Investigations
1st investigations to order
FBC
Test
Order on admission.
Result
white blood cell count >10.0 × 10⁹/L (>10,000/microlitre) (reference range 4.8 to 10.8 × 10⁹/L or 4800-10,800/microlitre); platelets decreased
serum urea
Test
Order on admission.
Result
raised in patients with severe disease
serum creatinine
Test
Order on admission.
Result
raised in patients with severe disease
ABG analysis
Test
Order on admission with suspicion of sepsis.
Result
in severe cases low bicarbonate with a raised anion gap; metabolic acidosis; raised lactate
serum LFTs
CRP
Test
Order on admission.
Result
raised
serum potassium
Test
Order on admission.
Result
may be decreased
serum magnesium
Test
Order on admission.
Result
may be decreased
blood cultures
Test
Order on admission.
Result
bacteria are usually gram-negative but gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes are also implicated in cholangitis
coagulation panel
Test
Order on admission with suspicion of sepsis.
Result
prothrombin time may be raised with sepsis
Investigations to consider
abdominal CT scan with intravenous contrast
Test
Order if high clinical suspicion of cholangitis and ultrasound is negative. This modality is superior to ultrasound for visualising the distal portion of the common bile duct and for defining the extent of neoplasms.
Result
bile duct dilation with possible aetiology of cholangitis such as mass, choledocholithiasis
endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Test
Best first intervention. Patients with a history of biliary disease, an indwelling biliary prosthesis, or other predisposing factors should be considered for early ERCP for rapid diagnosis and therapy.
Can assist in the diagnosis of cholangitis by finding stones causing obstruction. Is also therapeutic, as the procedure can be used for biliary stone extraction.
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography reveals a large common bile duct (CBD) stone (arrow) in the mid-common bile ductFrom the collection of Douglas G. Adler; used with permission [Citation ends].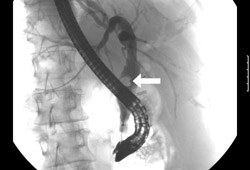 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopic photo of same patient following removal of large common bile duct (CBD) stone; note copious pus draining through the ampullaFrom the collection of Douglas G. Adler; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Endoscopic photo of same patient following removal of large common bile duct (CBD) stone; note copious pus draining through the ampullaFrom the collection of Douglas G. Adler; used with permission [Citation ends].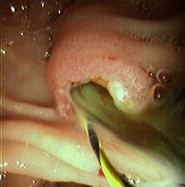
Result
direct observation of bile duct stone or other obstruction
magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Test
Order if ultrasound and CT are negative and a high clinical suspicion remains for cholangitis.[30][31]
While extremely valuable, virtually all patients with cholangitis will ultimately require biliary decompression, most commonly via endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). MRCP should thus not be viewed as a requisite study in patients with suspected cholangitis, but is often a helpful tool in looking for an aetiology and in planning for definitive therapy.
Result
mass impinging on biliary tree, stricture, and/or choledocholithiasis
percutaneous trans-hepatic cholangiography (PTC)
Test
Order if endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is unavailable or impossible (e.g., status post-Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, presence of oesophageal, pyloric or duodenal stricture, etc.).
Procedure allows for biliary catheter placement and, in some patients, stone extraction for purposes of biliary tree drainage/decompression. Patients undergoing PTC often require ERCP after clinical improvement to clear the biliary tree and/or to place internal stents.
Result
bile duct stone(s)/other obstruction(s)
endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS)
Test
Order if suspicion for common bile duct (CBD) stones is low to intermediate (e.g., a patient with prior cholecystectomy), or if there is suspicion of a CBD stricture or stone that hasn't been already seen on ultrasound or MRCP.[12][30][31] If EUS positive for CBD stones, ERCP can often be performed concomitantly. EUS is less widely available than comparable diagnostic modalities (MRCP). EUS can also facilitate direct bile duct access and decompression via biliary drainage and transluminal stenting.[37]
Result
CBD stone(s); ampullary, pancreatic and/or biliary masses.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer