Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
FBC with differential and calculation of the absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) is the initial laboratory investigation for all patients with suspected SCID.
Lymphopenia on a routine FBC should also alert the physician to consider SCID.
ALC is calculated by multiplying the percentage of lymphocytes by the absolute WBC count.
An ALC of <3000 cells/mm³ has been proposed as the cutoff to determine which infants require further evaluation for SCID.[38]
ALC may be normal in cases of maternal engraftment of lymphocytes, or in conditions where gene expression is partially intact (e.g., hypomorphic SCID variants), or in cases where B cells make up the majority of the lymphocyte population (e.g., T-B+ SCID).
Result
ALC <3000 cells/mm³
flow cytometry
Test
Flow cytometry is required for diagnosing SCID and classifying patients according to lymphocyte phenotype. It is the initial diagnostic test for all patients with suspected SCID.[2][4]
Flow cytometry measures the total numbers of T cells, T-cell subsets (i.e., CD4+ T cells, CD8 T+ cells), naive T cells (CD4+CD45RA+), memory T cells (CD4+CD45RO+), B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells in the peripheral blood.
The phenotypic classification of SCID is based on the absence or presence of B cells (B- or B+) and NK cells (NK- or NK+), in addition to the absence of T cells (T-).[2][3]
The majority of T cells in healthy infants are naive (e.g., CD45RA isotype +). In all forms of SCID, there is a profound decrease in the number of all T cells, including naive T cells.
Maternal engraftment of T cells or residual gene function in hypomorphic variants of SCID may result in low to normal numbers of T cells, but these T cells are almost all memory T cells (CD4+CD45RO+).[8]
The Primary Immune Deficiency Treatment Consortium defines SCID as absent, or very low numbers of T cells (CD3 T cells <300/microlitre), and absent or very low T-cell function (<10% of lower limit of normal), as measured by T-cell proliferation studies using phytohaemagglutinin.[39]
Result
absence or marked reduction in the total number of T cells
chest x-ray
Test
Demonstrates absence of the thymic shadow in all patients with SCID (except those with SCID due to coronin 1A deficiency).[40][4][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of an infant depicting an absent thymic shadow; infants with SCID may be athymic at time of presentationChildren's Hospital of Wisconsin, Department of Radiology; used with permission [Citation ends].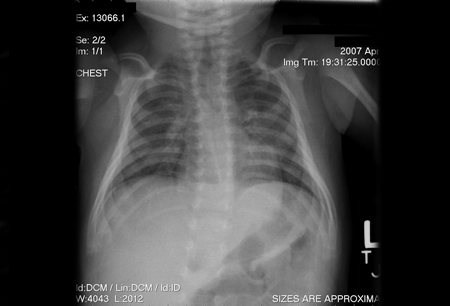 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of an infant depicting a normal thymic shadowChildren's Hospital of Wisconsin, Department of Radiology; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of an infant depicting a normal thymic shadowChildren's Hospital of Wisconsin, Department of Radiology; used with permission [Citation ends]. This observation supports the diagnosis of SCID.[4]
This observation supports the diagnosis of SCID.[4]
Patients with adenosine deaminase deficiency SCID may demonstrate anterior rib abnormalities on x-ray (i.e., cupping/fraying of the costochondral junctions).[41]
Result
absent thymic shadow (except in SCID due to coronin 1A deficiency) or costochondral junction abnormalities
quantitative immunoglobulin test (IgG, IgM, and IgA)
Test
A quantitative immunoglobulin test should be carried out in all patients with suspected SCID to help confirm diagnosis.
All SCID patients (including those with normal B cell numbers) have hypogammaglobulinaemia secondary to the lack of T-cell help to induce antibody production.[4] Patients also have absent isohaemagglutinins and absent specific antibody responses to inactivated protein-based vaccines, such as tetanus and diphtheria.[34]
Newborn infants commonly have measurable levels of IgG due to placental transfer of maternal IgG to the fetus, but IgM and IgA are absent or levels are low.
Result
absent or low number of immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM, and IgA)
Investigations to consider
chest ultrasound
Test
Demonstrates absence of the thymic shadow in patients with SCID.
Can be considered if chest x-ray is unavailable or if x-ray results are ambiguous.
Result
absent thymic shadow
CT scan of the chest
Test
Demonstrates absence of the thymic shadow in patients with SCID.
Can be considered if chest x-ray is unavailable or if x-ray results are ambiguous.
Result
absent thymic shadow
MRI chest
Test
Demonstrates absence of the thymic shadow in patients with SCID.
Can be considered if chest x-ray is unavailable or if x-ray results are ambiguous.
Result
absent thymic shadow
fundoscopy
Test
In infants with suspected SCID with cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection, regular fundoscopic evaluation for CMV retinitis should be performed.
Result
presence or absence of CMV retinitis
enzyme testing
Test
In suspected cases of purine metabolic defects (e.g., adenosine deaminase deficiency and purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency), enzyme levels and associated toxic metabolites (e.g., deoxy-ATP) should be measured.[34]
Adenosine deaminase levels are reduced in adenosine deaminase deficiency SCID, and purine nucleoside phosphorylase levels are reduced in purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency SCID.[34]
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency can be associated with decreased serum uric acid (<59 micromol/L [<1 mg/dL]).
Result
adenosine deaminase or purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency
serum uric acid
Test
Low serum uric acid level is suggestive of purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency.[42]
Result
serum uric acid <59 micromol/L (<1 mg/dL)
T-cell proliferation studies
Test
Functional testing of the immune system should be performed using T-cell proliferation studies, if there are measurable number of T cells.
Infants with SCID show diminished responses to mitogens including phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and concanavalin A.[34] Consider postponing T-cell proliferation studies with PHA if T cells are absent.
Result
absent response to mitogens
polymerase chain reaction-based viraemia testing
Test
Polymerase chain reaction-based viraemia testing for HIV-1, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) should be performed in all patients with suspected SCID.
Serological studies for viral infections should not be used as transplacentally-acquired maternal antibodies may lead to false-positive results.
Result
presence or absence of HIV-1, CMV, or EBV
radiation sensitivity of fibroblast cultures
Test
Consider ordering in patients with suspected defects in genes involved in DNA repair and recombination (e.g., Artemis/DNA cross-link repair 1C [DCLRE1C], DNA ligase IV, and Cernunnos/XLF).
Result
enhanced radiation sensitivity of fibroblast cultures from patients with DNA repair and recombination defects
genetic testing
Test
DNA testing to establish the underlying genetic aetiology of SCID should be performed.[31]
Result
presence or absence of specific gene depending on type of SCID
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer