Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
In the early post-transplant setting, cytopenia (particularly thrombocytopenia) may be associated with acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Autoimmune cytopenias (leukopenia, anaemia, and thrombocytopenia) may be seen at a later stage with chronic GVHD.
Eosinophilia may be present in acute or chronic GVHD.
Result
may show leukopenia, anaemia, thrombocytopenia, or eosinophilia
serum electrolytes
Test
Acute and/or chronic graft-versus-host disease affecting the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, weight loss, and failure to thrive [in infants and children]) can lead to a variety of electrolyte disturbances.
Result
may show abnormal values
liver functions tests
Test
Elevated transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, and/or bilirubin may be a manifestation of acute and/or chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Result
may show elevated liver transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin
urinalysis
Test
Proteinuria may be a manifestation of renal dysfunction seen with nephrotic syndrome associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Result
may show proteinuria
urine culture
Test
Useful in helping exclude the possibility of urinary tract infection.
Result
positive or negative for a pathogen
blood culture
Test
Important to exclude the possibility of bacteraemia and/or sepsis.
Result
positive or negative for a pathogen
stool culture
Test
Can help exclude potential infectious causes of diarrhoea that may closely resemble graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Positive stool studies and gastrointestinal GVHD can occur concurrently.
Result
positive or negative for a pathogen
viral polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies
Test
Can be used to test for infection with cytomegalovirus, HHV-6, adenovirus, hepatitis virus (A, B, C, D, E), and parvovirus.
Result
positive or a negative
Investigations to consider
CT abdomen
Test
Important to obtain in patients presenting with symptoms suggestive of gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD; e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, anorexia).
Ascites may be present; however, this is not diagnostic for GVHD.
Result
luminal dilatation with thickening of the small bowel wall (ribbon sign); air-fluid levels suggestive of an ileus; ascites
Doppler ultrasound of the liver
Test
To exclude other aetiologies of liver dysfunction in the post-transplant setting, such as veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstructive syndrome or total parenteral nutrition cholestasis.
Result
hepatomegaly and ascites may be noted in graft-versus-host disease; no hepatic venous occlusion, calculi, or thickening of gall bladder seen
tissue biopsy (skin, gastrointestinal [GI] tract, liver, or lung)
Test
A biopsy of the affected organ (e.g., skin, GI tract, liver, lung) may, however, be carried out to support or confirm a diagnosis, particularly if there is clinical uncertainty.[92][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of skin graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (low power): Vacuolar interface dermatitis at the dermoepidermal junction with involvement of follicular epithelium (100x, haematoxylin and eosin)Courtesy of Dr Lori Lowe, Professor, Dermatopathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of skin graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (high power): Vacuolar interface dermatitis with rare necrotic keratinocytes (200x, haematoxylin and eosin)Courtesy of Dr Lori Lowe, Professor, Dermatopathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of skin graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (high power): Vacuolar interface dermatitis with rare necrotic keratinocytes (200x, haematoxylin and eosin)Courtesy of Dr Lori Lowe, Professor, Dermatopathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends].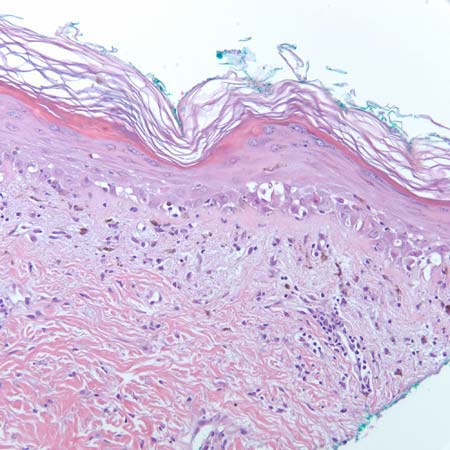 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of upper gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (medium-power photomicrograph of the stomach): Dilated gastric gland containing necrotic/apoptotic debris (arrow), typical of GVHDCourtesy of Dr Joel Greenson, Professor, Pathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of upper gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (medium-power photomicrograph of the stomach): Dilated gastric gland containing necrotic/apoptotic debris (arrow), typical of GVHDCourtesy of Dr Joel Greenson, Professor, Pathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends].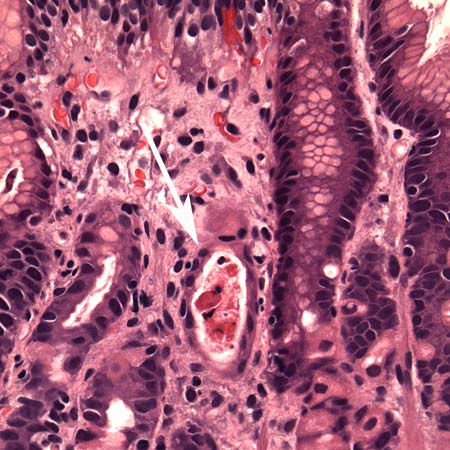 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of lower gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (high-power photomicrograph of colon, mild disease): Numerous apoptotic bodies (arrows) indicative of GVHD involving the colonCourtesy of Dr Joel Greenson, Professor, Pathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of lower gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (high-power photomicrograph of colon, mild disease): Numerous apoptotic bodies (arrows) indicative of GVHD involving the colonCourtesy of Dr Joel Greenson, Professor, Pathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends].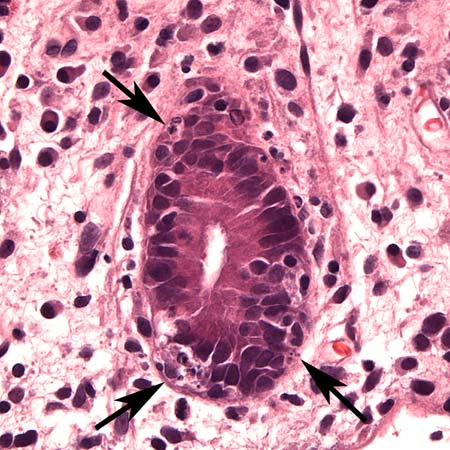 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of lower gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (medium-power photomicrograph of colon, severe disease): Almost complete denudation of the mucosa indicative of severe GVHD involving the colonCourtesy of Dr Joel Greenson, Professor, Pathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histology of lower gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) (medium-power photomicrograph of colon, severe disease): Almost complete denudation of the mucosa indicative of severe GVHD involving the colonCourtesy of Dr Joel Greenson, Professor, Pathology, University of Michigan; used with permission [Citation ends].
Result
histological features of graft-versus-host disease; skin: includes apoptosis at base of epidermal rete pegs, dyskeratosis, exocytosis of lymphocytes, satellite lymphocytes adjacent to dyskeratotic epidermal keratinocytes, perivascular lymphocytic infiltration in the dermis; GI tract: includes patchy ulcerations, apoptotic bodies in the base of crypts, crypt abscesses and loss, flattening of the epithelium surface; liver: includes endothelialitis, lymphocytic infiltration of the portal areas, pericholangitis, bile duct destruction; lung: includes small airway inflammation with fibrinous obliteration of the bronchiolar lumen
pulmonary function tests
Test
Used in identifying obstructive pulmonary disease (e.g., bronchiolitis obliterans) in chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Result
FEV1/FVC ratio may be <0.7 and FEV1 <75% of predicted in chronic GVHD involving the lungs
high-resolution CT chest
Test
Used in establishing the diagnosis of chronic graft-versus-host disease affecting the lungs.
Result
air trapping and bronchiectasis; bilateral patchy ground-glass opacities with air bronchograms (usually located peripherally) or a circular nodule in one lung (or 3-5 nodules across both lungs) suggest cryptogenic organising pneumonia (COP); the triangle sign (a triangular ground glass opacity with the base on the pleura and the apex towards the mediastinum) is characteristic for COP
bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and culture
Test
Can be helpful in assessing and excluding infection as a potential differential diagnosis of graft-versus-host disease.
Result
positive or negative culture
echocardiogram
Test
Helpful to detect pericardial effusions or cardiomyopathy in chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Result
may show pericardial effusion or cardiomyopathy
barium swallow or upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
Test
Useful in identifying features of chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
Result
characteristic features of chronic GVHD of the GI tract include oesophageal web, stricture, or concentric rings
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan
Test
May be useful in localising gastrointestinal tract (GI) graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), as well as predicting and monitoring treatment responsiveness.[91]
Result
may show hot spots of GVHD activity in the GI tract
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer