Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
In Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli HUS, thrombocytopenia is common, with median platelet counts of 30 x 10³/microlitre, but normal or near-normal platelet counts are seen in up to 30% of cases.[7]
Result
anaemia, thrombocytopenia
peripheral blood smear
Test
This is the critical step in establishing the diagnosis of a thrombotic microangiopathy. Review of the peripheral smear is necessary not only to detect the presence of schistocytes but also to obtain an accurate estimate of the platelet count, because automated counters can mistakenly count small red cell fragments as platelets.[39][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Peripheral smear with numerous fragmented erythrocytesFrom the personal collection of Dr A. Zimrin; used with permission [Citation ends].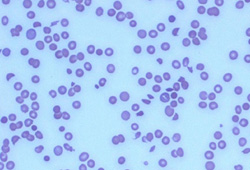
Result
presence of schistocytes
renal function/creatinine
Test
Renal endothelial cells are damaged in HUS. In Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli HUS, a rise in creatinine generally follows the development of thrombocytopenia and a fall in haemoglobin.
In sporadic HUS, an elevated creatinine is present at diagnosis.
Result
creatinine increased
serum electrolytes (sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate, calcium and phosphorus)
Test
Electrolyte abnormalities may be present due to diarrhoea and acute kidney injury.
Result
abnormalities may include hyperkalaemia, hyponatraemia, hypernatraemia, acidosis (due to bicarbonate loss), hyperphosphataemia
prothrombin time (PT), PTT
Test
Useful in ruling out other causes of thrombocytopenia, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Result
normal
LDH
Test
LDH is released from the red blood cells when they are destroyed. It is a non-specific sign in haemolytic anaemia.
Result
increased
haptoglobin
Test
Haptoglobin binds free haemoglobin released by the haemolysed red blood cells. The haptoglobin-haemoglobin complex is then removed by the liver and spleen, resulting in low levels of serum haptoglobin.
Result
decreased
stool culture on sorbitol-MacConkey agar to detect Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli
Test
May be negative if not done early in the course of the diarrhoeal illness.[31]
Result
Shiga toxin-producing E coli cannot ferment sorbitol and appears as white colonies
polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect Shiga toxin 1/Shiga toxin 2
Test
PCR assays can detect Shiga toxin 1 and Shiga toxin 2 genes from stool samples.
Confirms Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection.
Result
positive
proteins involved in complement regulation
Test
This test should be ordered initially if familial disease is suspected. Complement factor H and complement factor I levels can be tested.
Low C3 and C4 levels are common in patients with mutations in the alternative complement regulatory pathways, although this is not a sensitive screening test. Further analysis (factor B, membrane co-factor protein, factor H autoantibody) may require the services of a specialist laboratory.[40]
Result
abnormal levels of complement in familial and some cases of atypical HUS
Investigations to consider
urinalysis
Test
Not usually recommended as part of the initial investigations in children. It is very difficult to obtain a clean urine sample in the presence of diarrhoea and therefore WBCs are often seen. Excoriation and irritation in the perineal area can also result in the finding of haematuria. A catheterised urine specimen could be obtained, but this is challenging and painful, particularly for a child. There is also a risk of seeding bacteria in the bladder if a catheter is placed in the presence of diarrhoea.
Result
if renal involvement, haematuria, proteinuria, or elevated creatinine level (≥1 mg/dL in a child aged <13 years or ≥1.5 mg/dL in a person aged ≥13 years, or ≥50% increase over baseline)
ADAMTS13 level
LFTs
Test
To evaluate hepatic involvement once Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli HUS has been confirmed.
Result
transient transaminitis if hepatic involvement
serum amylase, lipase, glucose
Test
To evaluate hepatic involvement once Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli HUS has been confirmed.
Result
increased if pancreatic involvement (due to pancreatitis, and in rare cases, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus)
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer