Investigations
1st investigations to order
Tanner staging
Test
Pubertal development and progress are best ascertained by Tanner staging.[1][2]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Tanner staging: A, genital rating standards in boys; B, pubic hair rating standards in boys; C, breast rating standards in girls; D, pubic hair rating standards in girlsAdapted from Marshall WA, Tanner JM. Arch Dis Child. 1970;45:13-23; Marshall WA, Tanner JM. Arch Dis Child. 1969;44:291-303 [Citation ends].
Result
girls: presence of stage 2 breast development; boys: presence of stage 2 genital development
measurement of testicular size
Test
Testicular size is documented as a measurement of the longest axis or by the testicular volume using the Prader orchidometer.
Volume of 4 mL or a longitudinal length of 2.5 cm defines the onset of puberty.[2]
Most reliable indicator of puberty onset in boys.[55]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Prader orchidometerCreated by BMJ Knowledge Centre [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Method of comparing testicular size using the Prader orchidometerFrom the collection of Dr A. Mehta [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Method of comparing testicular size using the Prader orchidometerFrom the collection of Dr A. Mehta [Citation ends].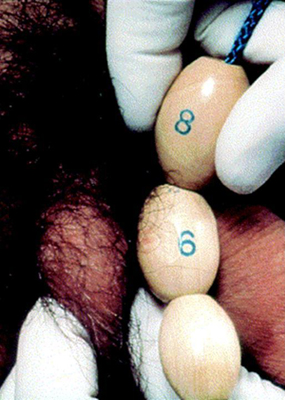
Result
boys: testes ≥4 mL
bone age assessment
Test
A left hand/wrist radiograph helps estimate skeletal age. The appearance of representative epiphyseal centers on the x-ray is compared with age- and sex-appropriate published standards. The most commonly used method is that of Greulich and Pyle or an automated bone age report such as BoneXpert.[50]
Result
advanced
basal follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinising hormone (LH)
Test
Laboratory measurement of serum FSH and LH concentrations will help differentiate patients with central precocious puberty (CPP), with elevated levels, from those with gonadotrophin-independent precocious puberty (GIPP), with low levels.
Before the onset of puberty, FSH is usually the predominant gonadotrophin, while during and after puberty LH concentrations are higher than FSH.
Basal LH is much more sensitive than basal FSH concentration. In cases of CPP, basal LH concentration is usually ≥0.3 IU/L.
An elevated basal LH has a high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of precocious puberty in males, but is less sensitive in females. Thus, in girls, basal LH measurement may be adequate to confirm, but not to refute, the diagnosis of CPP.[40]
Result
low in GIPP; elevated in CPP
gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulation test
Test
The GnRH test is used instead of basal FSH and LH testing in less clear-cut cases.
This involves measuring LH and FSH levels at baseline, and then again at 20 and 60 minutes after administration of GnRH.
A pubertal response is considered with a serum LH concentration after stimulation of ≥5 IU/L.[51]
GnRH analogues have also been used for the investigation of peak LH and FSH concentrations following stimulation if recombinant GnRH is unavailable.[52]
Result
elevated gonadotrophins in central precocious puberty; suppressed gonadotrophins in gonadotrophin-independent precocious puberty
serum testosterone
Test
Helps confirm the onset of puberty in males.
Elevated levels in females may point towards a diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia or virilising adrenal or ovarian tumour.
Result
elevated
serum oestrogen
Test
Helps confirm the onset of puberty in females.
Serum oestrogen is not always elevated, and some assays cannot detect levels of <50 picomol/L.
Result
elevated
ultrasound pelvis
Test
A pelvic ultrasound scan can help in the diagnosis of precocious puberty in girls.
The uterus may have a pre, peri, or post-pubertal shape and size depending on the stage of puberty.
An endometrial echo reflects an oestrogen effect, while the presence of follicles in the ovaries reflects gonadotrophin stimulation.
Endometrial thickening suggests that pubertal concentrations of oestrogen have been attained, and an endometrium of around 6-8 mm implies imminent menarche.
The sexual precocity in girls with McCune-Albright syndrome is caused by autonomously functioning multiple, luteinised, follicular cysts of the ovaries with an occasional large solitary cyst.
A pelvic ultrasound will also help to identify gonadal oestrogen-secreting tumours.
Result
ovarian cyst(s), tumours, uterine enlargement ± endometrial echo
Investigations to consider
MRI brain
Test
Consider if puberty is consonant especially in boys. In girls, central precocious puberty is typically idiopathic although imaging must be considered in very young girls. There is consensus that MRI of the brain needs to be done in all boys and MRI of the brain in girls with onset of puberty prior to age 6, but studies have found that the risk of finding a tumour or another serious lesion is very low (<1%) in girls with onset between ages 6 and 8 years, so many advise not routinely imaging such girls.[54]
Neoplasms include optic nerve gliomas (e.g., in association with neurofibromatosis), craniopharyngiomas, or hamartomas. Other tumours include astrocytomas, ependymomas, or pineal tumours.[27][28]
The characteristic appearance of a hamartoma is that of a sessile or pedunculated mass usually attached to the posterior hypothalamus between the tuber cinereum and the mamillary bodies.[53]
Result
pituitary tumour
CT brain
Test
Not as sensitive as MRI; may help determine presence/extent of cranial abnormalities.
Result
pituitary tumour; hyperostosis of base of skull in McCune-Albright syndrome
17-hydroxyprogesterone
Test
To rule out congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) when puberty is disconsonant, particularly in males.
CAH in females presents with signs of virilisation (e.g., pubic and axillary hair and clitoromegaly) but no oestrogenisation.
Result
elevated in CAH
urinary steroid profile
Test
To rule out congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) when puberty is disconsonant, particularly in males.
CAH in females presents with signs of virilisation (e.g., pubic and axillary hair and clitoromegaly) but no oestrogenisation.
Result
identifies adrenal steroid synthesis defects (e.g., CAH)
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulation test
Test
To rule out congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) when puberty is disconsonant, particularly in males.
CAH in females presents with signs of virilisation (e.g., pubic and axillary hair and clitoromegaly) but no oestrogenisation.
A standard dose of ACTH stimulation should be used.
Result
identifies adrenal steroid synthesis defects, (e.g., CAH)
CT or MRI adrenals
Test
Should be considered if an adrenal tumour is suspected in patients with virilisation.
Result
may reveal adrenal tumour
ultrasound adrenals
Test
Should be considered if an adrenal tumour is suspected in patients with virilisation.
Result
may reveal adrenal tumour
bone scan/skeletal survey
Test
In patients with McCune-Albright syndrome a bone scan and/or a skeletal survey to identify the bony lesions of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia are also indicated.
Result
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia in McCune-Albright syndrome
other pituitary hormone investigations
Test
Consider in patients with early pubertal development following cranial irradiation or pituitary surgery.
Result
may reveal pituitary hormone deficiencies
genetic testing
Test
Genetic testing should be carried out in patients suspected to have neurofibromatosis type 1, McCune-Albright syndrome, or familial testotoxicosis. Loss-of-function mutations in MKRN3 or DLK1, or gain-of-function mutations in KISS1R, a G protein-coupled receptor that is a ligand for kisspeptin, can cause central precocious puberty.[31]
Result
varying abnormalities
thyroid function tests
Test
Long-standing severe hypothyroidism results in high thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH); if present, FSH may also be elevated (by various mechanisms) leading to isolated breast development or testicular enlargement without other secondary sexual characteristics.
Thyroid function tests are mainly helpful in cases where symptoms are suggestive of hypothyroidism and where growth velocity is decreased instead of increased.
Result
low free thyroxine, elevated TSH in primary hypothyroidism
Emerging tests
overnight gonadotrophin profile
Test
Overnight sampling of gonadotrophins may demonstrate pulsatility. It is primarily undertaken in a research setting.
Result
low number of LH pulses in hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer