Summary
Definition
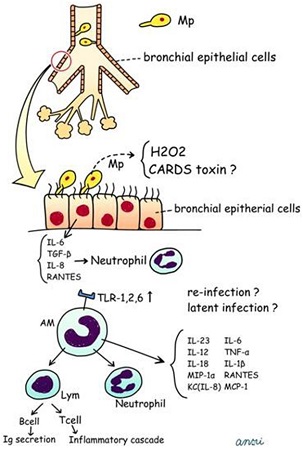
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- persistent cough
- dry cough
- prolonged symptoms
- fever
- adventitious sounds on physical examination
- exposure to a person with respiratory tract infection
Risk factors
- close community settings
- recent exposure
- cigarette smoking
- age <30 years
- immunosuppression
- asplenia
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- WBC count
- haemoglobin
- LFTs
- pulse oximetry
- urea and electrolytes
- C-reactive protein
- chest x-ray
Investigations to consider
- nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT)
- serology
- culture±/Gram stain
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Ran Nir-Paz, MD

Professor in Medicine and Clinical Microbiology
Department of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases
Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center
Jerusalem
Israel
Disclosures
RNP declares that he has no competing interests. RNP is an author of several references cited in this topic.
Takeshi Saraya, MD, PhD
Associate Professor
Department of Respiratory Medicine
Kyorin University School of Medicine
Tokyo
Japan
Disclosures
TS declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Enno Jacobs, MD
Director
Institute for Medical Microbiology and Hygiene
Dresden
Germany
Disclosures
EJ declares that he has no competing interests.
Laura J. Christie, MD
Research Scientist
Pediatric Infectious Disease
California Department of Public Health
Viral and Rickettsial Disease Laboratory
Richmond
CA
Disclosures
LC declares that she has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer