Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
Recommended as the first test to be ordered.
Folate deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, and megaloblastic anaemia virtually define TS.
If these findings are not present the diagnosis of TS should be questioned.
Result
macrocytic anaemia
quantitative faecal fat assay
D-xylose test
serum folate
Test
Folate deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, and megaloblastic anaemia virtually define TS.
If none of these findings are present the diagnosis of TS should be questioned.
Result
low
serum vitamin B12
Test
Folate deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, and megaloblastic anaemia virtually define TS.
If none of these findings are present the diagnosis of TS should be questioned.
Result
low
Investigations to consider
stool ova and parasites (O and P)
Test
Stool O and P test helpful in differentiating from parasitic cause.
Result
negative
stool culture
Test
May differentiate from bacterial cause.
Result
negative
upper gastrointestinal endoscopy with biopsy
Test
Biopsies should be taken distal to the level of the ampulla.
For patients in whom a biopsy is contraindicated, the use of a magnifying endoscope shows excellent promise as certain gross mucosal patterns are 94% to 100% specific for histological villous atrophy.[30][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tropical sprue; ridged and foveolar patterns, duodenumFrom the collection of Dr M. Guelrud; used with permission [Citation ends].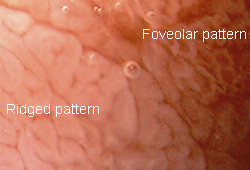 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopy, normal and tropical sprue (TS) villi changes, duodenumFrom the collection of Dr M. Guelrud; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopy, normal and tropical sprue (TS) villi changes, duodenumFrom the collection of Dr M. Guelrud; used with permission [Citation ends].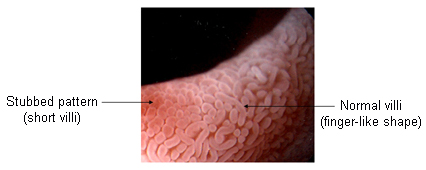 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tropical sprue; scalloping, mosaic appearance, and mucosal grooves; duodenumFrom the collection of Dr M. Guelrud; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tropical sprue; scalloping, mosaic appearance, and mucosal grooves; duodenumFrom the collection of Dr M. Guelrud; used with permission [Citation ends].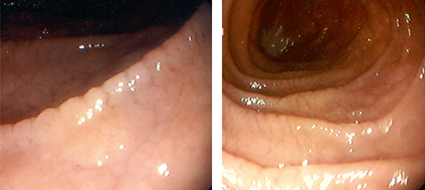
As this procedure is relatively safe and easily performed, the threshold to request it should be low.
In endemic tropical areas, a combination of other investigations and clinical judgment should be employed if endoscopy facilities are not available.
While histological changes seen in TS can be indistinguishable from those seen in patients with coeliac disease, TS is associated with a much more pronounced eosinophilic infiltrate in the duodenum than is seen in coeliac disease.[24]
Result
duodenal and/or jejunal biopsies typically reveal short villi, elongated crypts, and inflammatory cells in the lamina propria; none of these findings are specific for TS
folic acid therapeutic trial
Test
The benefits of this treatment have been shown in numerous studies.[31][32][33] A lack of response to folic acid supplementation should cast doubt on the diagnosis of TS.
As folic acid supplementation alone reverses most of the laboratory and endoscopical abnormalities, other studies should be performed prior to the initiation of this test.
Result
marked and prompt clinical, laboratory, and pathological improvement
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer