Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
Leukopenia is common, with lymphopenia reported in 98% of patients early in the disease.[3] Lymphopenia is due to reduced CD4 and CD8 cell counts. Thrombocytopenia is found in the presence of disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Result
leukopenia, lymphopenia with reduced CD4 and CD8 cell counts, thrombocytopenia
aminotransferases
Test
Mild elevation of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) has been reported in 23% to 50% of SARS patients, although this result shows low specificity for diagnosis of the disease.[19]
Result
elevated AST and ALT
lactate dehydrogenase
Test
Common, non-specific laboratory abnormality. Indicates liver injury or lysis of blood erythrocytes.
Result
elevated
creatine kinase
Test
Common, non-specific laboratory abnormality. Indicates muscle or myocardium injury. Has also been related to left ventricular dysfunction.[4]
Result
elevated
blood culture
Test
All patients with signs of severe infection should receive blood and sputum cultures to rule out other causes of a lower respiratory tract infection, especially those without a typical epidemiological history for SARS.
Result
negative for bacterial infection
sputum culture
Test
All patients with signs of severe infection should receive blood and sputum cultures to rule out other causes of a lower respiratory tract infection, such as community-acquired pneumonia, especially those without a typical epidemiological history for SARS.
Result
negative for Streptococcus pneumoniae or other infecting bacteria
nasopharyngeal virus culture
Test
To rule out presence of influenza infection.
Result
negative for influenza A and influenza B viruses
direct immunofluorescent antibody staining
Test
To rule out presence of influenza infection.
Result
negative for influenza A and influenza B viruses
chest x-ray
Test
About 20% to 25% of cases have a normal chest x-ray on presentation.[24][25]
Examine chest x-ray for unilateral or bilateral infiltrates in the peripheries of the lower zones. Infiltrates manifest as patchy, confluent, or diffuse consolidation, or nodular shadowing.
Cavitation, hilar lymphadenopathy, and pleural effusion are not typically seen.[26]
Pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax often occur with assisted ventilation.[27][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of a SARS patient showing multifocal opacitiesKetai L, et al. J Thorac Imaging. 2006;21:276-283; used with permission [Citation ends].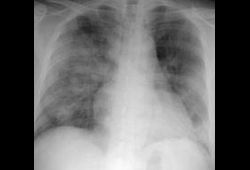
Result
unilateral or bilateral infiltrates
pulse oximetry
Test
Indicated in patients with respiratory distress and cyanosis.
Result
low oxygen saturation (SpO₂ <90%)
reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Test
For a positive diagnosis based on PCR testing, the patient must have either two positive clinical specimens from different anatomical sites or positive specimens from the same site on two separate occasions.[29][30]
Multiple specimen sources should be sampled: nasopharyngeal, oropharyngeal, and serum/plasma specimens (during first week); nasopharyngeal, oropharyngeal, and stool specimens (after first week).[41]
Preferred samples are a nasopharyngeal aspirate (often negative in first week of infection) or throat swab obtained in viral transport media. Dacron or rayon swabs with plastic shafts should be used rather than those with calcium alginate or wooden sticks. Specimens must be shipped in cold packs to keep the sample at 4°C (39.2°F).
Stool specimens or whole blood samples in ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) are also appropriate.
Quantitative measurement of blood SARS-CoV RNA with the technique of real time RT-PCR has a detection rate of 80% as early as day 1 of the disease.[33]
Result
positive for SARS-CoV-specific RNA
Investigations to consider
ABG
Test
Performed when the SpO₂ measured with pulse oximetry is <90%.
Result
low partial oxygen pressure
coagulation screen
Test
Indicated in patients with spontaneous bleeding.
Result
prolonged prothrombin time, raised D-dimers
high-resolution CT (HRCT) of thorax
Test
Imaging of the thorax with HRCT should be undertaken in those with a normal chest x-ray on presentation and a high suspicion of SARS for the detection of lung opacities.
Abnormal in 67% of patients with an initially normal chest x-ray.[28]
Result
ground glass opacities with interlobular septal thickening ± subpleural consolidation
serological testing for SARS-CoV-specific antibodies
Test
Tested using an immunofluorescent antibody assay (IFA) or ELISA.
Useful for epidemiological surveillance and retrospective diagnosis.
Serum specimens should be collected when the diagnosis is first suspected and at later times if indicated.
Seroconversion usually occurs 1 to 4 weeks (>90% after day 28) after the onset of symptoms, with an antibody response (4-fold increase in SARS-CoV antibody) occasionally detected during the first week of illness, likely to be detected by the end of the second week of illness, but not normally detected until >28 days into the illness.[30][34]
Result
4-fold increase in SARS-CoV antibody
Emerging tests
rapid immunoswab assay for SARS-CoV detection
Test
The key feature of this simple immunoswab diagnostic assay is its ability to detect the presence of the SARS-CoV antigen (nucleocapsid protein) within 45 to 60 minutes following availability of the body fluid samples.[35]
Result
detects presence of SARS-CoV antigen
monoclonal antibodies
Test
Five monoclonal antibodies against recombinant nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV were developed by hybridoma technology. Potentially ideal candidates for developing early and sensitive diagnostic assays for SARS-CoV.[36]
Result
detects presence of SARS-CoV with high specificity
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer