Differentials
Common
Bacterial vaginosis
History
often asymptomatic; fishy odour especially after condomless intercourse; off-white, thin, homogeneous discharge; rarely dysuria and dyspareunia; risk factors including new sexual partner or >3 in past year, douching, cigarette smoking
Exam
discharge typically homogeneous, thin, grayish-white and odorous
1st investigation
- Amsel's criteria:
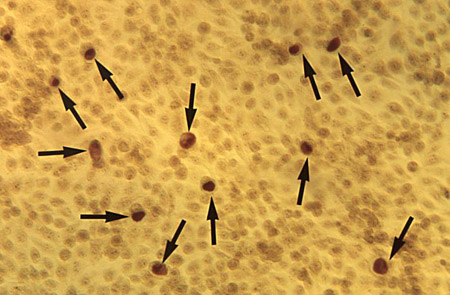
at least 3 out of 4 of: thin, homogeneous discharge; vaginal pH >4.5; a positive whiff test or release of amine odour with the addition of base (10% potassium hydroxide); clue cells on microscopic evaluation of saline wet preparation
- KOH test of vaginal discharge:
presence of fishy odour when 10% potassium hydroxide (KOH) is added to vaginal discharge
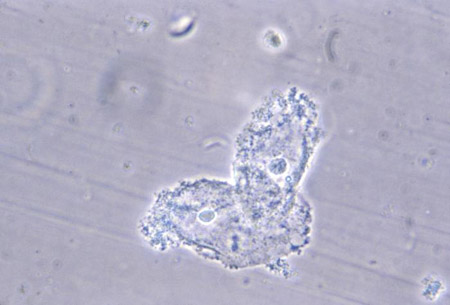
More - wet mount microscopy of vaginal discharge:
clue cells
More - Gram stain:
relative concentration of lactobacilli
More
Trichomoniasis
History
purulent, malodorous, thin discharge; can also present with burning, pruritus, dysuria, frequency, and dyspareunia; symptoms may be worse during menstruation
Exam
typically, erythema of the vulva and vaginal mucosa; vaginal discharge (green-yellow, frothy) and strawberry cervix are not reliable clinical signs but may be present
1st investigation
Other investigations
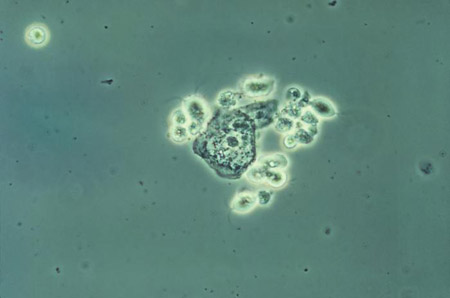
- culture from vaginal sample on Diamond medium:
positive
More
Vulvovaginal candidiasis
History
vulvar pruritus, dysuria, pain, burning, swelling, redness, soreness, irritation, dyspareunia; usually little or no discharge but if present, appears white and clumpy, curd-like; more frequent in patients with diabetes
Exam
erythema of the vulva, vaginal mucosa, and vulva oedema; with Candida albicans discharge usually thick, adherent, cottage cheese-like, but may be thin and loose; with Candida glabrata usually little discharge
1st investigation
Other investigations
- nucleic acid amplification test:
positive for Candida
More - nucleic acid probe:
positive for Candida
- serum fasting glucose:
may confirm diabetes in recurrent or resistant disease
- HbA1c:
may confirm diabetes in recurrent or resistant disease
Chlamydia trachomatis infection
History
often asymptomatic; or purulent or mucopurulent discharge from endocervix, intermenstrual or postcoital bleeding, dysuria, urinary frequency, dyspareunia, vulvovaginal irritation; pain and fever rare
Exam
cervix friable, erythematous and oedematous, with purulent or mucopurulent discharge; possible cervical motion tenderness; with Chlamydia trachomatis: yellow opaque endocervical discharge, easily induced cervical bleeding
1st investigation
- nucleic acid amplification test:
positive
More
Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection
History
asymptomatic; or vaginal pruritus and/or a mucopurulent discharge; abdominal pain or dyspareunia suggests extension to upper tract; may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, infertility if untreated
Exam
cervix normal or with friable mucosa and purulent discharge
1st investigation
Other investigations
- enzyme immunoassay of cervical or urine sample:
positive
More
Mycoplasma genitalium
History
often asymptomatic; or purulent or mucopurulent discharge from endocervix, intermenstrual or postcoital bleeding, dysuria, urinary frequency, dyspareunia, vulvovaginal irritation; abdominopelvic pain
Exam
cervix friable, erythematous with purulent or mucopurulent discharge; possible cervical motion tenderness; easily induced cervical bleeding
1st investigation
- nucleic acid amplification test:
positive
More
Other investigations
Irritant and allergic vaginitis
History
vaginal itching and discharge in association with use of topical medications, spermicidal products, douching solutions, condoms, or diaphragms; can be reaction to sperm, latex, dyes, soap, tampons, pads
Exam
vulvar erythema, non-specific vaginal discharge
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical
More
Other investigations
- patch testing:
may be positive for possible irritants
Physiological discharge in adults
History
usually consists of 1 to 5 mL discharge per 24 hours; typically transparent, odourless (but can also be slightly malodorous), mucousy, and white-to-yellowish; more noticeable with higher oestrogen states (e.g., during pregnancy, when using oestrogen-progestin contraceptives, or at ovulation)
Exam
scant transparent, mucousy, and white-to-yellowish discharge
1st investigation
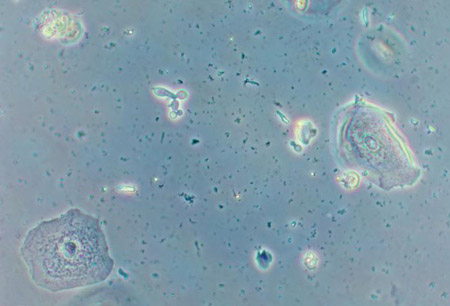
- microscopy of vaginal sample:
sheets of vaginal epithelial cells
Other investigations
Foreign body in children
History
discharge usually bloody and foul-smelling
Exam
foreign body, bloody and purulent discharge
1st investigation
- abdominal or pelvic x-ray:
foreign body visualised
Other investigations
- pelvic examination (may have to be under anaesthesia):
foreign body visualised
Non-specific vaginitis
History
irritation from bubble baths, perfumed soaps, tight-fitting clothes, back-to-front wiping, poor wiping after toilet training can lead to non-specific vaginitis; vulvar skin easily traumatised
Exam
scant to copious foul-smelling discharge
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical (after exclusion of other causes)
Other investigations
Physiological discharge in children
History
a few months before menarche (9-13 years old); grey-white physiological discharge due to increase in oestrogen levels
Exam
scant to moderate, clear to white discharge; otherwise normal
1st investigation
- microscopy of vaginal sample:
sheets of vaginal epithelial cells
Other investigations
Uncommon
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection
History
superficial sores or ulcers over the vulva; sometimes watery vaginal discharge appears 7-11 days after primary infection; general malaise and fever possible; central nervous system involvement rare
Exam
multiple crops of painful, shallow ulcers over the vulva, vagina and cervix, which often coalesce then heal spontaneously without scarring
1st investigation
- nucleic acid amplification test:
positive
More
Other investigations
- viral cultures of lesions:
virus detected
More
Streptococcal vaginitis in adults
History
predisposing factor present: household or personal history of upper respiratory tract infection with group A streptococci; sexual contact; vaginal atrophy
Exam
profuse/copious vaginal discharge
1st investigation
- vaginal culture swab:
positive for Streptococcus pyogenes (group A streptococci)
Other investigations
Genital schistosomiasis
History
living in endemic area; may be encountered in the West subsequent to increased tourism
Exam
erythematous cervix; copious vaginal discharge
1st investigation
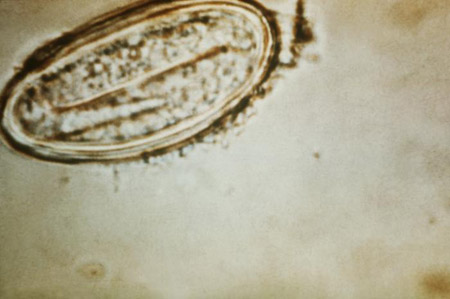
- microscopy of urine for parasites:
eggs present
Other investigations
- cervical punch biopsy:
eggs present
More - high-magnification colposcopy:
sandy patches with yellow colour on mucosal surfaces
Entamoeba gingivalis plus intrauterine device (IUD)
History
associated with intrauterine device use; identified in patients with concurrent oral infection and use of copper-T 380A IUD
Exam
profuse vaginal discharge may be present
1st investigation
- washings from IUD for direct and stained smears plus DNA extraction/polymerase chain reaction:
parasite present
- concurrent testing for oral infection:
parasite present
Other investigations
Inadequate hygiene
History
history of wiping from back to front, not changing tampons and pads in timely fashion, inadequate vaginal cleaning; pruritus; may have more frequent vaginal fungal infections
Exam
malodorous vaginal discharge, smegma
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical
Other investigations
Foreign body in adults
History
foul-smelling and/or bloody discharge
Exam
occasional irritation of labia and inner thighs; a longstanding foreign body can lead to extensive adhesion formation with near complete obstruction of the vagina inferior to the location of the foreign body
1st investigation
- pelvic examination:
visualisation or palpation of foreign body, may be full or partial obliteration of the vagina
- abdominal/pelvic x-ray:
visualisation of foreign body
More
Combined contraceptive or hormonal vaginal ring-related
History
symptom onset with use of contraceptive ring
Exam
possible irritation at the site of ring pressure in the vagina
1st investigation
- diagnosis is clinical:
ring causes mostly localised irritation rather than vaginitis, but vaginitis should be ruled out with a wet mount
Other investigations
Genitourinary syndrome of menopause
History
peri- or post-menopausal; itching, burning, discomfort, dyspareunia, yellowish malodorous vaginal discharge, or vaginal bleeding
Exam
atrophic epithelium appears pale, smooth, and shiny; inflammation with patchy erythema, petechiae and increased friability may be present
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical (based on menopausal status)
Other investigations
Postpuerperal atrophic vaginitis; lochia
History
recent childbirth, lochia undergoes changes from red to white; itching, burning, discomfort, dyspareunia, yellowish malodorous vaginal discharge, or vaginal bleeding
Exam
reddish discharge in first few days, pinkish in next few days, and whitish from approximately 10th postnatal day onwards; findings of atrophic vaginitis subsequently: epithelium appears pale, smooth, and shiny, and inflammation with patchy erythema, petechiae, and increased friability may be present
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical
Other investigations
Behcet's syndrome
History
known history of Behcet's syndrome; recurrent aphthous ulcers, genital ulcerations occasionally associated with vaginal discharge, and uveitis leading to blindness
Exam
recurrent genital ulcers in vulva and vagina, which are painful, and scarring; occasional vaginal discharge
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical
More
Other investigations
- biopsy of genital ulcers:
vasculitis as well as lymphocytic and plasma cell invasion in the prickle cell layer of the epidermis
More
Desquamative inflammatory vaginitis
History
chronic and exudative vaginitis associated with purulent and copious discharge; severe dyspareunia, minor vulvar symptoms such as irritation and/or pruritus
Exam
profuse and purulent vaginal discharge; spotted appearance or focal ecchymoses of vulva, vagina, and cervix
1st investigation
- wet mount microscopy of vaginal discharge:
polymorphonuclear infiltrate, basal and parabasal epithelial cells; absence of lactobacilli; no clue cells
More
Other investigations
Erosive lichen planus
History
chronic eruption mostly on flexor surfaces, mucous membranes, and vulvar skin; lesions usually extremely pruritic and sometimes painful
Exam
violaceous, shiny papules appearing mostly on flexor surfaces, mucous membranes, and vulvar skin; most lesions are located on the inner aspects of the vulva, especially on the labia minora and vestibule
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical
Other investigations
- punch biopsy of vagina or vulva:
hyperkeratosis, degeneration of basal cell layer, infiltration of inflammatory cells and Rete pegs
More
Post-operative sling/mesh procedure
History
history intravaginal slingplasty or fistula; purulent and offensive vaginal discharge
Exam
malodorous vaginal discharge, visualised mesh erosion or fistula on speculum examination
1st investigation
- none:
diagnosis is clinical
More
Other investigations
Postradiation
History
history of pelvic irradiation
Exam
vaginal atrophy may also be present
1st investigation
- wet mount microscopy of vaginal discharge:
may help exclude other causes of vaginal discharge
Other investigations
Cervical cancer
History
some women can present with malodorous vaginal discharge indicating infection of a large, necrotic tumour; in late-stage cervical cancer, may have watery or foul-smelling vaginal discharge most likely from necrotic tissue
Exam
on speculum examination possible watery, foul-smelling discharge as well as pelvic fungating mass
1st investigation
- Pap smear:
epithelial cell abnormality
- biopsy of cervical mass:
positive for cervical cancer
Other investigations
Carcinoma of the fallopian tube
History
rare; only about 16% of patients present with the classic triad (hydrops tubae profluens) of vaginal discharge, colicky pelvic pain, and palpable pelvic mass, although data are very limited; vaginal bleeding; clear vaginal discharge is the most common symptom reported by patients
Exam
features characteristic of malignancy (e.g., weight loss, ascites)
1st investigation
- pelvic ultrasound:
neovascularisation on transvaginal colour Doppler or ascites suggest malignancy
Other investigations
Pinworm infection
History
nocturnal vulvar and perianal pruritus
Exam
vulvar erythema, pinworms may be visible
1st investigation
- clear cellophane adhesive tape examined under the microscope:
pinworm eggs
More
Other investigations
Streptococcal vaginitis in children
History
current or recent symptomatic streptococcal pharyngitis; caused by transmission of respiratory flora from the nose and oral pharynx to the vulvar area
Exam
purulent discharge, beefy red-appearing vulva
1st investigation
- vaginal swab:
positive for Streptococcal pyogenes (group A streptococci)
Other investigations
Sexual abuse
History
foreign bodies in the vagina or rectum, genitourinary complaints, painful defecation or urination, vaginal discharge, bleeding or itching, grasp or rope marks, oral complaints, STIs, or possible pregnancy
Exam
most cases of sexual abuse of pre-pubertal girls have normal examination findings with a normal-appearing hymen; absence of all or parts of the hymen or a posterior hymenal tear represent signs of sexual abuse; profuse, yellow-to-green discharge may be a sign of infection; evaluation should be performed by a specialist in child sexual abuse
1st investigation
Transmitted maternal birth canal infection
History
vaginitis from Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia, and Trichomonas can be found in neonates due to acquisition through an infected birth canal up to 1 year or more after birth; it is very important to rule out sexual abuse in these infants
Exam
profuse, yellow to green discharge
1st investigation
- cervical and vaginal nucleic acid amplification test of mother:
may be positive for N gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia, and Trichomonas
- vaginal nucleic acid amplification test of infant:
may be positive for N gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia, and Trichomonas
More
Other investigations
Prolapsing fibroid
History
history of fibroids, profuse discharge or bloody discharge
Exam
fibroid would be visible on physical examination or palpable within the cervix on bimanual examination
1st investigation
- ultrasound:
sonographic appearance of uterine fibroid
Other investigations
Vaginal fistula
History
history of pelvic surgery, radiation, or Crohn's disease with continuous discharge consistent with urine or liquid stool
Exam
speculum examination, careful evaluation of the vaginal walls
1st investigation
- tampon test with placement of dye in bladder:
positive if visualisation of dye in tampon
Other investigations
- retrograde pyelogram:
shows leakage between ureter and vagina; sigmoidoscopy or anoscopy: fistula seen on probing
- cystoscopy:
fistula tract communicating with urinary bladder visualised
- fistulogram:
fistula tract visualised
Lymphoma of genital tract
History
mass, malodorous discharge or vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain or fullness
Exam
a mass may be palpated on bimanual examination or a mass may be visualised on speculum examination
1st investigation
- pelvic ultrasound:
confirms presence of mass
- biopsy:
positive for genital lymphoma
Other investigations
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer