Investigations
1st investigations to order
chest x-ray
Test
Reticular or granular opacities that are typically perihilar but may be diffuse. Less often they are asymmetric or progress to a reticular-alveolar pattern.
A variety of chest x-ray findings have been seen, including lobar consolidation, nodular lesions, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, and even a normal chest x-ray. There can be cysts or pneumatoceles present.[91][92]
Pleural effusion or adenopathy suggest an alternative diagnosis.
In patients who have been on aerosolised pentamidine for Pneumocystis pneumonia prophylaxis, the chest x-ray may have predominantly upper lobe infiltrates.[93][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Posteroanterior chest x-ray showing mild, reticular, bilateral pulmonary interstitial infiltratesFrom the collection of Matthew Gingo, UPMC [Citation ends].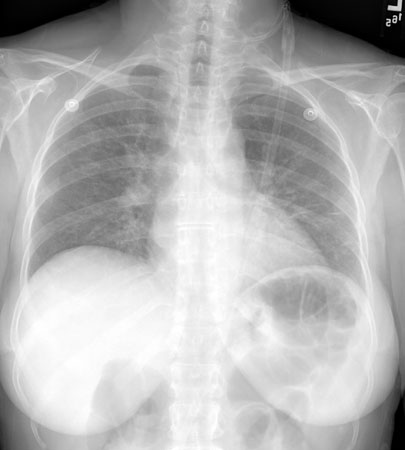 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Posteroanterior chest x-ray showing severe, bilateral pulmonary interstitial infiltrates with pneumatocelesFrom the collection of Matthew Gingo, UPMC [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Posteroanterior chest x-ray showing severe, bilateral pulmonary interstitial infiltrates with pneumatocelesFrom the collection of Matthew Gingo, UPMC [Citation ends].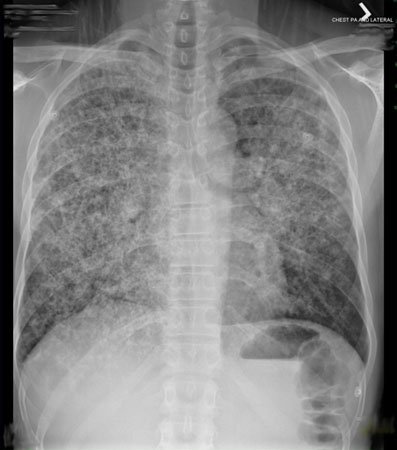
Result
bilateral symmetrical interstitial infiltrates
arterial blood gas
Test
A room air pO₂ ≥70 mmHg or an alveolar-arterial (A-a) gradient ≤35 mmHg define mild-to-moderate disease.
A room air pO₂ <70 mmHg or an alveolar-arterial O₂ (A-a) gradient >35 define moderate-to-severe disease.
Result
reduced pO₂ and elevated A-a gradient
serum LDH level
Test
LDH levels are elevated in 90% of patients with Pneumocystis pneumonia who are infected with HIV. LDH levels should decline with successful treatment.[68]
Result
elevated (>220 international units/L)
induced sputum
Test
Sputum should be induced and sent for staining for Pneumocystis jirovecii by the method that is best performed by the institution.
Sputum that is spontaneously expectorated has low sensitivity for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia and should not be used. Sensitivity of induced sputum testing is 50% to 90% depending on the quality of the sample, the pathogen load, the staining method used, and the experience of the institution.[32][63][64][65][66]
Expectorated sputum has poor sensitivity and should not be used.
Direct fluorescent-antigen testing is preferred because it is more sensitive and specific.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Photomicrograph of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid showing Pneumocystis cysts, stained black with Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stain (methyl green counterstain)From the collection of Matthew Gingo, UPMC [Citation ends].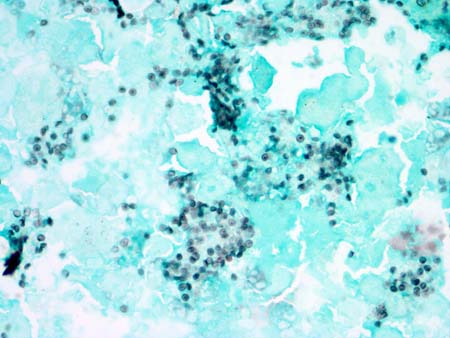
Result
positive for Pneumocystis
Investigations to consider
high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) chest
Test
Patients with a clinical presentation suggestive of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP), but a normal or unchanged chest x-ray, should undergo either an HRCT scan of the chest or pulmonary function tests with measurement of diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide.
If the HRCT scan shows ground glass opacities, the patient should undergo sputum induction followed by bronchoalveolar lavage (if sputum induction is negative), as the presence of ground glass opacities is sensitive, but not specific, for PCP.[69][70][71]
A negative HRCT makes PCP highly unlikely.[69][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography scan of the thorax showing bilateral pulmonary interstitial infiltrates and pneumatoceles (cysts), which are typical of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)From the collection of Matthew Gingo, UPMC [Citation ends].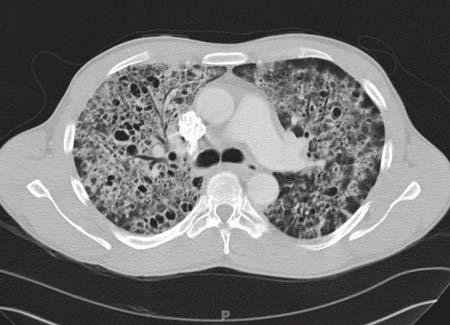
Result
diffuse, bilateral ground glass opacities
pulmonary function testing
Test
Patients with a clinical presentation suggestive of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP), but a normal or unchanged chest x-ray, should undergo either pulmonary function tests with measurement of diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) or an HRCT scan of the chest.
If the DLCO is decreased, then the patient should undergo sputum induction followed by bronchoalveolar lavage (if sputum induction is negative), as decreased DLCO is sensitive, but not specific, for PCP.[69][70][71]
A normal DLCO makes the diagnosis of PCP highly unlikely. If the DLCO is low (<80% predicted), then the patient should have sputum induction.
Result
reduced DLCO
bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
Test
Bronchoscopy with BAL should be performed if induced sputum is negative.
The lavage fluid should be sent for histochemical staining.
The sensitivity for BAL is between 90% to 99% in HIV-positive patients.[32]
Result
positive for Pneumocystis
biopsy
Test
In HIV-negative patients, transbronchial biopsy is more often necessary to confirm a diagnosis because BAL is less sensitive.
The sensitivity for transbronchial biopsy is 95% to 100%.[32]
If clinical suspicion for Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) remains high or prior testing does not reveal the aetiology for the patient's illness, an open lung biopsy can be considered to confirm or rule out PCP as well as to determine if another pathology is present. The sensitivity of open lung biopsies is 95% to 100%.[32]
Result
positive for Pneumocystis
Emerging tests
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Test
PCR, real-time PCR, and reverse transcriptase PCR can detect low levels of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA.
These assays may increase sensitivity of diagnosing Pneumocystis pneumonia but are often not clinically available. They have a higher false-positive rate than histochemical staining.[74][75][76][77][78][80]
Result
positive for Pneumocystis
plasma S-adenosylmethionine level
Test
May increase sensitivity of diagnosing Pneumocystis pneumonia but is not clinically available currently.[79]
Result
decreased
serum (1,3)-beta-D-glucan level
Test
There has been interest in measuring serum (1,3)-beta-D-glucan, an element of the fungal wall, for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP).[81][82][83][84][85]
These studies show (1,3)-beta-D-glucan to be significantly elevated in patients with PCP, although less so in HIV-negative patients with PCP, and the levels did not correlate with severity or response to therapy.[86]
In a study of 159 AIDS patients with at least one respiratory symptom, 139 of whom had PCP, the sensitivity and specificity of (1,3)-beta-D-glucan were 92.8% and 75.0%, respectively.[90]
Larger studies with appropriate comparison groups are necessary to determine relevant test characteristics, as this marker may also be increased in other fungal infections.
Result
elevated
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer