Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC with differential
Test
Increased eosinophils >10% of WBC count is present in almost all patients with EGPA.
Eosinophils, in turn, are known to have direct pathogenic effects due to the release of their cytotoxic proteins.
Result
increased eosinophils
serum anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)
Test
ANCA may be present in 30% to 40% of patients with active vasculitic manifestations, but may be as low as 10% in those whose disease is quiescent.[4][5][16] ANCA-positive patients have a higher incidence of severe vasculitic manifestations, including glomerulonephritis, alveolar haemorrhage, and mononeuritis multiplex. The pathogenesis of vasculitis in ANCA-negative patients remains unclear. In EGPA, these are usually perinuclear-ANCA.
Result
positive
serum CRP
Test
Non-specific marker of inflammation.
Usually increased in the setting of vasculitis, and can be followed to assess response to treatment.
Result
increased
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Test
Non-specific marker of inflammation.
Usually increased in the setting of vasculitis, and can be followed to assess response to treatment.
Result
increased
serum urea and creatinine
Test
Performed to assess for glomerulonephritis, which has management implications.
Result
normal or increased
urinalysis
Test
Performed to assess for glomerulonephritis (haematuria, proteinuria, red blood cell casts), which has management implications.
Result
normal or abnormal
pulmonary function test
Test
Consistent with asthma, and reversible airway obstruction is common in patients with EGPA.
Result
reversible airway obstruction
chest x-ray
Test
Chest x-ray or CT may show interstitial infiltrates or nodules (suggesting granuloma formation) that may be transient or migratory. These may occur in the absence of symptoms.
Result
may show interstitial infiltrates or nodules
echocardiogram
Test
EGPA may commonly involve the pericardium. It uncommonly involves the myocardium (leading to regional or global left ventricular systolic dysfunction) and, rarely, the coronary arteries. A finding of fibrotic thrombus lining the endocardial surface of the ventricle, at times extending proximally to involve the atrioventricular valves, is characteristic of eosinophilic heart disease.
Patients in whom there is a high suspicion of EGPA, or known EGPA who have shortness of breath, should have an ECG to screen for cardiac involvement.[24][34]
Result
may show left ventricular regional wall motion abnormalities, intracardiac thrombus, or pericardial effusion
Investigations to consider
flow cytometry of peripheral blood
Test
Rules out lymphoproliferative hypereosinophilic syndrome in patients for whom there is clinical suspicion. Usually performed in patients whose clinical picture of vasculitis is relatively mild, although some tertiary care institutions routinely test.
Result
normal
molecular testing for FIP1L1/PDGFR alpha mutation
Test
This mutation leads to a novel, functional tyrosine kinase and is seen in the myeloproliferative variant of lymphoproliferative hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) in patients for whom there is clinical suspicion. HES would be suggested by the absence of the CHIC2 locus on fluorescent in-situ hybridisation (FISH) studies, or presence of fusion protein on reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. HES would be suggested by T-lymphocyte abnormalities, in particular. HES is rarely associated with vasculitis abnormalities.
Result
normal
serum IgE
Test
Serum IgE is typically increased in EGPA. This is consistent with a disease with an allergic component: increased levels of serum IgE and immune complexes containing IgE have been noted, particularly during flares of EGPA.
Result
increased
serum-specific IgE and IgG to Aspergillus fumigatus
Test
If IgE increased, further specific IgE and IgG testing for Aspergillus should be performed to rule out allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis.[28]
Result
should be normal
stool culture for ova and parasites
Test
To rule out parasitic infection as an alternative cause of peripheral eosinophilia.
In the appropriate clinical setting, a travel history is required to rule out parasitic infections, particularly helminthic infection. Treatment with corticosteroids would make this infection worse. Parasitic infection would not be expected to cause vasculitis.
Result
normal
Toxocara serology
Test
Toxocariasis, a zoonosis typically transmitted to humans from dogs or cats, can cause severe eosinophilia.[28] Antibody detection tests are the only means of confirmation of a clinical diagnosis of Toxocara infection.
Result
should be normal
CT chest
Test
A chest x-ray should be performed on all patients, looking for any evidence that would be consistent with eosinophilic pneumonia or alveolar haemorrhage. If abnormalities are seen, the patient should have a CT scan of the chest.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT scan of the chest obtained (A) during symptom exacerbation, revealing pulmonary infiltrates in the right inferior lobe (A3) and the left inferior lobe (A4). Re-evaluation 15 days later (B) revealed the migratory character of the lesions, with complete disappearance of the previously described infiltrates and the presence of new areas of ground glass opacities within the right inferior lobe (B2) and the left lingular and left inferior lobe (B4). (C) Six months after treatment, all the lung lesions described had healed completelyBMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2009.1731. Copyright © 2011 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd [Citation ends].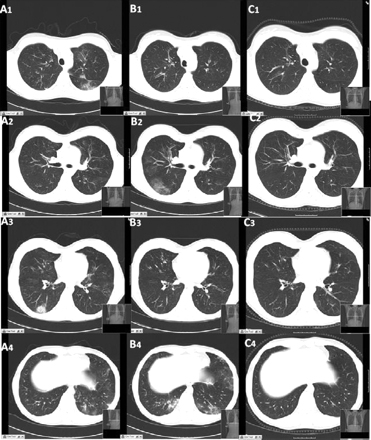
Result
may show infiltrative disease or pulmonary nodules
electromyogram
Test
Mononeuritis multiplex is commonly seen in vasculitis and is a surrogate marker of vasculitis.
Result
may confirm mononeuritis multiplex
bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
Test
Sequentially bloody BAL aliquots and increased haemosiderin-laden macrophages may be seen in alveolar haemorrhage.
Increased eosinophils on BAL are a feature of EGPA.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cytological examination of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, revealing the presence of a vast predominance of eosinophils (A), representing 27% of the cellular elements. The other cellular elements found were macrophages (C) and lymphocytes (B)BMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2009.1731. Copyright © 2011 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd [Citation ends].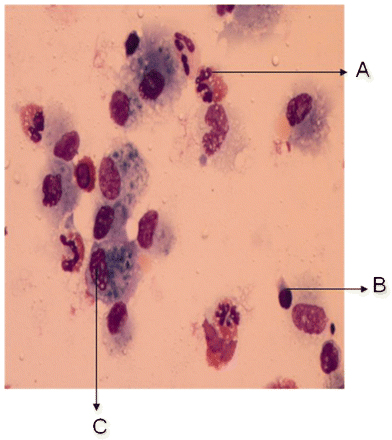
Eosinophilic pneumonia is typically associated with increased eosinophils on BAL.
Result
may be abnormal
biopsy of affected tissue
Test
Blood vessel biopsy demonstrates extravascular eosinophils. Tissue biopsy demonstrates small-vessel vasculitis. Biopsy is the confirmatory test for establishing the diagnosis of small-vessel vasculitis. The site of biopsy is driven by the likelihood of a positive finding with the least risk of complication. Common sites of biopsy include the sural nerve and the skin.
Severe involvement of the kidneys or lungs would indicate a need for aggressive therapy, and samples should be obtained from these organs if there is a question of their involvement.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histological evaluation of the lung biopsy specimen, revealing the presence of an inflammatory infiltrate composed predominantly of eosinophils found within both the vascular lumen and the vascular wallBMJ Case Reports 2009; doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2009.1731. Copyright © 2011 by the BMJ Publishing Group Ltd [Citation ends].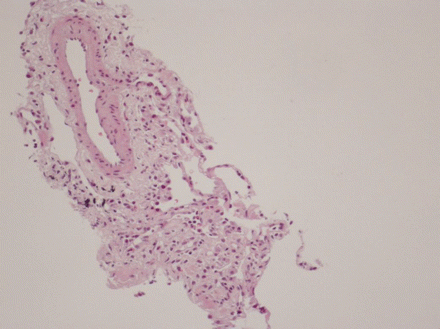
Result
may confirm vasculitis
lower extremity ultrasound
Test
Patients with active EGPA are at increased risk of thromboembolic disease. Should be performed if clinically indicated.
Result
may show evidence of deep venous thrombosis
CT angiography
Test
Patients with active EGPA are at increased risk of thromboembolic disease. Should be performed if clinically indicated.
Result
may show pulmonary embolism
bone marrow biopsy
Test
Occasionally, bone marrow biopsy is required for the differential diagnosis of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome.
Result
normal
thiopurine methyltransferase level
Test
Before starting azathioprine, where testing is available, thiopurine methyltransferase levels or genotype testing are helpful, to ensure that patients have sufficient enzyme levels to metabolise the drug.
Result
should be normal
HIV testing
Test
HIV infection may cause mild eosinophilia.[28]
Result
should be normal
Emerging tests
cardiac MRI
Test
The role of cardiac MRI is being investigated for the assessment of EGPA-related cardiomyopathy.
Result
may be abnormal
eotaxin-3
Test
In a study of 37 patients with EGPA, 123 healthy controls, and 138 disease controls (i.e., other vasculitides, connective tissue diseases, hypereosinophilic syndromes, parasitic diseases, ulcerative colitis), eotaxin-3 showed high specificity and sensitivity for the diagnosis of active EGPA.[32][33]
Result
elevated in active EGPA
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer