Investigations
1st investigations to order
serum total and direct or conjugated bilirubin
Test
These test results imply liver dysfunction.
Result
direct or conjugated bilirubin >17.1 micromoles/L (1 mg/dL)
newborn screen (includes tests for galactosaemia, thyroid dysfunction, cystic fibrosis, and a variety of metabolic diseases)
Test
Positive test for cystic fibrosis does not exclude biliary atresia, as pathology may co-exist.
Result
usually normal in biliary atresia
prothrombin time (PT), INR
Test
Coagulopathy is a serious and important complication.
It is common in late presentation disease and occurs with liver dysfunction due either to malabsorption of vitamin K or hepatic disease. If PT is abnormal, other fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies may be present. Coagulopathy is corrected with parenteral vitamin K1.
Result
usually normal, may be elevated INR >1.5, PT >14 seconds
FBC with differential
Test
This group of tests will give an overall picture of health of the child. They are not directly diagnostic.
Result
in advanced disease; low platelets, low WBC
serum AST, ALT, ALP, and gamma-GT
Test
An elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase supports biliary disease. Similarly elevated liver enzymes may support an alternative diagnosis such as hepatic infection.
Result
disproportionately high gamma-glutamyl transferase
abdominal ultrasound
Test
Ultrasound performed to evaluate gallbladder morphology, texture, and size; splenic appearance; ductal dilation; and vascular anatomy.[54] Gallbladder either shrunken or not seen. Can identify choledochal cyst or other structural problems. Triangular cord sign is a triangular echogenic density seen just above the porta hepatis on ultrasound scan. Its presence is highly suggestive of biliary atresia, but is rarely seen.[52]
Ultrasound may also identify laterality defects that could be consistent with a biliary atresia diagnosis, such as polysplenia or pre-duodenal portal vein.
Result
liver usually normal texture, possibly enlarged, unlikely ductal dilation; absent or multiple spleen; ascites, triangular cord sign possible
Investigations to consider
hepatobiliary scintigraphy (technetium Tc 99m-di-isopropyl-acetanilido-imino-diacetic acid scan)
Test
Failure of excretion is not diagnostic, and further investigation is warranted with either liver biopsy or cholangiogram.[52]
Generally not useful if stools are acholic.
Result
no tracer excretion into gut after 24 hours
liver biopsy
Test
The purpose of the liver biopsy is to differentiate biliary atresia from another intrahepatic cause of cholestasis. Expansion of the portal spaces, proliferation of bile ductules, and bile plugs are typical; the earliest histological changes may be relatively non-specific, and biopsies done too early may result in a false negative.[55] There is great overlap between histological findings in biliary atresia and other diseases such as cytomegalovirus infection, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, early Alagille syndrome, total parenteral nutrition, cystic fibrosis, and sepsis.[56][57][58][59][60][61][62][63][64][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Liver biopsy specimen at the time of diagnosis reveals extensive fibrosis with bile duct and ductular proliferation and bile plugsPathology Department at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia [Citation ends].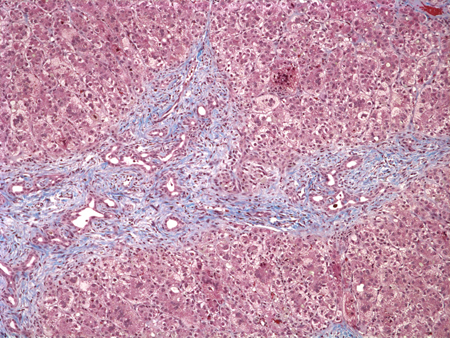
Result
bile duct proliferation with bile plugs is the most specific finding for biliary obstruction
cholangiogram
Test
A characteristic liver biopsy plus cholangiogram demonstrating lack of patency are the standard confirmatory tests.[53]
Contrast can be injected percutaneously into the gallbladder at some centres by the interventional radiologist prior to surgery but usually done intraoperatively.
Result
atresia of part or all of the biliary tree between liver and bowel
CXR
Test
Dextrocardia should prompt an evaluation for biliary atresia splenic malformation syndrome. Butterfly vertebrae, hemi vertebrae, pulmonary anomalies, and vascular anomalies are indicative of Alagille syndrome.
Result
dextrocardia
infection screen: blood and urine cultures
Test
To exclude alternative pathology; the most common infections causing jaundice are toxoplasmosis, herpes, rubella, syphilis, adenovirus, enterovirus, and cytomegalovirus. Bacterial sepsis or a urinary tract infection may also be responsible. Less commonly, parvovirus B19, paramyxovirus, HIV, listeriosis, and tuberculosis have also been reported to cause jaundice.
Culture may yield growth of the pathogen or raised IgM levels against the particular pathogen.
Result
usually negative in biliary atresia
urine PCR for cytomegalovirus
Test
Cytomegalovirus present in urine if infection active.
If the test result is positive and hepatobiliary scintigraphy demonstrates tracer excretion, liver biopsy may not be necessary.
Result
usually negative in biliary atresia
plasma or serum amino acids
Test
Increased levels of tyrosine, phenylalanine, and methionine are found in tyrosinaemia type 1.
Can present in a similar manner to generalised hepatic dysfunction, galactosaemia, hereditary fructose intolerance, and transient tyrosinaemia of the newborn, as some of the abnormalities overlap.
Result
usually normal in biliary atresia
alpha-1 level and protease inhibitor (Pi) type
Test
To exclude alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. PiZZ and PiSZ are the two most common types resulting in liver disease. There are many similarities in presentation between biliary atresia and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. A low alpha-1 AT level and a PiZZ phenotype, PiSZ phenotype, PiZZ genotype, or PiSZ genotype, is used to diagnose alpha-1 AT deficiency.
Result
usually normal in biliary atresia
random serum cortisol
Test
Low random cortisol level in panhypopituitarism or adrenal insufficiency.
Result
usually normal in biliary atresia
urinary organic acids
Test
Tests for a variety of diseases including organic acidaemias, peroxisomal diseases, mitochondrial diseases, primary lactic acidosis.
Result
usually normal in biliary atresia
urinary succinylacetone
Test
Presence in the urine suggests tyrosinaemia.
Result
usually normal in biliary atresia
urinary bile acids
Test
Primary bile acid defects can be detected by mass spectrometry of urine. Test should be done before ursodeoxycholic acid is started, as this is a bile acid and will affect results.
Result
usually normal in biliary atresia
serum lactate/pyruvate ratio
Test
False positives may be found in hypoxia. Abnormal ratios suggest a mitochondrial defect.
Result
usually normal in biliary atresia
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer