Differentials
Common
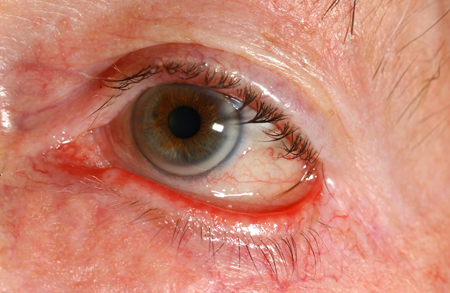
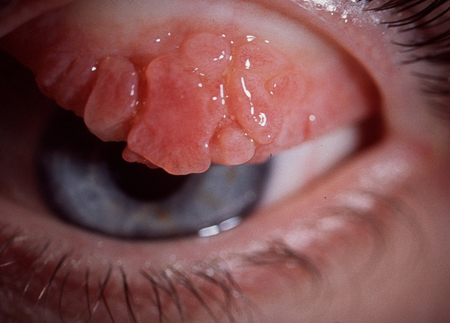
Trichiasis
History
insidious onset of ocular unease; patient may describe localised ocular irritation; no discharge present
Exam
an aberrant lash/cluster of lashes may be seen; corneal fluorescein stain seen; normal visual acuity and pupillary reactions
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
More
Other investigations
Entropion
History
sudden onset of ocular unease as the eyelid turns in; may result in the eyelashes rubbing on the cornea, causing localised irritation and watering
Exam
lower eyelid may be turned in; fluorescein stain may be present if the eyelashes have been rubbing on the cornea; normal visual acuity and pupillary reactions
1st investigation
- specialist clinic review:
To determine the underlying cause: involutional, cicatricial, or congenital (child).
More
Other investigations
Ectropion
History
patient may report ocular irritation and unease with associated watering; no discharge
Exam
the lower eyelid may be seen to be coming away from the globe; no fluorescein stain seen; normal visual acuity and pupillary reactions
1st investigation
- specialist clinic review:
To determine the underlying cause: involutional, cicatricial, or paralytic.
More
Other investigations
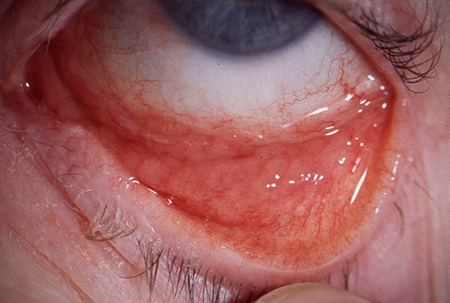
Blepharitis
History
patient may report an intermittent foreign body sensation, burning, or grittiness; symptoms often worse in the mornings but may flare at any time; no discharge present
Exam
inflamed crusting of the lid margins; normal visual acuity and pupillary reactions; no fluorescein stain visible
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
More
Other investigations
Dry eye
History
patient may report irritation, burning, foreign body sensation, or non-specific ocular unease; photophobia and stringy discharge may also be described
Exam
visual acuity can be affected; ocular vasculature may appear engorged, rose bengal or fluorescein staining may be present; stringy discharge may be seen
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
More
Other investigations
Corneal ulcer (bacterial, viral, or fungal)
History
patient may initially report a foreign body sensation, which progresses to photophobia, blurred vision, pain, and discharge; the eyelids may also swell
Exam
reduced visual acuity, often severe conjunctival injection; a swollen eyelid and discharge may be visible; corneal fluorescein stain seen; may be corneal haze; ulcer may be bacterial, viral, or fungal
1st investigation
- corneal scrape for microscopy culture and sensitivity:
positive in bacterial or fungal cause
More
Other investigations
Contact lens-related red eye
History
contact lens wearer may initially report a foreign body sensation that progresses to photophobia, blurring, pain, and discharge; the eyelid may also swell
Exam
reduced visual acuity; severe conjunctival injection may be present; a swollen eyelid and discharge may be visible; corneal fluorescein stain seen
1st investigation
- corneal scrape for microscopy culture and sensitivity:
positive in bacterial or fungal cause
More
Other investigations
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
History
burning or stinging pain in ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve dermatome; maculopapular erythematous rash, which develops into clear vesicles; eye pain; more common in immunosuppressed patients
Exam
reduced visual acuity; corneal ulcer; cells in the anterior chamber on slit-lamp biomicroscopy; Hutchinson’s sign (rash involving the side, tip, or root of the nerve) indicates increased risk of ocular inflammation
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
More
Other investigations
- viral swab:
positive for varicella zoster DNA
Keratitis
History
patient may report intense pain, discharge, photophobia, increased lacrimation; the eyelid may also swell
Exam
corneal ulcer that may be bacterial, viral, or fungal; reduced visual acuity; a swollen eyelid and discharge may be visible; corneal fluorescein stain seen; may be corneal haze
1st investigation
- corneal scrape for microscopy culture and sensitivity:
positive in bacterial or fungal cause
More
Other investigations
Corneal foreign body
History
a foreign body sensation progressing to photophobia and pain may be reported; the sensation is frequently preceded by a gust of wind or following use of hammering or grinding equipment
Exam
a foreign body may be seen either on the cornea, under the upper lid, or within the lower fornix; normal visual acuity and pupillary reactions
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
foreign body present on examination of the cornea, upper lid conjunctiva, or lower fornix
More
Other investigations
- imaging with CT of the orbits:
intra-ocular foreign body may be present
More
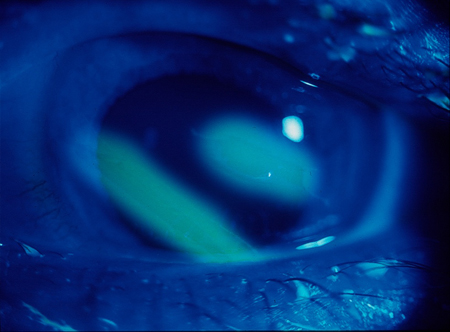
Corneal abrasion
History
acute onset of ocular unease; this may have been preceded by a history of minor trauma
Exam
reduced visual acuity; normal pupillary reactions; single eye, conjunctival injection with corneal fluorescein stain seen; the eyelid may be swollen; no discharge
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
More
Other investigations
Subtarsal conjunctival foreign body
History
often reduced vision; small particle foreign body into eye, often wind-blown with low velocity; persistent sharp scratching foreign body sensation, worse on blinking; watering, often profuse; no discharge
Exam
possible reduced visual acuity; injected conjunctiva, often localised; foreign body visible on conjunctiva on eversion of eyelid (either upper or lower), often best visualised with fluorescein staining; corresponding fine linear corneal abrasions; normal pupil response
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis with fluorescein staining:
fluorescein staining positive
More
Other investigations
Allergic conjunctivitis
History
history of allergen exposure (could include topical eye medication); possible seasonal recurrence or associated atopic symptoms (vernal); rapid onset after exposure; itch; watery, stringy discharge
Exam
normal visual acuity; diffusely injected conjunctiva; chemosis (bulging of the clear/injected conjunctival layer with fluid underneath, often described as looking like jelly on the white of the eye); fine velvety papillae on tarsal conjunctiva, may develop giant cobblestone appearance (vernal); clear cornea, no fluorescein stain; erythema and oedema to lids; normal pupil response; no pre-auricular lymph nodes palpable
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
More
Other investigations
Bacterial conjunctivitis
History
discomfort, foreign body sensation; purulent discharge (if severe, consider gonococcal aetiology); often initially unilateral, becoming bilateral; eyelid erythema and oedema; vision minimally or unaffected; not itchy
Exam
diffusely injected conjunctiva; mucoid or purulent discharge; clear cornea, no fluorescein stain; normal visual acuity and pupil response
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
Other investigations
- conjunctival swabs for microscopy culture and sensitivity including Chlamydia:
positive
More
Viral conjunctivitis
History
discomfort, foreign body sensation; watery discharge (not purulent), often profuse; usually initially unilateral, becoming bilateral; associated upper respiratory tract infection symptoms; recent contact history of someone with red eye; vision minimally or unaffected; COVID-19 contact (rare presentation)
Exam
diffusely injected conjunctiva; tarsal conjunctival follicles; clear cornea initially, possible small patches of sub-epithelial infiltrates developing 2 to 3 weeks after onset; occasionally palpable pre-auricular lymph nodes; no corneal fluorescein stain; normal visual acuity and pupil response
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
Other investigations
- conjunctival swabs for microscopy culture and sensitivity including Chlamydia:
positive in bacterial or fungal cause
More
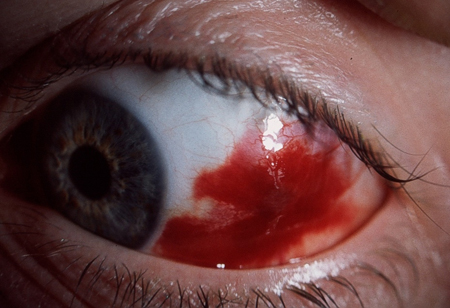
Non-traumatic subconjunctival haemorrhage
History
spontaneous; occasionally history of Valsalva manoeuvre, coughing, sneezing, or heavy lifting; usually asymptomatic; occasional mild discomfort, or popping sensation at onset; possible association with systemic hypertension or anticoagulants
Exam
well-circumscribed area of confluent haemorrhage underneath conjunctiva (if the posterior border cannot be seen then it may originate from intra-cranial haemorrhage, which warrants immediate emergency referral), often sectorial; cornea clear, no fluorescein stain; normal visual acuity and pupil response; possible systemic hypertension; blood pressure should be measured in all patients and managed as per guidelines
1st investigation
- clinical diagnosis:
no initial test
More
Other investigations
Uncommon
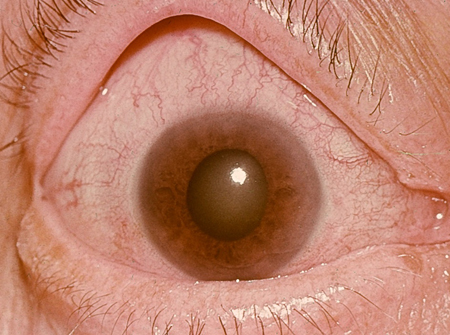
Angle-closure glaucoma
History
severe ocular pain often associated with vomiting; blurred vision and halos around light sources; the patient's past ocular, medical, and drug history should be reviewed to exclude any known associations
Exam
reduced visual acuity; cloudy cornea and a fixed, semi-dilated oval pupil; on gentle digital palpation the globe feels hard
1st investigation
- intra-ocular pressure measurement:
elevated intra-ocular pressure
More
Other investigations
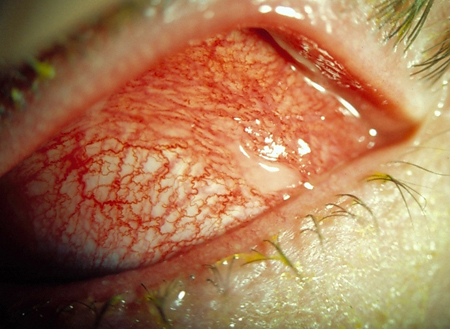
Chlamydial conjunctivitis
History
discomfort, foreign body sensation; mucus discharge, often profuse; usually initially unilateral, becoming bilateral; chronic symptoms despite topical antibiotics; rarely associated genito-urinary symptoms of inflammation or discharge; vision minimally or unaffected; minimally or not itchy
Exam
diffusely injected conjunctiva; large tarsal conjunctival follicles; clear cornea, no fluorescein stain; normal visual acuity and pupil response
1st investigation
- conjunctival swab/scrape specifically for Chlamydia:
positive
More
Other investigations
Neonatal conjunctivitis
History
vaginal delivery, presentation within 1 month of birth; purulent or mucoid discharge, often profuse, usually bilateral; occasionally associated genito-urinary symptoms of inflammation or discharge in the mother
Exam
diffusely injected conjunctiva; purulent discharge; clear cornea, no fluorescein stain; normal pupil response; tarsal conjunctival follicular reaction does not occur in neonates, even with chlamydial infection
1st investigation
- conjunctival swabs for microscopy culture and sensitivity including chlamydial:
positive for Chlamydia
More
Other investigations
Penetrating ocular trauma
History
identification of the nature, force, and time of the injury, particularly with high-velocity small fragments (e.g., produced by metal-on-metal hammering or power tools); often reduced vision; pain from onset, can be minor
Exam
reduced visual acuity; conjunctival injection; subconjunctival haemorrhage, often extensive; conjunctival or corneal laceration at entry site, with possible uveal tissue prolapse (dark pigmented tissue); shallow anterior chamber (space between cornea and iris) compared with the other eye; hyphaema (blood in the anterior chamber); irregular pupil; cataract; reduced red reflex; associated lid and facial injuries
1st investigation
- CT head/orbits:
observation of radio-opaque foreign body
More
Other investigations
Chemical trauma
History
history of irritant chemical instillation; exact details of the time, duration, pH, and constituents of the chemical are vital, as well as any treatment provided acutely; often reduced vision; pain from onset, can be severe; watering, often profuse
Exam
possible reduced visual acuity; injected conjunctiva, areas of pallor could indicate severe burn; particles may be observed and removed from fornices on lid eversion; epithelial fluorescein staining to conjunctiva and cornea; corneal haze with obscuring of iris details if severe; lid erythema, oedema, and burns; normal pupil response
1st investigation
- pH of tear film:
may be elevated in alkali injury and lowered in acid injury
More
Other investigations
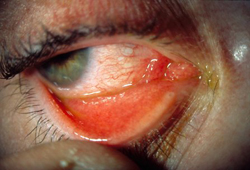
Episcleritis
History
acute onset of redness and pain; often the patient describes the redness in a specific area of the eye and may have noticed a small nodule adjacent to this area; no discharge; patient may have associated underlying rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis), or systemic lupus erythematosus
Exam
sectorial redness in one or both eyes; a nodule can be present over the area; no fluorescein stain; normal visual acuity and pupillary reactions
1st investigation
- FBC:
result depends on underlying cause
More - urea and electrolytes:
result depends on underlying cause
More - erythrocyte sedimentation rate:
elevated in inflammatory conditions
More - C-reactive protein:
elevated in inflammatory conditions
More - rheumatoid factor:
positive in some patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus
More - c-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (c-ANCA):
positive in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis)
More
Other investigations
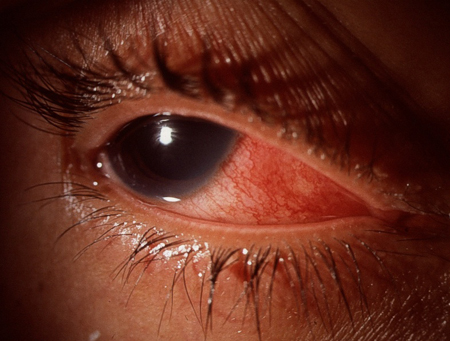
Scleritis
History
severe ocular pain and redness (prominent feature); no discharge; reduced visual acuity may be present; past medical history should be reviewed for any known systemic associations such as connective tissue disorders including rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis), systemic lupus erythematosus, and relapsing polychondritis
Exam
deep scleral vessel engorgement and pain on ocular palpation; no fluorescein stain; visual acuity and pupillary reactions may be abnormal depending on the position of the scleritis on the globe (anterior or posterior)
1st investigation
- FBC:
result depends on underlying cause
More - urea and electrolytes:
result depends on underlying cause
More - erythrocyte sedimentation rate:
elevated in inflammatory conditions
More - C-reactive protein:
elevated in inflammatory conditions
More - rheumatoid factor:
positive in some patients with rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus
More - c-antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (c-ANCA):
positive in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly known as Wegener's granulomatosis)
More
Other investigations
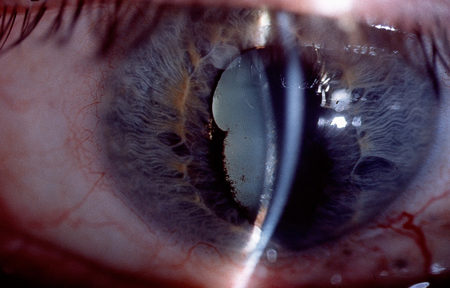
Anterior uveitis
History
pain and photophobia within the affected eye; the pain may be exacerbated when reading or performing close work; reduced vision, depending on the severity; past history of similar episodes; past medical history should be reviewed for any known systemic associations, such as HLA-B27 histocompatibility complex-positive patients, tuberculosis, syphilis, Lyme disease, sarcoidosis, Behcet's disease, and pauciarticular juvenile chronic arthritis
Exam
visual acuity may be reduced; ciliary flush pattern of redness in the affected eye; close examination of the cornea and anterior chamber may show the presence of keratic precipitates (cellular aggregates on the inner corneal surface), inflammatory cells, and flare (increased protein within the anterior chamber, allowing visualisation of the light beam within the aqueous), and in severe cases a hypopyon; the pupillary margin may appear irregular and reactions abnormal if posterior synechiae (adhesion of the iris to the anterior lens capsule) are present
1st investigation
- FBC:
result depends on underlying cause
More - urea and electrolytes:
result depends on underlying cause
More - CRP:
elevated in infectious and inflammatory conditions
More - syphilis serology:
positive in syphilis[28]
More - chest x-ray:
may show evidence of sarcoidosis (bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy and/or pulmonary infiltrates)
More - HLA-B27 histocompatibility complex:
positive in affected patients[28]
More - auto-antibody screen:
positive according to underlying autoimmune disease[28]
More
Other investigations
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer