Investigations
Investigations to consider
pathergy testing
Test
A subcutaneous skin prick is performed using a 20- or 21-gauge sterile needle, usually in the forearm, and observed for the formation of induration with or without a papule or pustule within 48 hours.
Pathergy test is positive in up to 60% of patients, with highest frequency in those of Middle Eastern origin.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: PathergyFrom the collection of Yusuf Yazici, MD [Citation ends].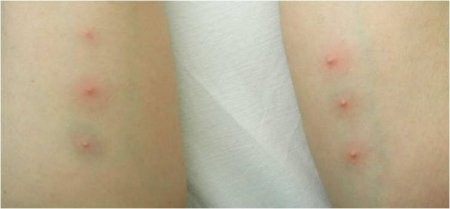
Result
induration with or without formation of a pustule within 48 hours
rheumatoid factor
Test
Indicated if joint symptoms are present to assist in ruling out alternative diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Result
negative
anti-nuclear antibodies
Test
If positive, should prompt further evaluation for other auto-immune diseases.
Result
negative
anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
Test
May indicate an alternative diagnosis, such as necrotising vasculitis.
Result
negative
HLA-B51
Test
This association varies with ethnicity. HLA-B51 is the most strongly associated known genetic factor for Behcet's syndrome.[20] It is also seen in a healthy population but it is more common in patients with Behcet's syndrome, especially around the Mediterranean and in eastern Asian populations.[21] It may be an indicator of severity but this is still not well established.
Result
present
lumbar puncture
Test
Indicated when neurological involvement is suspected. Measurement of opening pressure and cerebrospinal fluid analysis are used to rule out infections, such as tuberculosis, listeriosis, or herpes simplex virus.[5]
Result
hypercellularity; mostly lymphocytosis and less frequently polymorphonuclear cells or pleocytosis
MRI, magnetic resonance angiography brain with contrast
Test
Indicated when large vessel phlebitis or central nervous system involvement is suspected.
Result
white matter changes commonly involving midbrain, brainstem, and basal ganglia
colonoscopy
Test
Behcet's features on colonoscopy are usually distinct, single, deep ulcers. However, at times it may be difficult to differentiate from Crohn's disease.
Result
inflammation and aphthous-type ulcers, possibly vasculitis on biopsy
upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
Test
For patients with gastrointestinal symptoms, endoscopy is indicated to rule out alternative diagnoses.
Result
inflammation and aphthous-type ulcers, possibly vasculitis on biopsy
high-resolution chest CT
Test
Indicated when haemoptysis occurs to evaluate for pulmonary aneurysm. Also may be used to screen for pulmonary aneurysm if thrombophlebitis or other aneurysms have been diagnosed. Less invasive than angiography; choice depends on local expertise and preference.
Result
haemorrhage, pulmonary aneurysm
CT angiography of chest
Test
Indicated when haemoptysis occurs to evaluate for pulmonary aneurysm. Also may be used to screen for pulmonary aneurysm if thrombophlebitis or other aneurysms have been diagnosed. More invasive than high-resolution CT; choice depends on local expertise and preference.
Result
haemorrhage, pulmonary aneurysm
pulmonary angiography
Test
Further testing for pulmonary aneurysm, invasive.
Result
pulmonary aneurysm
Emerging tests
anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies
Test
May be elevated when gastrointestinal symptoms are present, but further study is needed to confirm.[22]
Result
may be elevated
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer