Investigations
1st investigations to order
skin biopsy
Test
The definitive test for diagnosis. It is necessary to get the skin biopsy as soon as possible if there is a suspicion that the patient may have SJS or TEN. A dermatologist should take a biopsy at the transition point of blistering to assess the level of skin desquamation.
The area of separation may contain several CD8-positive T lymphocytes, and the dermis may contain CD4-positive T lymphocytes and macrophages, depending on the stage of the disease when the biopsy is taken.[19][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Histopathology of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysisFrom the personal collection of Dr A. Kowal-Vern [Citation ends].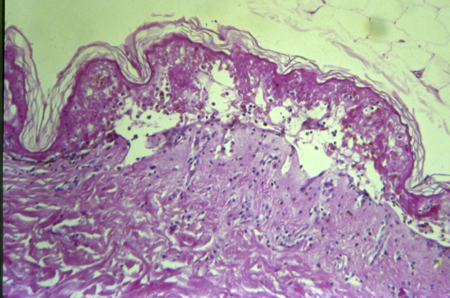
Result
keratinocyte apoptosis with detachment of the epidermal layer of the skin from the dermal layer
blood cultures
Test
Necessary to rule out toxic shock syndrome and scalded skin syndrome, which would show positive culture for Staphylococcus or Streptococcus species.
Result
negative in SJS/TEN
full blood count
Test
If FBC shows eosinophilia, consider hypersensitivity syndrome (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms [DRESS]). The WBC count may be elevated if there is a wound infection or sepsis.
Result
results depend on the stage at which patients are brought in for testing and the severity of the skin loss; TEN patients may present with sepsis and an elevated WBC count
glucose
Test
Necessary to rule out comorbidities such as diabetes or hypoglycaemia, which may be present on admission.
Result
hyperglycaemia; hypoglycaemia
magnesium
Test
Patient may present with low magnesium, as seen in patients with thermal injury skin loss.
Result
hypomagnesaemia; hypermagnesaemia
phosphate
Test
Elevated or decreased levels suggest muscle damage, joint pain or weakness, seizures, or renal comorbidities.
May require evaluation for endocrine disorders or vitamin D deficiency.
Result
elevated; decreased
urea
Test
Elevated urea suggests hypovolaemia.
Result
may be elevated
bicarbonate
Test
High or low levels may indicate diabetes or kidney disease.
Result
metabolic acidosis or alkalosis
serum electrolytes
Test
Low potassium and sodium levels suggest volume depletion.
Result
hypokalaemia; hyponatraemia
serum creatinine
Test
Elevated serum creatinine suggests renal failure or renal disease.
Result
may be elevated
liver function tests
Test
The exact abnormalities in LFT results depend in part on toxicity of the medication that precipitated the SJS or TEN, as well as on the percentage of total body surface area involvement. Depending on the severity of the SJS or TEN, the inflammatory response produced by the cytokines as a reaction to the insults may be similar to that which occurs in thermal injury: a fatty liver, hepatocyte apoptosis, and necrosis.
Result
variable abnormalities
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Test
Typically elevated in patients with SJS/TEN.
Result
elevated
C-reactive protein
Test
Typically elevated in patients with SJS/TEN.
Result
elevated
arterial blood gases and saturation of oxygen
Test
Arterial blood gases and oxygen saturation will help to determine the patient's clinical respiratory status. One of the complications of SJS/TEN is mucosal involvement of the upper and lower respiratory tract, with vesicle formation, ulceration, and actual mucosal sloughing that may lead to laryngeal stridor, possible retractions, and oedema of the nasopharynx.
Result
hypoxaemia, acidosis
chest x-ray
Test
Due to the high risk of pneumonia and interstitial pneumonitis all patients should have a chest x-ray.[63]
Result
possible pneumonia/interstitial pneumonitis
coagulation studies
Test
To detect disseminated intravascular coagulation associated with SJS/TEN. Patients with ≥20% total body surface area (TBSA) SJS/TEN have been reported to have haemostatic abnormalities consistent with those observed in patients with ≥20% TBSA burn injury coagulopathies.[64]
Result
abnormal
skin swab from lesional skin
Test
To detect secondary infection of lesional skin.
Result
may be positive for organism
Mycoplasma serology
Test
To detect Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection as a trigger for SJS/TEN.
Result
may be positive
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer