Investigations
1st investigations to order
CXR
Test
An appropriate initial test. However, CXR visualises the pleura poorly and will miss subtle abnormalities. Furthermore, it does not assess the mediastinal lymph nodes.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray demonstrating total left-sided collapse and replacement of hemithorax with mesothelioma; there is reduced expansion on this sideFrom BMJ Case Reports 2011;doi:10.1136/bcr.09.2010.3319 [Citation ends].
European guidelines recommend CXR for patients with relevant symptoms and signs (e.g., dyspnoea, chest pain, and weight loss).[35][36][37]
Result
unilateral pleural effusion, irregular pleural thickening, reduced lung volumes, and/or parenchymal changes related to asbestos exposure (e.g., lower zone linear interstitial fibrosis)
CT scan of the chest and upper abdomen with intravenous contrast
Test
A more sensitive modality than CXR, providing more detail of the pleura, lungs, and mediastinum. However, differentiating benign from malignant pleural processes with CT alone can be difficult.
Findings suggesting a malignant process include circumferential or nodular pleural thickening, involvement of the mediastinal pleura, or enlarged regional lymph nodes.[39][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography scan of the lung showing a right-sided pleural mesothelioma and left-sided calcified pleural plaqueFrom the collection of Dr Chris R. Kelsey; used with permission [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography scan of the mediastinum showing a right-sided pleural mesothelioma and left-sided calcified pleural plaqueFrom the collection of Dr Chris R. Kelsey; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography scan of the mediastinum showing a right-sided pleural mesothelioma and left-sided calcified pleural plaqueFrom the collection of Dr Chris R. Kelsey; used with permission [Citation ends].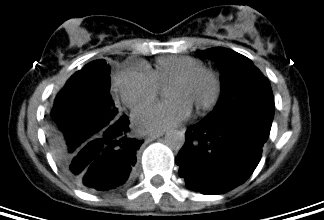
Result
pleural thickening and/or discrete pleural plaques, pleural and/or pericardial effusions; enlarged hilar and/or mediastinal lymph nodes; chest wall invasion and/or spread along needle tracts can occur
Investigations to consider
thoracentesis
Test
The sensitivity of cytology for mesothelioma is relatively low and typically requires further pathological assessments.[40]
Video demonstrating how to perform a pleural aspiration
Result
exudate; may show malignant cells within the pleural fluid
pleural biopsy
Test
Cytology of pleural fluid obtained via transthoracic needle aspiration biopsy (typically using CT guidance) facilitates pathological confirmation of malignancy. This is not, however, as reliable for diagnosis as a tissue core specimen.
Pleural biopsies performed during video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) exploration is the most invasive but also the most accurate modality (biopsy three distant sites when possible).[36][42]
Result
specimen for pathological diagnosis
video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)
Test
Regarded as the best study to evaluate the pleural lining of the lung and to obtain optimal biopsy specimens for histology.[38]
Pleural biopsies performed during VATS exploration is the most invasive but also the most accurate modality (biopsy three distant sites when possible).[36][42]
Result
pleural thickening or discrete plaques; lymphadenopathy
immunohistochemistry
Test
Immunohistochemistry is recommended.[35][38] This should use selected markers expected to be positive in mesothelioma (e.g., calretinin, keratins 5/6, and nuclear WT1) as well as markers expected to be negative in mesothelioma (e.g., CEA, EPCAM, claudin 4, TTF-1).
Other markers can also be used to help exclude differential diagnoses.[38]
Result
positive results for certain markers (e.g., calretinin, keratins 5/6, and nuclear WT1) make mesothelioma more likely, while positive results for other markers (e.g., CEA, EPCAM, claudin 4, TTF-1) make mesothelioma less likely
chest MRI
Test
MRI has the potential to differentiate between benign fibrous mesothelioma (low signal intensity on T2-weighted images) and malignant mesothelioma (high signal intensity), but it is not as reliable as biopsy and will seldom alter management.
Result
degree of tumour extension, especially to the chest wall and diaphragm
PET scan
Test
PET has the potential to distinguish benign pleural abnormalities from malignant processes.[43]
PET can help define the extent of intrathoracic and mediastinal disease and detect regional and distant metastases.[38][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Positron emission tomography scan showing hypermetabolic right-sided pleural mesotheliomaFrom the collection of Dr Chris R. Kelsey; used with permission [Citation ends].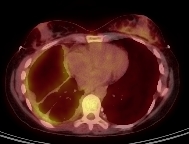
Result
further evaluates location and extent of primary tumour; evaluates for distant metastases
cervical mediastinoscopy
Test
Mediastinal (N2) lymph node involvement is a poor prognostic factor, and such patients are not ideal candidates for aggressive multimodality therapy.[44]
Mediastinoscopy, especially in patients with abnormal lymph nodes on CT scan or PET, should be considered before surgery.
Result
spread to mediastinal lymph nodes
pulmonary function tests
Test
FEV1 and diffusion capacity of lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) should be performed on all patients with mesothelioma who are being evaluated for surgery. Patients with marginal function can be further assessed with radionuclide studies as needed.
In general, postoperative FEV1 and DLCO should be >40% of predicted values.
Spirometry is a sensitive predictor of postoperative complications after thoracotomy.
Result
spirometry and lung volumes
FBC
Test
Baseline blood counts are necessary before treatment is initiated or invasive procedures are performed.
Chemotherapy, and to a lesser degree radiotherapy, can decrease haematopoiesis, necessitating baseline and periodic analysis of blood counts.
Result
usually normal; low haemoglobin, high platelet count, high white blood cell count are usually found in advanced disease and are poor prognostic factors
basic metabolic panel
Test
Recommended as baseline before treatment is initiated.
Some chemotherapy agents, cisplatin in particular, can affect electrolytes and kidney function.
Result
usually normal
Emerging tests
biomarkers
Test
Soluble mesothelin-related peptide (SMRP) levels may correlate with disease status.[2]
However, biomarkers, including SMRP, cannot be used alone to confirm malignant pleural mesothelioma.[35][36][45]
Research into potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers is ongoing.[46][47][48]
Result
positive for marker
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer
