision-making.
Result
may be positive or negative
serum BUN and creatinine
Test
Renal failure is rare.
Result
may show renal insufficiency
serum ketones
Test
Result may be positive, particularly in children with salicylate poisoning.
Result
may be positive or negative
blood glucose
Test
May be elevated because of derangement of carbohydrate metabolism, although hypoglycemia has also been reported. Abnormal results are more common in children.
Result
hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia
CBC
Test
Nonspecific.
Result
WBC count may be elevated
serum LFTs
serum PT, activated PTT, INR
Test
Hemostatic defects as a result of platelet dysfunction, decreased factor VII, and hypoprothrombinemia usually do not cause clinically significant manifestations unless there is a bleeding site.
Result
coagulopathy may be present
toxicology screen
Test
In cases where the diagnosis is uncertain, a broader workup for suspected poisoning should be conducted.
Because patients and caregivers may err when reporting analgesic exposures, measurement of serum acetaminophen levels is indicated in most cases.
Serum ethanol levels, levels of other toxicants that cause metabolic acidosis (e.g., methanol, ethylene glycol), and urine screens for drugs of abuse should be ordered when needed to answer specific clinical questions.
Result
may show increased concentrations of coingestants
chest x-ray
Test
In the setting of salicylate poisoning, patients with respiratory symptoms should have a chest x-ray to evaluate for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Point of care ultrasonography is an alternative test for pulmonary edema.[12]
ARDS is an indication for urgent hemodialysis.[13][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray image of bilateral infiltrates in a patient with ARDSFrom the personal collection of Dr Lorraine Ware; used with permission [Citation ends].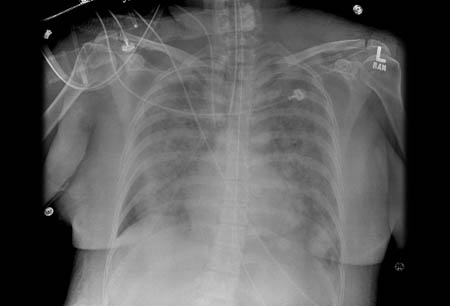
Result
pulmonary edema may be present
ECG
Test
Should be obtained in all cases of suspected salicylate poisoning. Prolonged corrected QT interval is associated with severe ventricular dysrhythmias and may be life-threatening.[14]
Result
sinus tachycardia is common; prolonged corrected QT interval or ventricular dysrhythmias may occur; monomorphic ventricular tachycardia and torsades de pointes may be present
Tests to consider
echocardiogram
Test
May be considered to evaluate cardiac function and help differentiate noncardiogenic from cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Result
variable
head CT scan
Test
Indicated for patients who present with lateralizing neurologic signs or who require an evaluation or a structural lesion of the central nervous system.
For patients with known salicylism who have altered mental status, a CT scan of the head should not be pursued when it will cause a delay in the initiation of hemodialysis or require intubation of a spontaneously breathing, tachypneic patient.
Result
variable
EEG
Test
May help exclude an underlying seizure disorder in patients presenting with seizures.
Result
variable
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer