Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
Should be ordered in patients with visceral leishmaniasis.
Anaemia is the most common finding, followed by leukopenia and thrombocytopenia.
Pancytopenia was found in only 16% of patients in Nepal, but specificity was high (98%).[85] Pancytopenia is more frequent in HIV-co-infected patients.[86]
Result
anaemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
liver function tests and urea/creatinine
Test
Treatment with paromomycin, pentavalent antimonial compounds, amphotericin-B, or miltefosine requires monitoring of liver and renal function; therefore, baseline liver function tests and urea/creatinine should be ordered.
Result
variable; may be elevated in visceral leishmaniasis, particularly alkaline phosphatase
serum human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG)
Test
Pregnancy status determines treatment choices and later in pregnancy the immunological response, so all women of child-bearing age should be tested prior to treatment.
Result
may be positive or negative
Investigations to consider
microscopic examination of relevant specimen
Test
Recommended to confirm diagnosis of suspected cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) or visceral leishmaniasis (VL). Probably the most common confirmatory test used in CL-endemic countries.[1]
CL: biopsy aspirates, smears, scrapings, and skin slit smears are used.[77] Sensitivity is variable and depends on sampling technique, duration of lesions, presence/absence of ulceration, and presence of super-infection. Sensitivity is poor (<50%) in mucosal leishmaniasis.[1][87]
VL: specimen can be obtained by aspiration of splenic tissue (discouraged due to risk of fatal haemorrhage), bone marrow, liver, or lymph nodes. Microscopic examination of splenic aspirates is the most sensitive technique (>95%), but carries a 1:1000 risk of major bleeding; considerable technical expertise is required.[88] Examination of bone marrow aspirate or lymph node fluid is safer, but is of lower sensitivity (70% to 90% and 58%, respectively). The sensitivity of a bone marrow examination is increased to 85% in patients with immunosuppression.[89][90] In people with HIV infection who are immunocompromised, tissue biopsy of gastrointestinal mucosa or buffy coat smears may be diagnostic.
May also be used to confirm diagnosis of post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL). Sensitivity is improved if large or nodular skin lesions are sampled in PKDL.[6][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Skin touch preparation showing Leishmania tropica amastigotes. Intact macrophage is practically filled with amastigotes, several of which have a clearly visible nucleus and kinetoplast (arrows)Image courtesy of CDC; NCID; DPDx [Citation ends].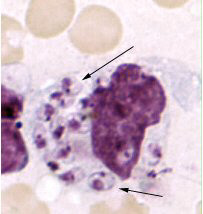
Result
amastigote form of the Leishmania species in macrophages or monocytes
blood (buffy coat) or tissue culture
Test
Recommended to confirm diagnosis of suspected cutaneous or visceral leishmaniasis, and is especially useful when the goal is to characterise infecting parasite species.
Novy-Nicolle-McNeal medium or other biphasic-type media are often used, although modified Schneider’s medium is often sufficient.[91]
While 100% specific, sensitivity is variable (typically <50%), and depends on sampling technique and quality of culture media, sample processing and laboratory infrastructure, duration of lesions, and presence of super-infection. Culture with isoenzyme characterisation permits species identification.
May also be used to confirm diagnosis of post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis (PKDL). Sensitivity is improved if large or nodular skin lesions are sampled in PKDL.[6]
Result
promastigote forms of the Leishmania species in culture media
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
Recommended to confirm diagnosis of suspected cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) or visceral leishmaniasis (VL), if available. More sensitive than microscopic examination or parasite culture for the diagnosis of suspected CL and VL.[8]
Sensitivity estimates range from 70% to 100% when using tissue biopsies for CL diagnosis and when using peripheral blood for VL diagnosis.[78][82][92][93]
Particularly useful in cases with a low parasite load (e.g., mucosal leishmaniasis [ML]).[78]
May also be used to confirm diagnosis of post-kala-azar dermal leishmaniasis. Sensitivity is improved if large or nodular lesions are sampled.[6]
Recommended when species characterisation is needed (e.g., to determine whether a patient may be at risk of ML in the future because of Leishmania [Viannia] species infection). There is no clinically available PCR on offer at a species level of determination; many are genus only.
The diagnostic value of PCR in patients with relapsed VL is uncertain, as PCR can remain positive in patients with clinical cure; however, quantitative PCR may show rising levels of DNA in relapse.[82]
Result
Leishmania DNA
serology
Test
Recommended to support diagnosis of suspected visceral leishmaniasis (VL).[8]
A useful test in immunocompetent patients with suspected VL, but less sensitive in patients who are immunosuppressed. However, it may be used in patients who are immunosuppressed if parasitological diagnosis is not feasible.[19][81]
Various highly sensitive and specific tests are available, and the choice depends mainly on availability and laboratory expertise.[2]
Direct agglutination test: one meta-analysis of 30 studies showed 94.8% sensitivity and 97.1% specificity.[94]
rK39 dipstick: rapid diagnostic test that takes 10 to 20 minutes. One meta-analysis of 18 studies showed 91.9% sensitivity and 92.4% specificity.[95] Less sensitive in East Africa than on the Indian subcontinent and in Latin America.[65][95][96][97]
Indirect fluorescent antibody test: moderate to high sensitivity (>85%) and high specificity (>90%) have been reported.[98][99]
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): highly sensitive and specific. Crude soluble Leishmania antigen or various recombinant proteins (including rK39) can be used; use of recombinant antigen may increase sensitivity.[2]
Western blot: promising test but experience is restricted to a few laboratories.[100]
Diagnosis of relapse cannot be based on serological tests, as antibodies against Leishmania donovani or Leishmania infantum (synonym: Leishmania chagasi) usually remain detectable for years after initial diagnosis.[83][84]
Result
positive for Leishmania antibodies, or antibody titre above locally validated threshold
leishmanin skin test (Montenegro skin test)
Test
A test to support the diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis when healing lesions are primarily present.
Killed Leishmania parasites are inoculated intradermally, with the response to the inoculation read 48 hours after inoculation.[77]
May be useful to rule out leishmaniasis in a patient with consistent skin lesions and travel to an endemic region who resides in a non-endemic area.
Past and present infection cannot be discerned.
This test is not recommended or available in the US or South America.
Result
≥5 mm induration 48 hours after inoculation
serum HIV testing
Test
Visceral leishmaniasis is an opportunistic infection in patients with HIV/AIDS. Newly diagnosed patients should be assessed for HIV/AIDS.
Result
may be positive or negative
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer