Investigations
1st investigations to order
platelet count
Test
Degree of thrombocytopenia varies, but decreased platelets are required for the diagnosis of TTP. Platelet count is <20 x 10⁹/L in approximately 95% of patients.[44]
Result
decreased
haemoglobin
Test
Approximate prevalence 80%.[44]
Result
<8 g/L
haptoglobin
Test
Haptoglobin is significantly decreased during haemolysis.[45]
Result
decreased
peripheral smear
Test
Schistocytes might be absent from the blood film in the first 24 to 48 hours, but they are usually found on evaluation of the blood film at presentation.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Peripheral smear of a patient with TTP showing many fragmented, partly rounded cells. Also note the lack of plateletsFrom the collection of Dr R.F. Connor, Harvard Medical School, Boston [Citation ends].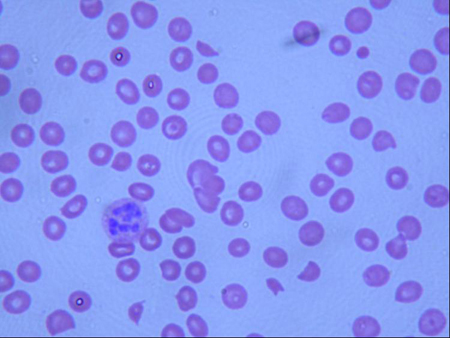
Result
microangiopathic blood film with schistocytes
reticulocyte count
Test
Typically raised in TTP.
Result
raised
urinalysis
Test
Mild renal abnormalities of proteinuria and renal insufficiency occur in approximately 40% of patients.[44]
Result
proteinuria
urea and creatinine
Test
Severe renal failure occurs in approximately 5% of patients.[44]
Result
increased
direct Coombs' test
Test
To rule out autoimmune haemolytic anaemia.
Result
negative
Investigations to consider
ADAMTS-13 activity assay and inhibitor titres
Test
There is debate over whether the von Willebrand factor cleaving enzyme (ADAMTS-13) activity assay can help in the management of patients with TTP. It does not appear to predict who will respond to plasma exchange. [46] For the diagnosis of TTP, ADAMTS-13 activity levels of <5% to 10% are diagnostic.[1][3][4]
Result
decreased activity
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer