Investigations
1st investigations to order
plasma AAT level
Test
Serum AAT levels should be measured when the clinician has increased suspicion of disease.[8][53]
Disease states may still be represented by borderline or even normal AAT levels, meaning that such results warrant continued suspicion.
Levels below 11 micromol/L (80 mg/dL) confer inadequate protection against inflammatory lung disease.[7]
Exact threshold values vary depending on testing method and regional guidance; appropriate regional guidelines should be consulted for interpretation of serum AAT levels.[6][8][9][10]
AAT is an acute phase reactant and can be artificially elevated in some clinical settings (e.g., exacerbation of COPD).[30]
Result
reduced plasma level <20 micromol/L
pulmonary function testing
Test
Significantly abnormal results are usual, including reduced FEV1, which is only partially reversible with bronchodilation.
Result
significantly reduced FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC; increased TLC; impaired CO-diffusing capacity
chest x-ray
Test
Emphysematous changes may be evident if pulmonary disease is present. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of AAT deficiency (PA view)From the personal collection of D. Kyle Hogarth, MD, FCCP; used with permission [Citation ends].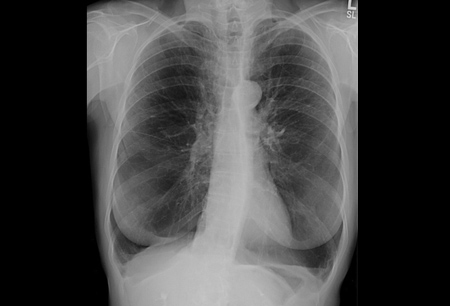 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of AAT deficiency (lateral view)From the personal collection of D. Kyle Hogarth, MD, FCCP; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Chest x-ray of AAT deficiency (lateral view)From the personal collection of D. Kyle Hogarth, MD, FCCP; used with permission [Citation ends].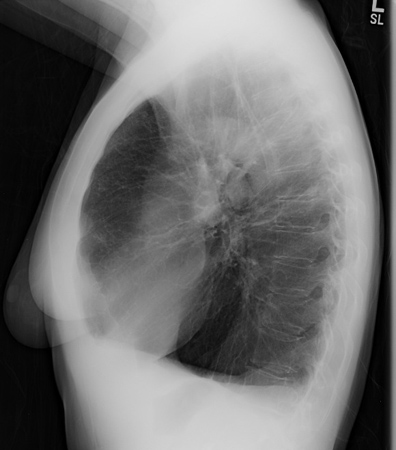
Result
large lung volumes and basilar predominant emphysema
chest CT
Test
CT is more sensitive than chest x-ray or pulmonary function tests for identifying panacinar emphysema and bronchiectasis.[8][40] Panacinar emphysema is predominantly seen in the lower lobes, although upper lobe-only disease has been described. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT of advanced emphysema in a patient with AAT deficiencyFrom the personal collection of D. Kyle Hogarth, MD, FCCP; used with permission [Citation ends].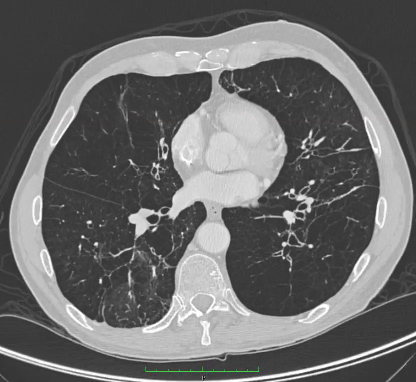
Result
panacinar emphysema and/or bronchiectasis
Investigations to consider
phenotyping
Test
Phenotyping can be used when a quick decision is needed, whereas genotyping should be used for definitive diagnosis when available.[1]
Performed if AAT levels are <20 micromol/L.
Low-normal plasma AAT measurements may correspond to heterozygous phenotypes that may place the individual and family members at risk for associated disease. Patients, and first-degree relatives of patients, with normal-low but protective AAT levels (12-35 micromol/L) should also undergo qualitative testing through phenotyping.
Result
characteristic AAT-variant proteins
genotyping
Test
Phenotyping can be used when a quick decision is needed, whereas genotyping should be used for definitive diagnosis when available.[1] Genetic testing may be performed when the actual phenotype does not correspond with the phenotype predicted by the serum AAT level.
Polymerase chain reaction is typically used for genotyping.[8][10]
Result
characteristic AAT alleles responsible for the AAT-variant proteins
gene sequencing
exercise testing with ABG analysis
Test
With exercise, these results are typical of people with emphysema.
Result
reduced PaO₂ and elevated A-a gradient
alpha-fetoprotein
Test
Rising alpha-fetoprotein levels may indicate hepatocellular carcinoma.
Result
elevated in cases of hepatocellular carcinoma
liver ultrasound
abdominal CT
Test
If hepatocellular carcinoma is present, abdominal CT may demonstrate abnormal liver imaging with typical hypervascular pattern.
CT can also be helpful for assessing signs of liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension, particularly in those with obesity.[53]
Result
abnormal liver imaging
abdominal MRI
Test
MRI can be helpful for assessing signs of liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension, particularly in those with obesity.[53]
Result
abnormal liver imaging
liver biopsy
Test
As serum liver tests may sometimes yield inconclusive results, the European Association for the Study of the Liver recommends considering liver biopsy in patients with otherwise unexplained, recurrently elevated liver enzymes.[1]
Result
abnormal hepatocellular cytoplasmic eosinophilic globules
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer