Images and videos
Images
Assessment of steatorrhoea
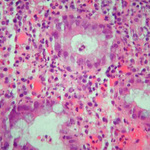
Cryptitis and crypt abscess with morphological distortion of the crypts accompanied by inflammation and abundant lymphatic and plasma cells
Courtesy of Drs Wissam Bleibel, Bishal Mainali, Chandrashekhar Thukral, and Mark A. Peppercorn; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
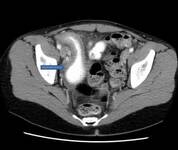
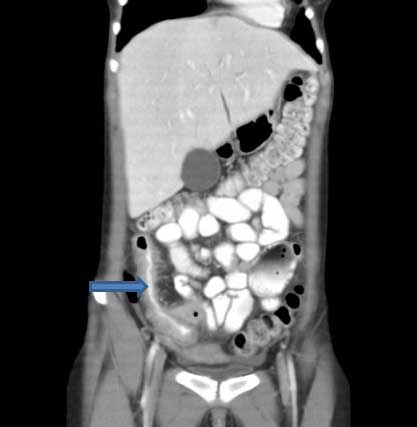
CT scan demonstrating thickening of the terminal ileum in a patient with Crohn's disease exacerbation
Courtesy of Drs Wissam Bleibel, Bishal Mainali, Chandrashekhar Thukral, and Mark A. Peppercorn; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
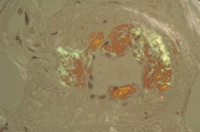
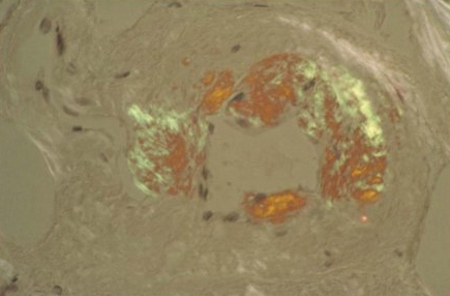
Congo red stain blood vessel in a bone marrow biopsy demonstrating green birefringence pathognomonic of amyloidosis
Courtesy of Morie A. Gertz, MD/Mayo Clinic; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
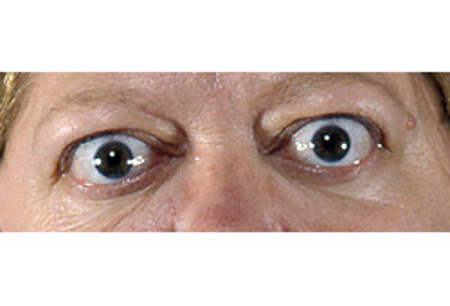
Lid retraction and mild proptosis
Courtesy of Dr Vahab Fatourechi; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
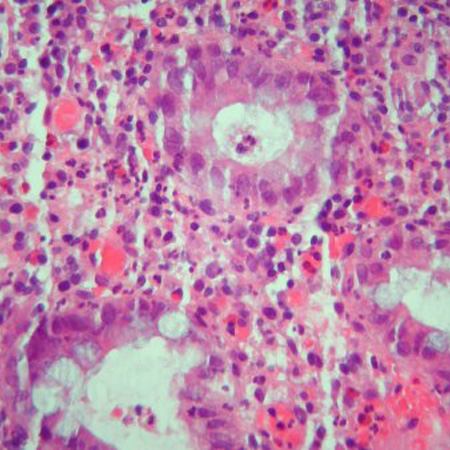
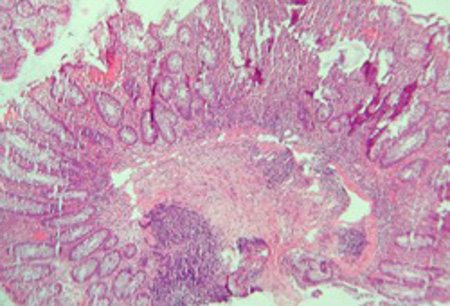
Significant inflammation in the colonic wall, widening of submucosa, and dense lymphoid aggregates in the submucosa
Courtesy of Drs Wissam Bleibel, Bishal Mainali, Chandrashekhar Thukral, and Mark A. Peppercorn; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
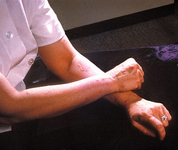
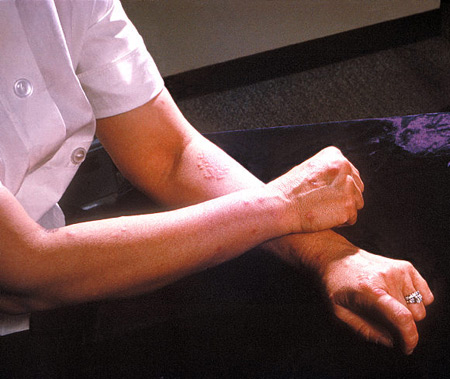
A patient's arms and hands show the presence of erythema nodosum
Courtesy of CDC/ Margaret Renz; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
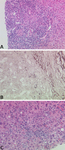
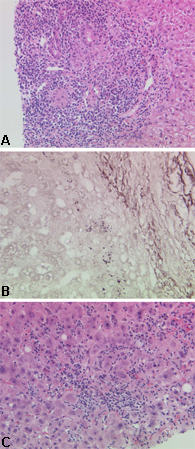
Characteristic histological appearances of primary biliary cholangitis: (a) early stage disease; (b) advanced-stage disease; (c) disease with a significant inflammatory component
Courtesy of Professor Alastair Burt, Newcastle University; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
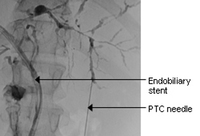
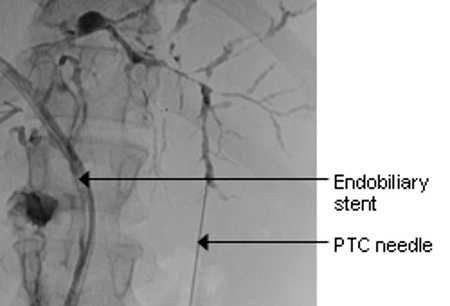
Typical endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) findings in a patient with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC): multifocal strictures of the intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts
Courtesy of Dr Kris Kowdley; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
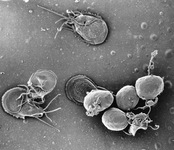
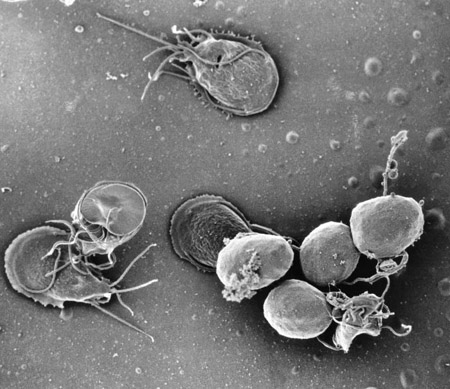
A scanning electron micrograph of an in vitro Giardia lamblia culture. The image shows trophozoites and a cluster of maturing cysts (bottom right)
Courtesy of CDC/ Dr Stan Erlandsen; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Assessment of steatorrhoea
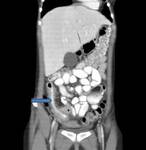
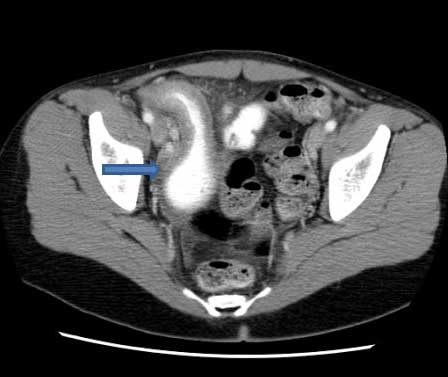
CT scan demonstrating thickening of the terminal ileum in a patient with Crohn's disease exacerbation
Courtesy of Drs Wissam Bleibel, Bishal Mainali, Chandrashekhar Thukral, and Mark A. Peppercorn; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Assessment of steatorrhoea
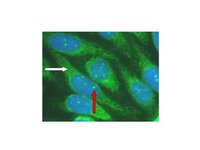
Characteristic auto-antibody patterns in primary biliary cholangitis. White arrow: anti-mitochondrial staining; red arrow: multiple nuclear dot ANA staining
Courtesy of DEJ Jones; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Assessment of steatorrhoea
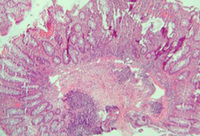
Histological image demonstrating small-intestinal villous atrophy and crypt hyperplasia in coeliac disease
Courtesy of Dr Daniel A. Leffler; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer