Investigations
1st investigations to order
pure-tone air and bone conduction with masking
Test
Pure-tone audiometry is the basic measurement of hearing sensitivity and the integrity of the entire auditory receptive pathway. Air-conduction thresholds are measured under headphones or with insert earphones. Bone measurements attempt to by-pass the outer and middle ear and test the function of the cochlea and the auditory nerve.
In MD (as well as in other cochlear disorders), air and bone conduction are equal, indicating that the underlying pathology is in the cochlea or auditory nerve, not the outer and the middle ear. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Pure-tone audiometry typical of Meniere's diseaseFrom the collection of Maurice H. Miller, PhD [Citation ends].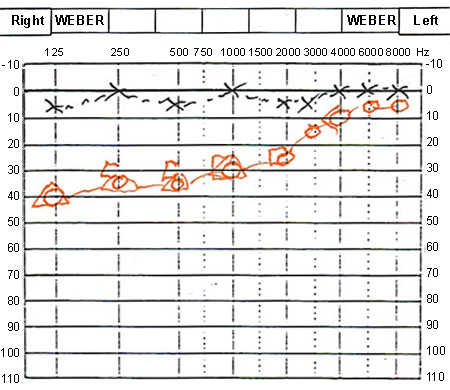
Result
unilateral sensorineural hearing loss; usually low-frequency hearing loss is present in early stages of meniere's disease (MD) and during or before attacks; as disease progresses, middle and high frequencies are affected
speech audiometry
Test
Speech recognition threshold (SRT) measures the threshold (50% correct response) for a series of simple, everyday bisyllabic words such as keyboard, football, and pavement.
Discrepancies between SRT and pure-tone averages can suggest pseudohypacusis (non-organic hearing loss) or a severe problem in word recognition ability (discrimination). Such discrepancies are not characteristic of meniere's disease (MD).
Word recognition score (WRS) measures the percentage of correct monosyllabic words, which are heavily loaded with high-frequency consonantal material (at increasing levels of intensity), above the SRT.
WRS at multiple levels above the SRT is used to access the rollover phenomenon. The roll-over ratio is calculated by subtracting the lowest speech discrimination score of phonetically balanced (PB) words (PB min) from the highest score (PB max) and dividing this figure by the PB max. A ratio ≥0.45 indicates a retro-cochlear lesion. MD patients should not show a positive roll-over index.[36]
Serial audiometry is helpful in making the diagnosis as well as a means of follow-up on the degree of hearing loss.
Result
no discrepancies on SRT, absence of positive roll-over index
tympanometry/immittance/stapedial reflex levels
Test
Immittance evaluation including tympanometry stapedial reflex measurements (both ipsilateral and contralateral) and measurement of acoustic reflex decay.
Result
normal tympanogram; elicitation of acoustic reflex <60 dB patient threshold; no abnormal reflex decay
oto-acoustic emissions (OAE)
Test
OAE are an electrophysiological measure of outer hair cell dysfunction.
Although measurable OAE is absent in the frequency range affected by meniere's disease (MD), 18% of hydropic ears had unexpectedly present emissions even when the pure-tone thresholds were ≥50 dB.[37]
Sounds produced by the cochlea are measured with a sensitive microphone in the ear canal, using a brief stimulus such as a click (transient-evoked OAE) or 2 stimulus tones of different frequency (distortion product OAE).
These findings are not specific to MD but also apply to other cochlear disorders. OAE may also be affected by middle-ear disease.
Result
absence of measurable OAE in frequency range affected by MD
Investigations to consider
electrocochleography
Test
Measures electrical potentials that are derived from the hair cells in the cochlea and the auditory nerve.
Should be repeated during the quiescent stage of the disease.
Result
abnormally large summating potential amplitude relative to the action potential amplitude
electronystagmography
Test
Records eye movements and responses to ocular and vestibular stimuli.
A unilateral decreased vestibular response in the affected ear suggests peripheral aetiology, such as vestibular neuronitis.[38]
Caloric response diminishes with increased disease duration, and a canal paresis of 35% to 50% is commonly observed in the affected ear.[9]
Great care should be exercised in performing vestibular testing when the patient is having an acute attack of meniere's disease (MD). Some vestibular evaluation procedures may precipitate an acute attack and should be avoided if not necessary for diagnosis.
Result
abnormal in MD; unilateral decreased vestibular response in the affected ear is common
rotary chair test
Test
Sinusoidal harmonic acceleration or rotating chair testing involves a variety of measurements of nystagmus on a patient who is rotated from side to side during the procedure in a computer-controlled chair.
Result
decreased gain, abnormal phase, and asymmetry in the response
vestibular-evoked myogenic potential (VEMP)
Test
VEMP uses an intense, brief auditory stimulus to assess the saccule ipsilateral to the stimulus.
Result
increased amplitude in early disease; attenuated or absent in later stages
MRI of internal auditory canals
Test
Any patient with unilateral, sudden, or asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss should have MRI with gadolinium to exclude a retro-cochlear cause of hearing loss (such as acoustic neuroma).
Result
normal in meniere's disease
thyroid function tests
Test
Elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone and low thyroxine if hypothyroidism is cause of hearing loss.
Result
normal in meniere's disease
Lyme disease and syphilis serology
Test
Positive titres suggest these conditions are the cause of acute or recent deterioration in hearing.
Result
normal in meniere's disease
anti-nuclear antibody
Test
High sensitivity, but low specificity for systemic lupus erythematosus.[35]
Result
negative in most cases; positive titre in the presence of associated autoimmune pathology
anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody
Test
Associated with vasculitis.
Result
negative in most cases; positive titre in the presence of associated autoimmune pathology
rheumatoid factor
Test
Sensitive, but non-specific for rheumatoid arthritis.[35]
Result
negative in most cases; positive titre in the presence of associated autoimmune pathology
Emerging tests
3-dimensional MRI
Test
3-D MRI protocols have been developed to delineate endolymphatic hydrops, but they are still in the investigational stages. MRI, after both intravenous and intratympanic injection of gadolinium, is being studied.[32][33][34]
Result
perilymphatic space surrounding the endolymph is either small or unable to be visualised
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer