Last reviewed: 16 Mar 2025
Last updated: 13 Mar 2025
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- older age
- vitamin D and calcium deficient diets
- lack of sunlight exposure
- fractures
- malabsorption syndromes
- diffuse bone pain and tenderness
- proximal muscle weakness
- family history of osteomalacia
- waddling gait
Risk factors
- dietary calcium and vitamin D deficiency
- chronic kidney disease
- limited sunlight exposure
- inherited disorders of vitamin D and bone metabolism
- hypophosphatasia
- anticonvulsant therapy
- mesenchymal tumours
- Fanconi's syndrome
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- serum calcium level
- serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level
- serum phosphate level
- serum urea and creatinine
- intact PTH
- serum alkaline phosphatase
- 24-hour urinary calcium
Investigations to consider
- bone x-rays
- 24-hour urinary phosphate
- dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
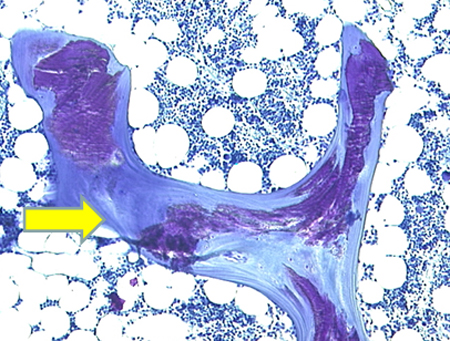
- iliac crest biopsy with double tetracycline labelling
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Bridget Sinnott, MD

Professor of Medicine
Medical College Georgia
Augusta
GA
Disclosures
BS declares that she has no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Dr Bridget Sinnott would like to gratefully acknowledge Dr Jelena Kravarusic, a previous contributor to this topic. JK declares that she has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Udaya Kabadi, MD, FRCP(C), FACP, FACE
Director
Endocrinology
Department of Internal Medicine
VA Medical Center
University of Iowa
Iowa City
IA
Disclosures
UK declares that he has no competing interests.
Stephan Scharla, MD
Department of Internal Medicine
Endocrinology & Diabetes
LMU University Munich
Munich
Germany
Disclosures
None declared.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer