Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
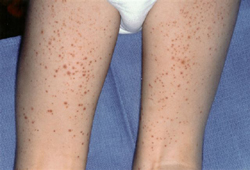
- rash
- arthralgias
- abdominal pain
- signs of renal disease
Other diagnostic factors
- drug history
- scrotal pain or swelling
- headaches
- seizures
- pulmonary haemorrhage
Risk factors
- genetics
- allergy
- male sex
- age 2 to 10 years
- increasing age at onset
- winter season/prior infection
- medication
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- blood pressure
- urinalysis
- serum creatinine and electrolyte levels
Investigations to consider
- serum IgA levels
- FBC and coagulation studies
- skin biopsy
- renal biopsy
- ultrasound, abdomen
- ultrasound, testicles
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Louise Oni, MBChB, MRCPCH, MA, PhD
Senior Lecturer in Paediatric Nephrology and Honorary Consultant Paediatric Nephrologist
University of Liverpool
Department of Paediatric Nephrology
Alder Hey Children's NHS Foundation Trust Hospital
Liverpool
UK
Disclosures
In the past 12 months LO has contributed to expert advisory roles for Boehringer Ingelheim and Biocryst pharmaceuticals. LO has received a travel grant from Sandoz. These are unrelated to this article and all monetary payments are placed into an institutional educational charity account. LO is an author of references cited in this topic.
Peer reviewers
David Kershaw, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor
MI
Disclosures
DK is co-medical director for the board of directors of Nephcure.
Rajan Madhok, MD, FCRP
Consultant Physician and Rheumatologist
Centre for Rheumatic Diseases
Glasgow Royal Infirmary
Glasgow
UK
Disclosures
RM declares that he has no competing interests.
Richard A. Watts, MA, DM, FRCP
Consultant Rheumatologist
Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust
Ipswich
UK
Disclosures
RAW declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer