The diagnostic workup of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) includes a full history and physical examination, laboratory tests (including examination of peripheral blood to identify leukaemic [hairy] cells), bone marrow evaluation (including morphological, immunophenotypic, and molecular analysis), and in some cases imaging.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[33]Grever MR, Abdel-Wahab O, Andritsos LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with classic hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2017 Feb 2;129(5):553-60.
https://www.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-689422
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27903528?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hairy cell leukemia [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx
Clinical presentation
Patients may present with fatigue, lethargy, infection, and/or weight loss.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[35]Quest GR, Johnston JB. Clinical features and diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2015 Dec;28(4):180-92.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.017
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26614896?tool=bestpractice.com
The spleen may be palpable.
Other patients are asymptomatic at presentation, and are diagnosed following an incidental finding of splenomegaly or pancytopenia discovered during evaluation for an unrelated cause.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[35]Quest GR, Johnston JB. Clinical features and diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2015 Dec;28(4):180-92.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.017
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26614896?tool=bestpractice.com
Patients may report recurrent infections, bleeding (gingival bleeding, epistaxis), or easy bruising.[33]Grever MR, Abdel-Wahab O, Andritsos LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with classic hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2017 Feb 2;129(5):553-60.
https://www.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-689422
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27903528?tool=bestpractice.com
[35]Quest GR, Johnston JB. Clinical features and diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2015 Dec;28(4):180-92.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.017
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26614896?tool=bestpractice.com
Petechiae may be present.
Physical examination findings
Splenomegaly is a common physical finding.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[36]Flandrin G, Sigaux F, Sebahoun G, et al. Hairy cell leukemia: clinical presentation and follow-up of 211 patients. Semin Oncol. 1984 Dec;11(4 suppl 2):458-71.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6505708?tool=bestpractice.com
[37]Hoffman MA. Clinical presentations and complications of hairy cell leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1065-73.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990107?tool=bestpractice.com
Hepatomegaly is present in 40% to 50% of patients, while lymphadenopathy is present in 10% of patients.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[36]Flandrin G, Sigaux F, Sebahoun G, et al. Hairy cell leukemia: clinical presentation and follow-up of 211 patients. Semin Oncol. 1984 Dec;11(4 suppl 2):458-71.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6505708?tool=bestpractice.com
[37]Hoffman MA. Clinical presentations and complications of hairy cell leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1065-73.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990107?tool=bestpractice.com
[38]Mercieca J, Matutes E, Moskovic E, et al. Massive abdominal lymphadenopathy in hairy cell leukaemia: a report of 12 cases. Br J Haematol. 1992 Nov;82(3):547-54.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1283078?tool=bestpractice.com
Pallor (due to anaemia) and petechiae (due to thrombocytopenia) are common findings during physical examination.[36]Flandrin G, Sigaux F, Sebahoun G, et al. Hairy cell leukemia: clinical presentation and follow-up of 211 patients. Semin Oncol. 1984 Dec;11(4 suppl 2):458-71.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6505708?tool=bestpractice.com
[37]Hoffman MA. Clinical presentations and complications of hairy cell leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1065-73.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990107?tool=bestpractice.com
Less commonly, skin lesions can be due to vasculitis related to infiltration of the vessel wall by hairy cells.[39]Hasler P, Kistler H, Gerber H. Vasculitides in hairy cell leukemia. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Oct;25(2):134-42.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8578313?tool=bestpractice.com
Neurological findings, though rare, may be present (e.g., Guillain-Barre syndrome, signs of meningitis, and nerve compression).[40]Kraut EH. Clinical manifestations and infectious complications of hairy-cell leukaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2003 Mar;16(1):33-40.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12670463?tool=bestpractice.com
HCL may manifest as a variety of immune dysfunctions (e.g., polyarteritis nodosa, pyoderma gangrenosum, scleroderma, polymyositis, and erythematous maculopapules), but this is uncommon.[41]Foucar K, Falini B, Catovsky D, et al. Hairy cell leukemia. In: WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, vol 2, 4th ed. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization Press; 2008:188-90.
Initial laboratory workup
Initial tests to order include a full blood count (FBC) with differential, and peripheral blood smear.[33]Grever MR, Abdel-Wahab O, Andritsos LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with classic hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2017 Feb 2;129(5):553-60.
https://www.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-689422
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27903528?tool=bestpractice.com
[37]Hoffman MA. Clinical presentations and complications of hairy cell leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1065-73.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990107?tool=bestpractice.com
[42]Robak T, Matutes E, Catovsky D, et al. Hairy cell leukaemia: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2015 Sep;26(suppl 5):v100-7.
https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(19)47171-8/fulltext
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26269205?tool=bestpractice.com
The FBC may show pancytopenia (decreased cell count in all three cell lines), which is characteristic of classic HCL.[6]Paillassa J, Cornet E, Noel S, et al. Analysis of a cohort of 279 patients with hairy-cell leukemia (HCL): 10 years of follow-up. Blood Cancer J. 2020 May 27;10(5):62.
https://www.doi.org/10.1038/s41408-020-0328-z
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32461544?tool=bestpractice.com
[35]Quest GR, Johnston JB. Clinical features and diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2015 Dec;28(4):180-92.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.017
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26614896?tool=bestpractice.com
The majority of patients with classic HCL present with leukopenia.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[43]Forconi F, Sozzi E, Cencini E, et al. Hairy cell leukemias with unmutated IGHV genes define the minor subset refractory to single-agent cladribine and with more aggressive behavior. Blood. 2009 Nov 19;114(21):4696-702.
https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/114/21/4696/26391/Hairy-cell-leukemias-with-unmutated-IGHV-genes
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19667403?tool=bestpractice.com
However, in approximately 10% of patients, leukocytosis (WBC count >10×10⁹/L to 20×10⁹/L [>10,000 to 20,000/microlitre]) is present.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[43]Forconi F, Sozzi E, Cencini E, et al. Hairy cell leukemias with unmutated IGHV genes define the minor subset refractory to single-agent cladribine and with more aggressive behavior. Blood. 2009 Nov 19;114(21):4696-702.
https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/114/21/4696/26391/Hairy-cell-leukemias-with-unmutated-IGHV-genes
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19667403?tool=bestpractice.com
Neutropenia and monocytopenia are generally present.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[35]Quest GR, Johnston JB. Clinical features and diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2015 Dec;28(4):180-92.
https://www.doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.017
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26614896?tool=bestpractice.com
Monocytopenia is a consistent finding (present in approximately 90% of patients) and is characteristic of classic HCL.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[36]Flandrin G, Sigaux F, Sebahoun G, et al. Hairy cell leukemia: clinical presentation and follow-up of 211 patients. Semin Oncol. 1984 Dec;11(4 suppl 2):458-71.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6505708?tool=bestpractice.com
[44]Golomb HM, Catovsky D, Golde DW. Hairy cell leukemia: a clinical review based on 71 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Nov;89(5 Pt 1):677-83.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/717940?tool=bestpractice.com
Some automated haematology analysers may classify hairy cells as monocytes, which can mask monocytopenia unless peripheral blood is examined.[45]Sharpe RW, Bethel KJ. Hairy cell leukemia: diagnostic pathology. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1023-49.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990105?tool=bestpractice.com
Hairy cells are identified on the peripheral blood smear in almost all patients (95%).[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
The hairy cells usually account for ≤20% of the total WBC count.[45]Sharpe RW, Bethel KJ. Hairy cell leukemia: diagnostic pathology. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1023-49.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990105?tool=bestpractice.com
In patients who present with leukocytosis, hairy cells are the predominant circulating WBC.
Confirmatory diagnostic tests
To confirm the diagnosis of HCL, a bone marrow trephine biopsy and aspiration should be carried out for morphology assessment and immunophenotyping (using immunohistochemistry or flow cytometry).[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hairy cell leukemia [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx
Bone marrow aspiration is often difficult to carry out in patients with classic HCL and usually results in a dry tap (due to bone marrow fibrosis).
Morphology assessment
Assessment of the bone marrow specimen will show hairy cell infiltration and reticulin fibrosis. Hypocellular bone marrow is present in approximately 10% of patients; avoiding a misdiagnosis of aplastic anaemia is important in these patients.[33]Grever MR, Abdel-Wahab O, Andritsos LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with classic hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2017 Feb 2;129(5):553-60.
https://www.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-689422
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27903528?tool=bestpractice.com
Immunophenotyping
Immunohistochemistry (using bone marrow biopsy specimen) or flow cytometry (using bone marrow aspirate or peripheral blood) can help differentiate classic HCL from other lymphoproliferative disorders (including HCL variant [HCL-V]; also known as splenic B-cell lymphoma/leukaemia with prominent nucleoli [SBLPN]), and is important for establishing the diagnosis.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hairy cell leukemia [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx
Immunophenotyping should test for CD19, CD20, CD5, CD10, CD11c, CD22, CD25, CD103, CD123, cyclin D1, CD200, and annexin A1 (ANXA1).[34]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hairy cell leukemia [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx
Immunohistochemistry may test for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), which is expressed on HCL cells.[23]Cawley JC. The pathophysiology of the hairy cell. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1011-21.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990104?tool=bestpractice.com
[46]Yam LT, Li CY, Lam KW. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase isoenzyme in the reticulum cells of leukemic reticuloendotheliosis. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 18;284(7):357-60.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/5275977?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cytospin prepared from bone marrow aspirate illustrates the typical cell cytology, with oval- to bean-shaped nuclei and moderate amounts of cytoplasm with irregular cytoplasmic borders (Wright Giemsa 100x oil)From the collection of Lynn Moscinski, MD [Citation ends].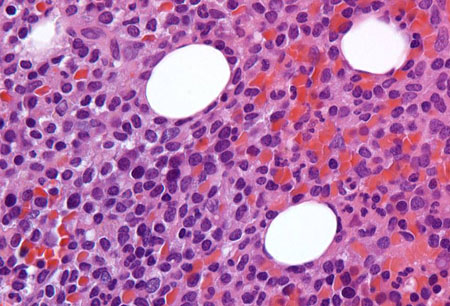 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sections of core biopsy demonstrate lymphocytes with obvious cytoplasm within the marrow interstitium, associated with dilatation of marrow sinuses and red blood cell collections (H&E 50x oil)From the collection of Lynn Moscinski, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sections of core biopsy demonstrate lymphocytes with obvious cytoplasm within the marrow interstitium, associated with dilatation of marrow sinuses and red blood cell collections (H&E 50x oil)From the collection of Lynn Moscinski, MD [Citation ends].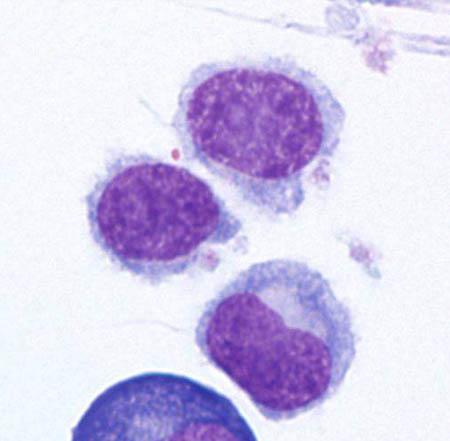
Pre-treatment evaluation
The following tests can guide treatment and should be ordered before initiating pharmacotherapy:[37]Hoffman MA. Clinical presentations and complications of hairy cell leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1065-73.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990107?tool=bestpractice.com
Comprehensive metabolic panel (including urea, serum creatinine, electrolytes, serum albumin, and liver function tests [LFTs])
Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Viral serology for hepatitis B and C
Other tests to order
A number of tests may be of value in specific circumstances.
Molecular analysis
May be considered to detect the BRAF V600E mutation (if there is diagnostic uncertainty following immunophenotyping) and IGHV4-34 rearrangements.[7]Parry-Jones N, Joshi A, Forconi F, et al. Guideline for diagnosis and management of hairy cell leukaemia (HCL) and hairy cell variant (HCL-V). Br J Haematol. 2020 Dec;191(5):730-7.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/bjh.17055
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33053222?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hairy cell leukemia [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx
The BRAF V600E mutation is present in almost all patients with classic HCL, but absent in HCL-V/SBLPN.[27]Troussard X, Maître E, Paillassa J. Hairy cell leukemia 2024: update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and treatment - annual updates in hematological malignancies. Am J Hematol. 2024 Apr;99(4):679-96.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ajh.27240
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/38440808?tool=bestpractice.com
Patients with IGHV4-34 mutant HCL do not respond well to standard HCL treatments and have a poor prognosis. The BRAF V600E mutation is usually absent in these patients.[47]Xi L, Arons E, Navarro W, et al. Both variant and IGHV4-34-expressing hairy cell leukemia lack the BRAF V600E mutation. Blood. 2012 Apr 5;119(14):3330-2.
https://www.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-09-379339
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22210875?tool=bestpractice.com
Imaging studies
Imaging is not required except in milder forms of disease, in which computed tomography (CT) scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis may be used to detect mild organomegaly and adenopathy.[37]Hoffman MA. Clinical presentations and complications of hairy cell leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2006 Oct;20(5):1065-73.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16990107?tool=bestpractice.com
[34]National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hairy cell leukemia [internet publication].
https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx
[48]Hakimian D, Tallman MS, Hogan DK, et al. Prospective evaluation of internal adenopathy in a cohort of 43 patients with hairy cell leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Feb;12(2):268-72.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7906724?tool=bestpractice.com
CT can detect internal adenopathy in approximately 15% of patients.[48]Hakimian D, Tallman MS, Hogan DK, et al. Prospective evaluation of internal adenopathy in a cohort of 43 patients with hairy cell leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Feb;12(2):268-72.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7906724?tool=bestpractice.com
Osteolytic lesions have been described rarely in HCL and have been reported as a finding on x-rays, typically when patients present with bone pain.[49]Robak P, Jesionek-Kupnicka D, Kupnicki P, et al. Bone lesions in hairy cell leukemia: diagnosis and treatment. Eur J Haematol. 2020 Dec;105(6):682-91.
https://www.doi.org/10.1111/ejh.13505
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32757401?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sections of core biopsy demonstrate lymphocytes with obvious cytoplasm within the marrow interstitium, associated with dilatation of marrow sinuses and red blood cell collections (H&E 50x oil)From the collection of Lynn Moscinski, MD [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Sections of core biopsy demonstrate lymphocytes with obvious cytoplasm within the marrow interstitium, associated with dilatation of marrow sinuses and red blood cell collections (H&E 50x oil)From the collection of Lynn Moscinski, MD [Citation ends].