Investigations
1st investigations to order
full blood count
Test
Anaemia: mild for gambiense human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) (haemoglobin 100 to 119 g/L [10.0 to 11.9 g/dL] in women, 100 to 129 g/L [10.0 to 12.9 g/dL] in men); severe in rhodesiense HAT (<80 g/L [8.0 g/dL]).
Thrombocytopenia: mild for gambiense HAT ( platelets 100 to 150 x 10⁹/L [100,000 to 150,000/microlitre]); may be severe in rhodesiense HAT (platelets <50 x 10⁹/L [<50,000/microlitre]).
Moderate leukocytosis (WBC 12 to 25 x 10⁹/L [12,000 to 25,000/microlitre]).
Result
anaemia, thrombocytopenia, moderate leukocytosis
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Test
Does not establish diagnosis, but commonly elevated in infected patients.
Result
elevated (>20 mm/hour)
serum immunoglobulins (Ig)
rapid diagnostic tests
Test
Rapid and simple, individual 15-minute tests for detection of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense-specific antibodies. Sensitivity between 89% and 99%, and specificity between 88% and 99%, depending on the test, specimen, and region.[38][39][40][66][67]
Positivity is indicative of the disease, but further parasitological examination should be performed for confirmation.
Probably not relevant for monitoring treatment response.
Not useful for T b rhodesiense diagnosis.
Result
presence of trypanosome-specific antibody in blood
card agglutination test for trypanosomiasis (CATT)
Test
Rapid and simple 10-minute test for detection of T b gambiense-specific antibodies.[68]
Sensitivity between 83% and 98%. False negativity may be due to prozone (antibody excess in the agglutination reaction), or absence of the CATT antigen (LiTat 1.3) gene from the infecting parasite, as observed in some foci in Cameroon.[69]
Specificity around 95%, but limited positive predictive value when prevalence is <2%. False positives may be due to other parasitic infections.
Positivity is indicative of the disease, but further parasitological examination should be performed for confirmation.
Antibodies may be present for >5 years after cure.[70][71] Conversely, normalisation of antibody levels does not mean that a cure has been achieved.[72] CATT is therefore not useful for monitoring treatment response.
Not for T b rhodesiense diagnosis.
Result
whole blood antibody positive; serum or plasma antibody positive in dilution 1:4 or more.
immunofluorescence
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
chancre aspirate microscopy
Test
Earliest way to diagnose trypanosome infection. Trypanosome finding establishes definitive diagnosis.
Especially useful for diagnosis of T b rhodesiense infection.
Chancres rarely occur in T b gambiense patients.
Result
fresh or stained preparation containing trypomastigotes
lymph node aspirate microscopy
Test
Especially useful for diagnosis of T b gambiense infection. Trypanosome finding establishes definitive diagnosis. Sensitivity 40% to 80%.
Enlarged cervical lymph nodes rarely present in T b rhodesiense patients.
Result
fresh preparation containing trypomastigotes
blood microscopy
Test
Trypanosome finding establishes definitive diagnosis. Fresh preparation or stained, thin blood film has insufficient sensitivity for diagnosis of T b gambiense infection because detection limit is only around 6000 to 10,000 trypanosomes/mL.
Detection limit of thick blood film is 600 to 5000 trypanosomes/mL, thus limited sensitivity for T b gambiense of 30% to 40%.[41][42] Owing to the high parasitaemia, T b rhodesiense infection is usually detected applying these techniques. For diagnosis of T b gambiense infection, concentration techniques are to be preferred, owing to the usual low parasitaemia. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Trypanosoma brucei species in thick blood smear stained with GiemsaFrom the collection of Dr V. Lejon [Citation ends].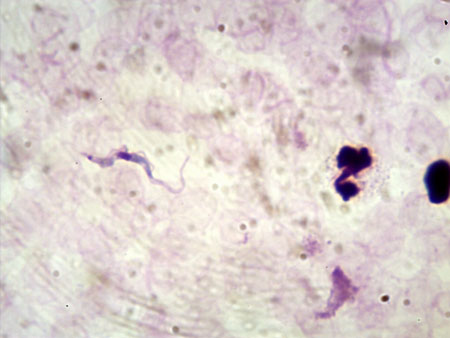
Result
fresh or stained preparation containing trypomastigotes
microhaematocrit centrifugation technique
Test
Concentration technique with detection limit of 500 to 600 trypanosomes/mL.[82] Trypanosome finding establishes definitive diagnosis. Especially useful for T b gambiense detection, with sensitivities about 50% to 60%.[41][42]
Sensitivity increases with number of capillaries examined (minimum 2).
Trypanosomes may be difficult to recognise for inexperienced readers.
Result
mobile trypanosomes present in and on top of buffy coat
quantitative buffy coat technique
Test
Concentration technique with detection limit of 15 to 300 trypanosomes/mL.[83] Trypanosome finding establishes definitive diagnosis. Especially useful for T b gambiense. Along with mini-anion exchange centrifugation technique, best test, with sensitivity about 80% to 90%.[84]
Result
mobile trypanosomes with fluorescent kinetoplast and nucleus between the white blood cells in the expanded buffy coat
mini-anion exchange centrifugation technique (mAECT)
Test
Concentration technique with detection limit of 15 to 100 trypanosomes/mL.[85][86] Trypanosome finding establishes definitive diagnosis.
Especially useful for T b gambiense. Best test, with sensitivity around 75% to 85%.[41][42] Sensitivity can be increased to between 91% and 96% when the buffy coat of larger volumes of blood is applied onto the column.[43][44]
Blood should be taken in heparin; ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid should be avoided as it may interfere with binding of red blood cells to the gel. Use of the concentrated buffy coat may improve sensitivity.[43]
mAECT is only available from production units in Democratic Republic of the Congo and Côte d'Ivoire, and therefore rather limited to health structures specialised in HAT.
Result
mobile trypanosomes in column flow through
Investigations to consider
electrocardiogram
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) white blood cell (WBC) count
Test
CSF examination is usually performed for disease staging, after finding trypanosomes in other body fluids, or in case of very high suspicion for HAT (e.g., elevated CATT end titre and/or highly suggestive neurological symptoms, in an epidemiological context of well-known transmission of the disease).
Lumbar puncture is not imperative in patients with gambiense HAT who are eligible for treatment with fexinidazole. Patients who can be managed without lumbar puncture are patients ≥6 years of age and body weight ≥20 kg who meet both of the following conditions: low index of suspicion of severe disease based on clinical judgement; and high confidence that the patient will have appropriate follow-up to detect relapse early. Patients who do not meet the above criteria or who reject or do not tolerate fexinidazole require a lumbar puncture.[32]
The pleocytosis mainly consists of B-lymphocytes (CD19+).[87]
Morular cells of Mott, which are plasma cells with large IgM-containing vesicles, may be present and are indicative of second-stage disease.[36]
Result
first stage (haemolymphatic stage): ≤5 WBC/microlitre and absence of trypanosomes;second stage (meningoencephalitic stage): >5 WBC/microlitre or trypanosomes; severe second stage (severe meningoencephalitic stage): ≥100 WBC/microlitre with or without trypanosomes
CSF microscopy
Test
Sensitivity of simple techniques (fresh or stained preparation) is very limited. Concentration techniques on CSF are recommended, especially for treatment outcome assessment. Trypanosome finding establishes definitive diagnosis in second-stage disease.
Result
presence of trypanosomes in second-stage disease
double centrifugation of CSF
Test
Concentration technique on CSF.[88] Sensitivity increases with the volume of CSF that is centrifuged. Trypanosome finding establishes definitive diagnosis in second-stage disease.
Result
presence of trypanosomes between WBC deposit in the bottom of the capillary in second-stage disease
modified single centrifugation of CSF
CSF protein
Test
Already increased in early stage, thus no longer recommended for disease staging.[91]
Result
mildly elevated
Emerging tests
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
Most primers are specific for the Trypanozoon subgenus and derived from satellite sequences or multicopy genes providing detection limits of 1 to 40 trypanosomes/mL and high sensitivities.[92][93][94][95] Diagnostic specificities are 97% or greater, but these PCRs do not differentiate between T b gambiense and T b rhodesiense infections, and positive reactions are possible with T b brucei, T evansi, and T equiperdum.
Differentiation between T b gambiense and T b rhodesiense infections is possible using for T b rhodesiense the serum resistance-associated (SRA) gene, and for T b gambiense the T b gambiense-specific glycoprotein (TgsGP) gene.[96][97][98][99] Use of these single copy genes provides lower sensitivity. There is a lack of standardisation and comparative studies. Significance for staging of a positive PCR on CSF remains unclear.[100] For treatment outcome assessment, PCR has been shown to be unreliable.[101][102][103]
Other molecular techniques include loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA), and oligochromatography, but proper standardisation and validation is needed.[95][104][105][106][107][108][109] In the first evaluation on clinical samples of T b gambiense HAT, the Loopamp Trypanosoma brucei Detection Kit (a brand name), based on detection of the Trypanozoon repetitive insertion mobile element DNA, showed similar performance to conventional PCR.[110]
Positivity in PCR or LAMP is indicative of human African trypanosomiasis, but further parasitological examination should be performed for confirmation.
Result
trypanosomal DNA
reverse transcriptase real-time PCR (RT-PCR)
Test
RT-PCR for detection of Trypanozoon-specific spliced leader RNA in blood has shown 92% to 97% sensitivity and >95% specificity.[54][55][56] It is accurate for disease staging and considered more reliable than PCR for treatment outcome assessment. Other RNA targets and other nucleic acid detection formats are emerging but need further evaluation of their diagnostic performance.
Result
trypanosomal RNA
intrathecal immunoglobulin production
Test
High IgM concentrations of >100 mg/L are common in CSF of patients with second-stage T b gambiense.[17]
Calculation of intrathecal IgM fraction shows dominant IgM immune response pattern.[17][18] Detection of oligoclonal IgG may be negative.[111] Positivity is indicative of second-stage disease, but further parasitological examination should be performed for confirmation.
Result
intrathecal IgM production
stage biomarkers
immune trypanolysis
Test
Live T b gambiense trypanosomes are incubated with human serum or plasma. The test can be performed only in highly specialised laboratories.[49][50] Specificity of immune trypanolysis is considered to be 100%, and a positive immune trypanolysis appears to be an indicator for contact with T b gambiense.
Result
parasites are killed by antibody-mediated complement lysis if the test sample contains T b gambiense-specific antibodies
T b gambiense inhibition ELISA (g-iELISA)
Test
g-iELISA has been developed as a user-friendly alternative for immune trypanolysis, which can be performed in any lab equipped for ELISA. Using trypanolysis as the reference test, g-iELISA was shown to have 98.0% and 92.6% sensitivity and 99.5% and 100% specificity on, respectively, plasma and dried blood spots.[112]
Result
antibodies from gambiense HAT patient blood inhibit binding of labelled monoclonals to their corresponding trypanosome-specific epitope
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer