Images and videos
Images
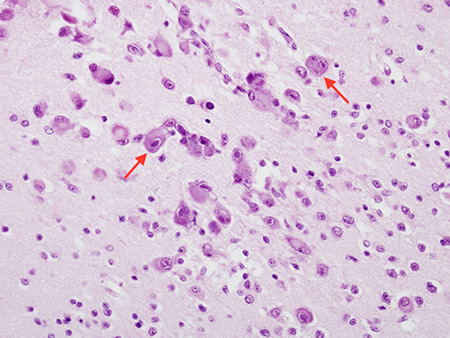
Encephalitis
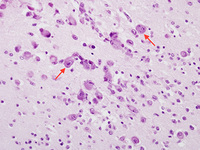
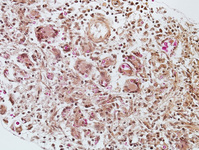
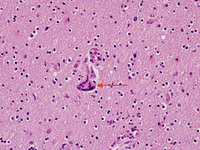
Biopsy from cortex of neonate with CMV encephalitis showing enlarged cells (arrows) with intranuclear inclusions. The top arrow points to a neuron with two nuclei each with a nuclear inclusion
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
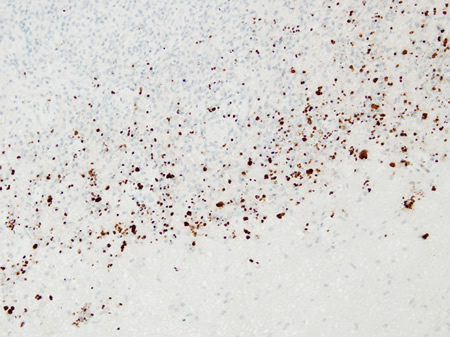
Encephalitis
Biopsy of HIV patient with toxoplasmosis, with the tachyzoites identified using immunohistochemistry
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
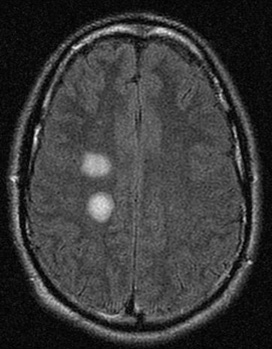
Encephalitis
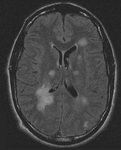
Series of MRI images of brain of patient with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: centrum semiovale
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
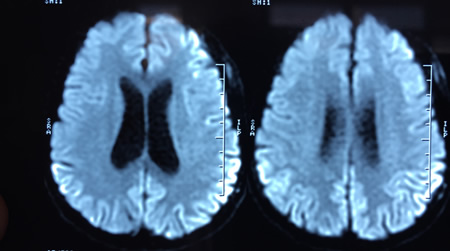
Encephalitis
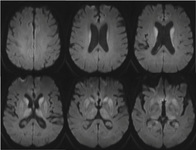
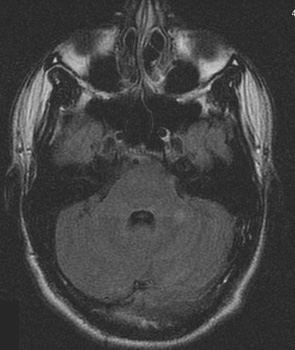
MRI brain: cortical ribboning in a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease on diffusion-weighted images
From the personal collection of Leo H. Wang; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
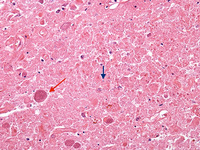
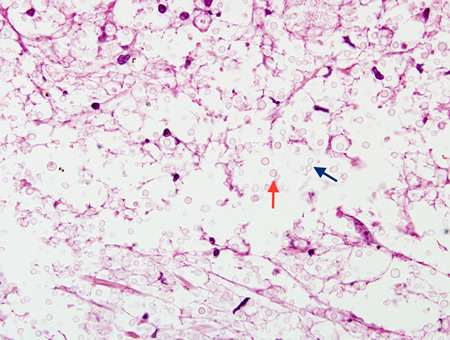
Biopsy from brain of immunocompromised patient with cryptococcal meningitis showing the meninges with round translucent cryptococcal organism (red arrow) as well as a budding yeast (blue arrow)
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
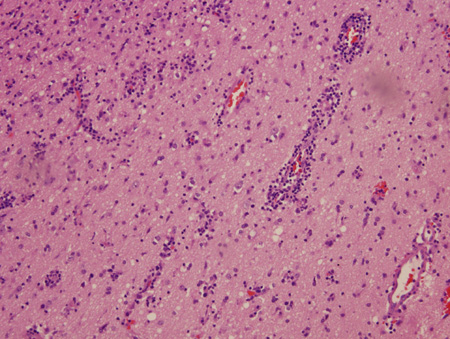
Biopsy of brain from right temporal lobe: the classic H&E stain shows evidence of patchy but extensive inflammatory infiltrate of small mononuclear cells (lymphocytes) in the brain parenchyma, predominantly around the blood vessel walls. PCR studies of the biopsy sample were positive for EBV infection
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
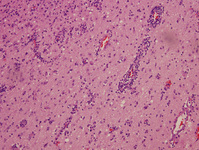
Biopsy from brain of patient with subacute HIV encephalitis showing the distinctive multinucleated giant cell (red arrow), which contains the HIV virus. The multinucleated giant cells are from histiocyte/macrophage lineage. There is also associated astrocytosis
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
Series of MRI images of brain of patient with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: asymmetric 'fluffy' lesions over the bilateral ventricular horns and thalami
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
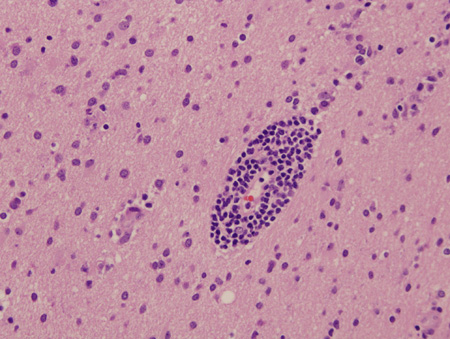
Encephalitis
Biopsy of brain from right temporal lobe: a close-up view of a blood vessel with its surrounding marked inflammatory infiltrate is also seen. PCR studies of the biopsy sample were positive for EBV infection
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
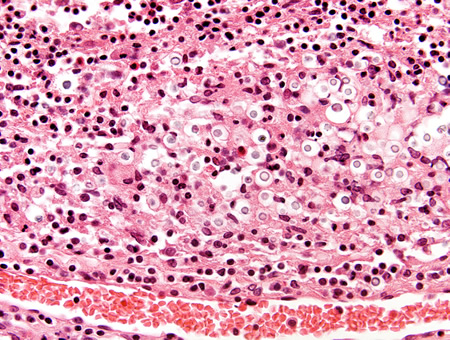
Encephalitis
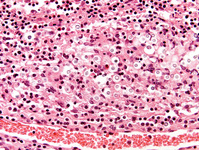
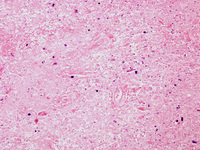
Biopsy from brain of immunocompetent patient with cryptococcal meningitis showing the meninges with inflammatory cells and Cryptococcus
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
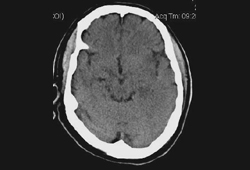
Encephalitis
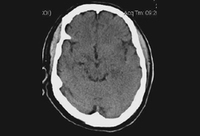
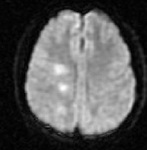
Non-contrast head CT of a patient with HSV encephalitis: shows subtle hypodensities involving the left insular region. Some blurring of grey-white margins and sulcal effacement over the left temporal region is discernible
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
Series of MRI images of brain of patient with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: hyperintense lesions of fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) involving the left cerebellar peduncle
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
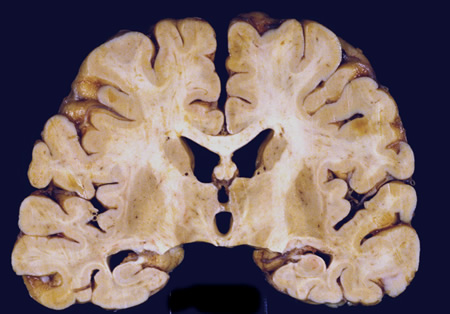
Encephalitis
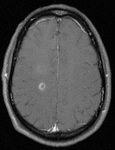
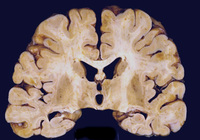
Coronal slice of the brain of HIV patient in his 30s. He had subacute HIV encephalitis involving both the white matter and gray matter diffusely. The ventricles were enlarged reflecting white matter and cortical loss
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
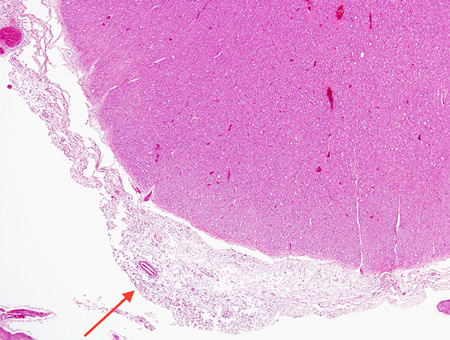
Encephalitis
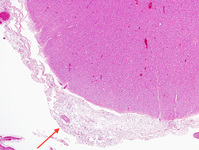
Biopsy from brain of immunocompromised patient with cryptococcal meningitis at low magnification. The meninges are expanded (arrow), but the cortex is histologically relatively uninvolved
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
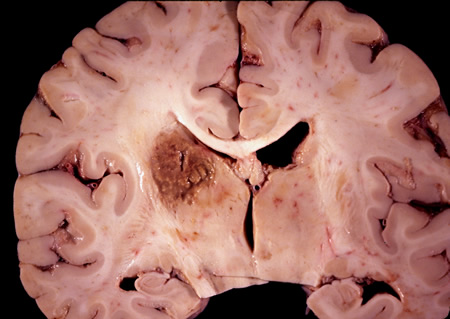
Encephalitis
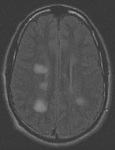
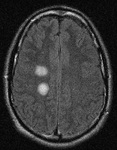
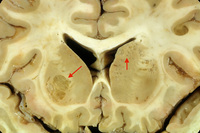
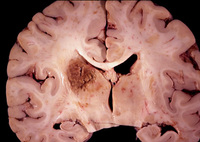
Coronal slice of the brain of an HIV patient with toxoplasmosis, showing infection of the periventricular superior part of the left thalamus
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
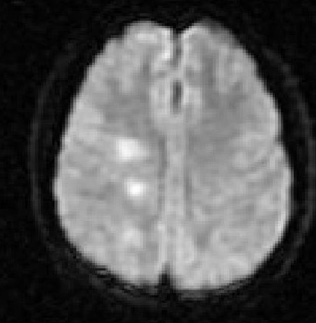
Encephalitis
Series of MRI images of brain of patient with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: diffusion-weighted images from the same patient show high signal intensity in the same area, and this correlates with increased (bright on ADC maps) diffusion
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
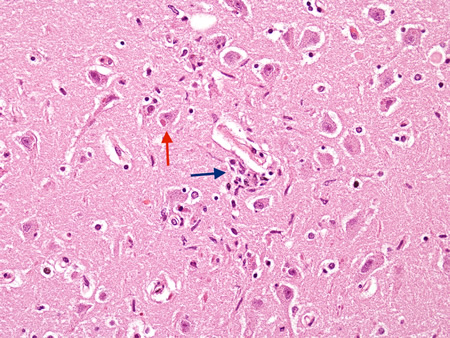
Encephalitis
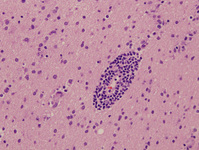
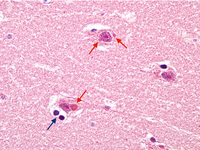
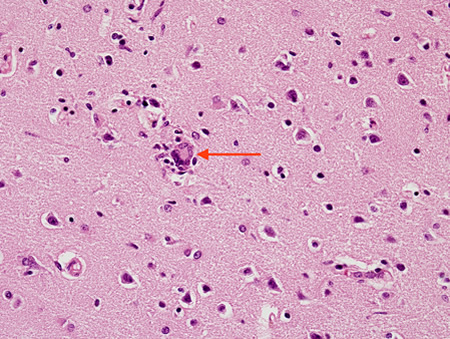
Biopsy from hippocampus of patient with rabies showing a neuron with an eosinophilic cytoplasmic Negri body (red arrow). The blue arrow highlights a collection of microglial cells next to a blood vessel
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
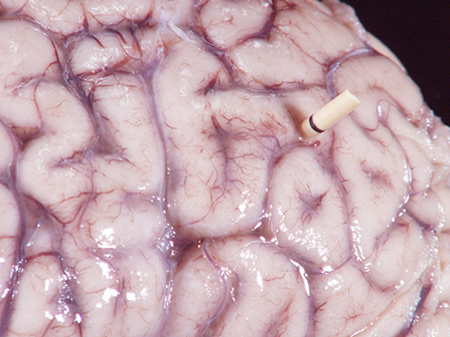
Encephalitis
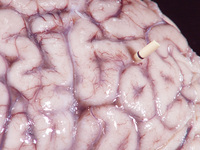
Gross autopsy of brain of patient with cryptococcal meningitis showing the surface with a 'glazed' look. There is also a shunt present
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
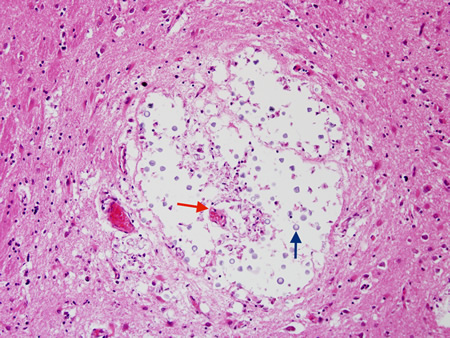
Encephalitis
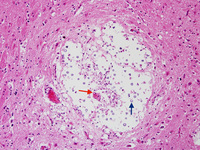
Biopsy from basal ganglia of patient with cryptococcal meningoencephalitis showing cryptococcal (blue arrow) expansion of Virchow-Robbin spaces around a lenticulostriate vessel (red arrow)
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
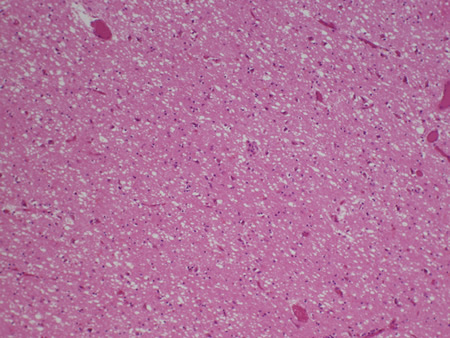
Encephalitis
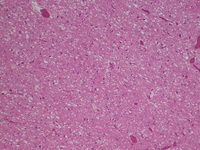
Biopsy of the posterior thalamus of the patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease showing the spongiform changes
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
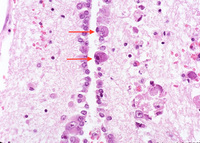
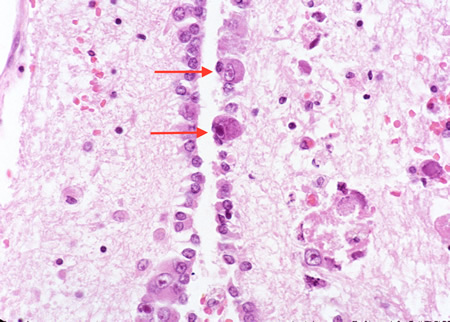
Biopsy from the brainstem of an HIV patient with CMV encephalitis. The ependymal lining shows enlarged cells (arrows) with intranuclear inclusions
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
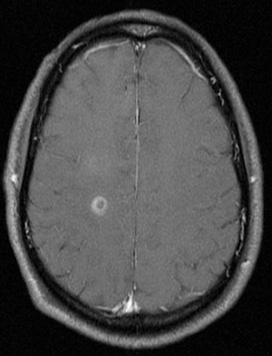
Series of MRI images of brain of patient with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: T1 post-gadolinium enhanced image shows ring enhancement around a lesion in the right centrum semiovale region and faint diffuse enhancement just above this area
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
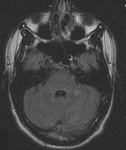
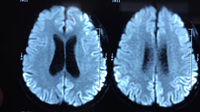
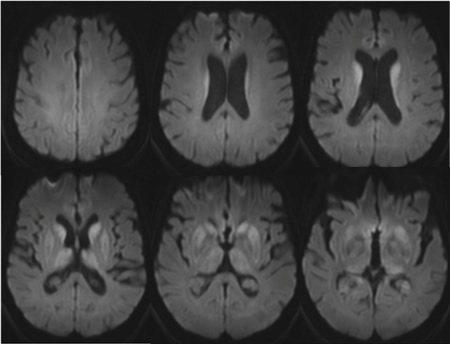
MRI brain: the pulvinar sign (a term referencing bilateral pulvinar hyperintensity) in a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease on diffusion-weighted images
From the personal collection of Leo H. Wang; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
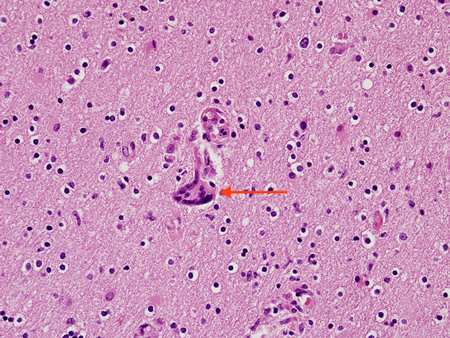
Biopsy from brain of patient with subacute HIV leukoencephalitis showing the distinctive multinucleated cell (red arrow) in the white matter
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
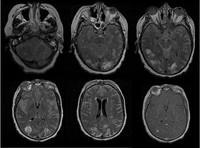
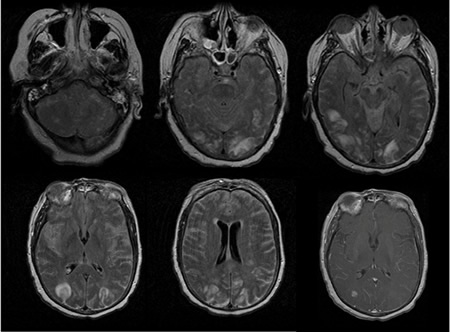
The first 5 images are FLAIR images of patient with varicella zoster virus meningoencephalitis showing white and gray matter hyperintensities. The last image is T1 image with contrast showing parenchymal and diffuse leptomeningeal enhancement
From the personal collection of Eric E. Kraus; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
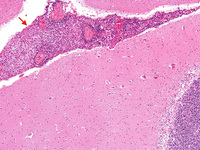
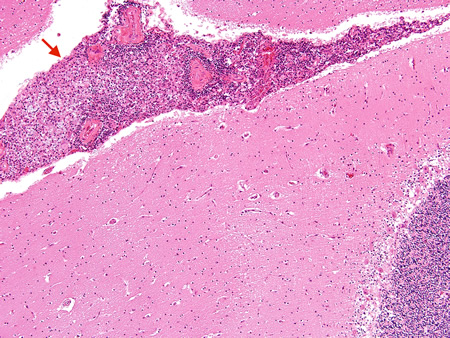
Biopsy from brain of an immunocompetent patient with cryptococcal meningitis at low magnification showing the meninges with inflammation (red arrow)
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
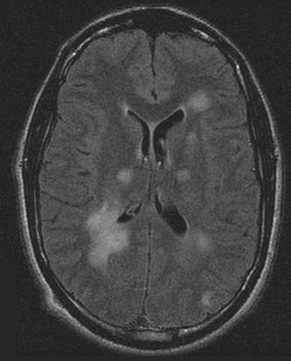
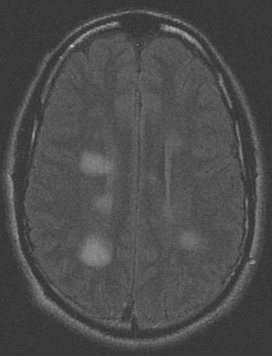
Series of MRI images of brain of patient with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: periventricular regions
From the personal collection of Catalina C. Ionita, MD; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
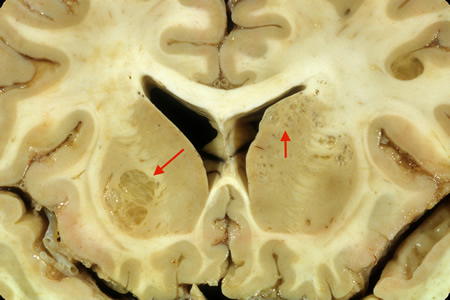
Coronal slice of the brain of patient with cryptococcal meningoencephalitis showing classical appearance of “soap bubble” structures in the basal ganglia (arrows) resulting from the cryptococcal expansion of Virchow-Robbin spaces around the lenticulostriate vessels
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
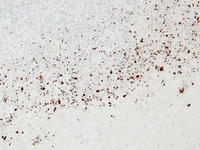
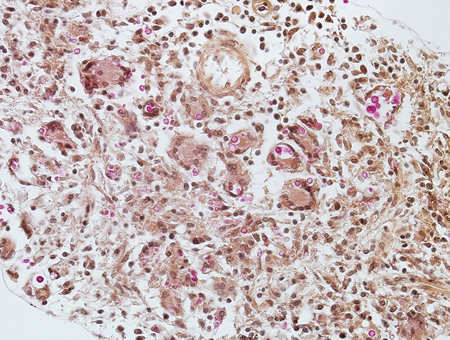
Biopsy from meninges of patient with cryptococcal meningitis stained with mucicarmine, demonstrating fungal organisms, particularly in giant cells
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
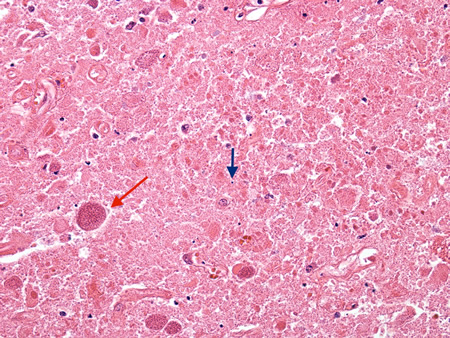
Biopsy of the brain of an HIV patient with toxoplasmosis, showing encysted bradyzoites (red arrow) and tachyzoites (blue arrow)
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
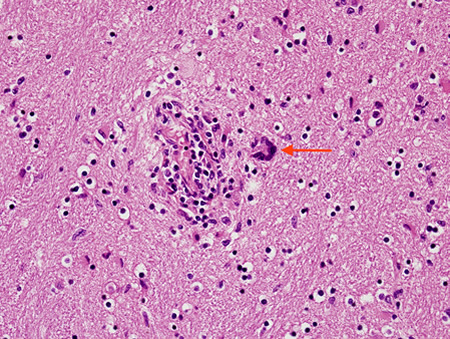
Biopsy from brain of patient with subacute HIV leukoencephalitis showing the distinctive multinucleated cell (red arrow) in the white matter next to inflammatory cells in the Virchow-Robin space
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Encephalitis
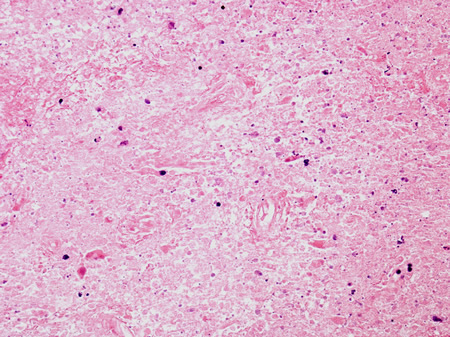
Biopsy of HIV patient with toxoplasmosis, showing both pieces of cellular debris and tachyzoites. The tachyzoites are round, smooth and hard to identify without antibody staining (see next image)
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
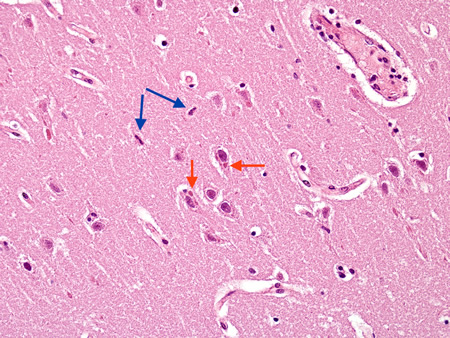
Encephalitis
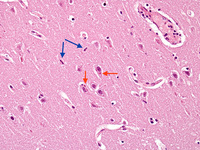
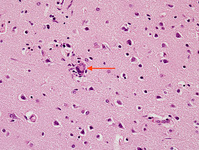
Biopsy from hippocampus of patient with rabies showing 2 neurons with eosinophilic Negri bodies (red arrows). These are found in areas, often with little inflammatory reaction. The blue arrows highlight microglial cells
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
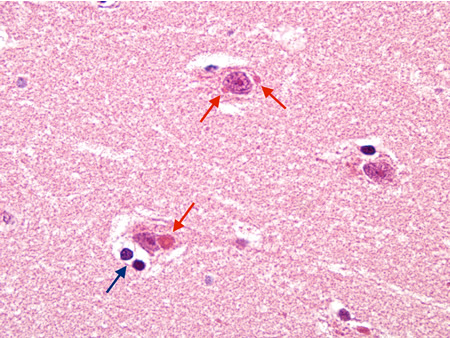
Encephalitis
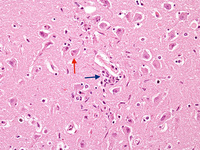
Biopsy from hippocampus of patient with rabies showing neurons with eosinophilic Negri bodies (red arrow). The blue arrow highlights a collection of satelliting oligodendrocytes
From the personal collection of Robert E. Schmidt; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer