Investigations
1st investigations to order
sleep electroencephalogram (EEG)
Test
EEG typically, although not universally, reveals hypsarrhythmia.[27] Hypsarrhythmia is characterised by random high-voltage spike and slow waves of varying amplitude, arising from multiple foci that vary over time. The background is asynchronous and generally chaotic.[28][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: EEG demonstrating hypsarrhythmiaFrom the collection of Dr Teesta Soman and Dr Shelly Weiss [Citation ends].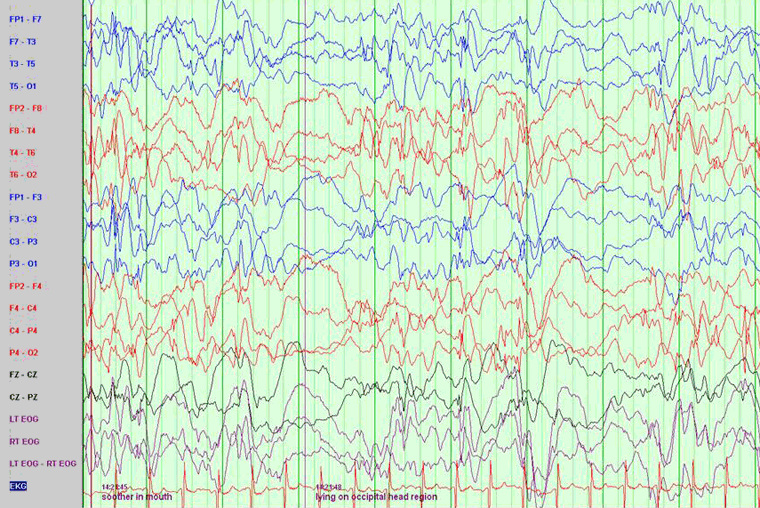
Typical hypsarrhythmia is more likely in the early phase of infantile spasms and in younger patients.[27] It may evolve over time into multifocal and interictal epileptic discharges.
The interictal EEG is very abnormal in this syndrome, but occasionally only during sleep. Hypsarrhythmia may disappear during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and is found with greater sensitivity during other sleep stages. If there is a strong clinical suspicion of infantile spasms, a prolonged sleep recording is required as the typical hypsarrhythmic pattern may be missed.[27] Hypsarrhythmia may be asymmetrical, suggesting a lesional epilepsy, cortical malformation, or disorder of neuronal migration. Modified hypsarrhythmia may be more synchronous, be less symmetrical, and show more focal changes or areas of attenuation.
The ictal EEG is variable but may show suppression, fast activity, or attenuation of the background activity (an electrodecremental response), which may be preceded by high-amplitude vertex slow waves or spindle-like activity.
Result
hypsarrhythmia or modified hypsarrhythmia
full blood count
Test
May reveal signs of infection such as leukocytosis that could cause or contribute to seizures.
Result
may reveal leukocytosis
urea and electrolytes
Test
May reveal electrolyte abnormalities such as hyponatraemia or hypokalaemia that can cause or contribute to seizures. May also demonstrate associated renal function abnormalities.
Result
may reveal electrolyte abnormalities
plasma glucose
Test
To identify hypoglycaemia.
Result
may reveal hypoglycaemia
serum calcium
Test
To identify hypocalcaemia.
Result
may reveal hypocalcaemia
serum magnesium
Test
To identify hypomagnesaemia.
Result
may reveal hypomagnesaemia
liver function tests
Test
Elevated creatine kinase, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, total bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase.
Abnormalities can be seen with intrauterine infections such as cytomegalovirus and toxoplasmosis.
Result
may reveal abnormalities
ammonia
Test
Indicates urea cycle disorders or organic acidaemias.
Result
may be elevated
blood gas
Test
This is a rapid test that may reveal acidaemia (low pH, low bicarbonate), electrolyte disturbances, or elevated lactate (which can be elevated in infection or in mitochondrial disorders) that could cause or contribute to seizures.
Result
may reveal abnormalities
plasma lactate/pyruvate
Test
Elevated in mitochondrial disorders.
Result
may be elevated
plasma amino acids
Test
To screen for inborn errors of metabolism (e.g., non-ketotic hyperglycinaemia, homocitrullinaemia, phenylketonuria).
Result
may reveal varying abnormalities
urine organic acids
Test
To screen for inborn errors of metabolism (e.g., non-ketotic hyperglycinaemia, homocitrullinaemia, phenylketonuria).
Result
may reveal varying abnormalities
acylcarnitines (blood spot)
Test
Indicated in disorders of fatty acid metabolism.
Result
may reveal abnormalities
biotinidase
Test
Indicates biotinidase deficiency.
Result
low in biotinidase deficiency
urine alpha-amino adipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (AASA)
Test
Indicated in pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy.
Result
may be elevated
urine and plasma creatine and guanidinoacetate
Test
Indicated in cerebral creatine deficiency disorders such as guanidinoacetate methyltransferase deficiency (GAMT).
Result
may reveal abnormalities
next-generation sequencing: gene panel/whole-exome sequencing/whole-genome sequencing
Test
May reveal pathogenic variants in: CDKL5, STXBP1, ARX, IQSEC2, TSC1, TSC2, or one of over 100 developmental and infantile epileptic encephalopathy (DEE) genes.
Result
may reveal missense mutations, and small-scale deletions and duplications
microarray comparative genome hybridisation (CGH)
Test
May reveal intermediate-scale genomic rearrangements not detected by standard chromosome analysis.
If microarray CGH is not available, chromosomal analysis should be performed.
Result
may reveal deletions and duplications
brain MRI
Test
MRI brain may identify underlying structural and migrational abnormalities.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Cortical tubers on MRI in tuberous sclerosisFrom the collection of Dr Teesta Soman and Dr Shelly Weiss [Citation ends].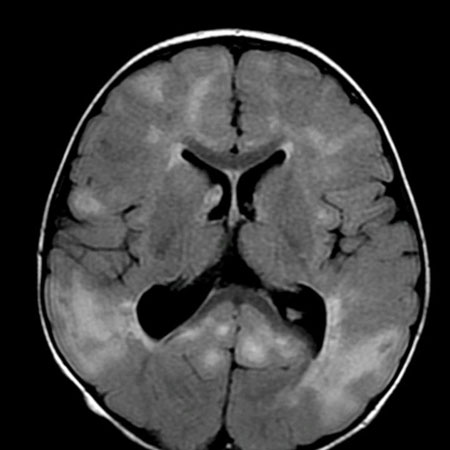
The scan may show areas of malformation or lesions secondary to haemorrhage, calcification, cystic changes, encephalomalacia, infarction, infection, or tumour.
Cortical hamartomas, subependymal nodules, and subependymal giant cell astrocytomas may be seen in tuberous sclerosis.
Lesions may suggest other aetiologies, including various neurocutaneous syndromes and inborn errors of metabolism.
The scan may be entirely normal.
Result
structural and parenchymal abnormalities
Investigations to consider
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination
Test
Should include CSF glucose and lactate paired with plasma, amino acids, pyridoxal-5-phosphate, and methyltetrahydrofolate.
CSF neurotransmitters to screen for PNPO (pyridoxine phosphate oxidase deficiency) and folinic acid responsive seizures.
Result
may detect low CSF-to-blood-glucose ratio in glucose transporter defects and high CSF lactate in mitochondrial disorders; various amino acid abnormalities suggest an aminoacidopathy
thyroid function tests (free thyroxine [FT4], thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH])
Test
May reveal thyroid function abnormalities that can cause or contribute to seizures.
Result
may reveal thyroid function abnormalities
plasma transferrin glycoforms
Test
May reveal abnormalities associated with congenital defects of glycosylation (CDG).
Result
may reveal abnormalities
very long-chain fatty acids
Test
May reveal abnormalities associated with peroxismal disorders such as X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.
Result
may reveal abnormalities
serum copper, ceruloplasmin
Test
May reveal abnormalities associated with Menke's disease.
Result
may reveal abnormalities
urine sulfocysteine
Test
To screen for molybdenum cofactor deficiency, isolated sulfite oxidase deficiency, and hereditary xanthinuria.
Result
may be abnormal
CT brain
Test
A CT brain scan is less sensitive and should be considered only if it is not possible to perform an MRI scan.
Result
structural and parenchymal abnormalities
cytomegalovirus (CMV) culture, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), or serology
Test
Serology could include IgG and/or IgM.
Result
may reveal underlying CMV infection
toxoplasmosis serology
Test
Toxoplasmosis IgG and/or IgM.
Result
may reveal underlying toxoplasmosis infection
echocardiogram
Test
May reveal rhabdomyomas in case of underlying tuberous sclerosis.
Result
may reveal rhabdomyomas
renal ultrasound
Test
May reveal renal angiomyolipomas in case of underlying tuberous sclerosis.
Result
may reveal renal angiomyolipomas
ophthalmology examination
Test
May reveal abnormalities including chorioretinitis in intrauterine infections, and hamartomas in tuberous sclerosis.
Result
may reveal abnormalities
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer