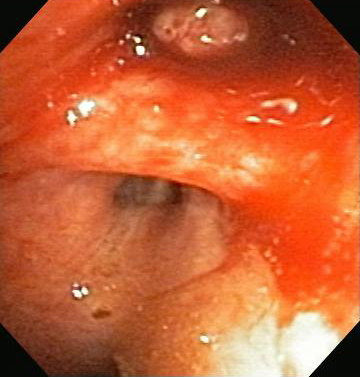
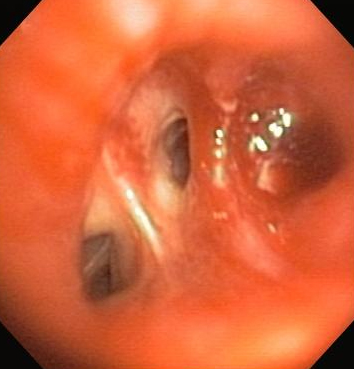
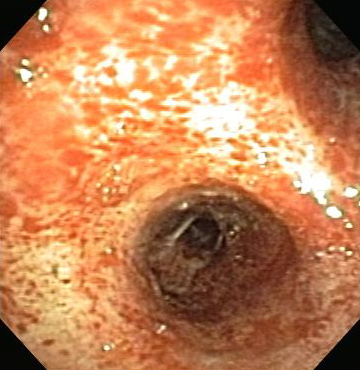
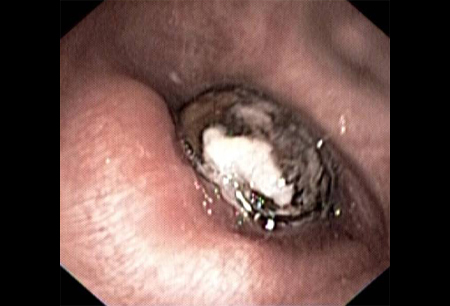
Differentials
Common
Acute bronchitis
History
acute onset cough, wheeze and/or dyspnoea, rhinorrhoea, sore throat
Exam
may be normal, cough with variable degrees of haemoptysis, normal to mildly elevated temperature, rhonchi, expiratory wheezing
1st investigation
- CXR:
normal or faint diffuse infiltrates
- sputum culture:
bacteria most often recovered: Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, less commonly Bordetella pertussis; viral agents: respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, echovirus, parainfluenza, herpes virus, Coxsackie virus, influenza, coronavirus, adenovirus
More
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy:
non-diagnostic, or small amount of blood in airways, signs of inflammation
More
Chronic bronchitis
History
frequent cough with excessive mucus production; chest pressure or pain; triggers include tobacco smoke, cannabis, air pollutants, and various infectious agents
Exam
may be normal, cough with variable degrees of haemoptysis, rhonchi, expiratory wheezing, barrel chest, hyper-resonance on percussion, poor air movement on auscultation
1st investigation
- CXR:
Increased anteroposterior ratio, flattened diaphragm, increased intercostal spaces, and hyperlucent lungs may be seen
More - spirometry:
FEV1/FVC ratio <0.70
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy:
non-diagnostic, or small amount of blood in airways, signs of chronic inflammation
Pulmonary tuberculosis
History
history of travel to endemic areas, exposure to people with tuberculosis (TB), risk factors for HIV, history of incarceration or homelessness; cough, dyspnoea, weight loss, fever, joint aches, night sweats
Exam
cachexia, fever, lymphadenopathy, rales, consolidation, decreased breath sounds if pleural effusion is present
1st investigation
- CXR:
may demonstrate atelectasis from airway compression, pleural effusion, consolidation, pulmonary infiltrates, mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy, upper zone fibrosis
More - sputum acid-fast bacilli smear and culture:
presence of acid-fast bacilli (Ziehl-Neelsen stain) in specimen.
More - nucleic acid amplification (NAAT):
positive for M tuberculosis
More
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage:
positive for acid-fast bacilli
More - contrast-enhanced chest computed tomography scan:
primary TB: mediastinal tuberculous lymphadenitis with central node attenuation and peripheral enhancement, delineated cavities; postprimary TB: centrilobular nodules and tree-in-bud pattern
More - lateral flow urine lipoarabinomannan (LF-LAM) assay:
positive
More
Lung abscess
History
high fever (>38.5°C [>101°F]), productive cough, purulent sputum, weight loss, malaise, fever, night sweats, alcoholism, risk factors for aspiration; massive haemoptysis may occur with chronic abscesses
Exam
fever, cardiac murmur, signs of gingival disease, cachexia, halitosis, amphoric or cavernous breath sounds, inspiratory crackles and/or bronchial breathing, decreased breath sounds; nail clubbing may occur with chronic abscesses
1st investigation
- FBC:
leukocytosis, anaemia
- CXR:
consolidation with central cavitation and air-fluid level, cavity wall thick and irregular
- sputum Gram stain:
one predominant gram-positive or -negative organism and neutrophils in aerobic infections; mixed flora with many neutrophils in anaerobic infections
- sputum culture:
often only see growth of normal respiratory flora in polymicrobial anaerobic infections; growth of infecting organism in aerobic infections
- blood culture:
positive for infecting organism in aerobic infections, bacteraemia, and septic embolism; seldom positive in anaerobic infections
Other investigations
- contrast-enhanced chest CT scan:
thick-walled, usually round cavity with irregular margins forming an acute angle with chest wall, no signs of compression of surrounding lung
More
Pneumonia
History
fever, cough, dyspnoea, chest pain, malaise
Exam
dullness to percussion, fever, unilateral rales, hypoxaemia
1st investigation
- CXR:
lobar or segmental infiltrates
More - sputum Gram stain:
visualisation of suspected infecting organisms such as gram-negative rods, gram-positive cocci
- sputum culture:
growth of infecting organism
- blood culture:
may be positive for infecting organism
Other investigations
Primary lung cancer
History
new cough, dyspnoea (worse at night or in recumbent position), chest pain, weight loss, occurrence of para-neoplastic syndrome
Exam
clubbing, focal wheezing, diminished breath sounds in pleural effusion or central obstruction
1st investigation
- CXR:
may be normal or show segmental atelectasis, lobar collapse, obstructive pneumonitis, pleural effusion
More - chest CT scan:
from solitary lung nodule to endobronchial obstruction with atelectatic lobe or lung, mediastinal/hilar lymphadenopathy, and/or pleural effusion
- bronchoscopy:
vascular lesions: may obstruct airways distal to tumour, subtle granular appearance, or erythematous mucosa; polypoid or papillary infiltrative with superficial erosions
More
Other investigations
- PET-fluorodeoxyglucose scan:
positive uptake of 18-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) in metabolically active nodules
More
Lung metastasis
History
symptoms related to the primary neoplastic site, pain, weight loss, malaise, cough, dyspnoea
Exam
clubbing, focal wheezing
1st investigation
- chest CT scan:
one or multiple nodules of variable sizes, from diffuse micronodular shadows (miliary) to well-defined masses, often irregular, often in the periphery of the lower lung zones, sometimes with cavitation; may see lymphadenopathy
More
Anticoagulants, thrombolytic agents
Toxic inhalation
History
exposure to smoke inhalation, solvents, trimellitic anhydride
Exam
may be normal, cough with variable degrees of haemoptysis
1st investigation
- CXR:
atelectasis; airspace opacity
- ABG with carboxyhaemoglobin (CO-Hg) level:
severe metabolic acidosis; CO-Hg level >15%
- pulse oximetry:
hypoxaemia
- ECG:
arrhythmias, ischaemia
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy:
bleeding
More
Bronchiectasis
History
frequent cough with excessive mucus production and little seasonal variation, dyspnoea, pleurisy, fatigue, weight loss; history of cystic fibrosis, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, underlying immunodeficiency
Exam
cough almost always present, with variable degrees of haemoptysis, crackles, wheezing, clubbing
1st investigation
- CXR:
may be normal or show obscured hemidiaphragm, thin-walled ring shadows with or without fluid levels, tram lines, tubular or ovoid opacities
- chest CT scan:
dilated bronchi with thickened walls extending to the lung periphery; bronchial diameter larger than accompanying pulmonary artery, creating 'signet ring' appearance, endobronchial mucus impaction
More - sputum culture:
pathogens most often recovered: Pseudomonas, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Mycobacterium avium, Aspergillus, viral pathogens
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy:
small amount of blood in airways, signs of chronic inflammation
More - spirometry:
obstructive physiology with decrease in FEV1/FVC ratio below normal limit
Pulmonary thromboembolism
History
dyspnoea, pleuritic chest pain, syncope
Exam
tachycardia, unilateral lower-extremity oedema, split S2 with loud P2, diaphoresis, tachypnoea
1st investigation
- CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA):
low-attenuation filling defects within a well-opacified pulmonary artery, clot, vessel cut-off, rim sign
More - Echocardiography:
abnormal RV ejection pattern (‘60-60 sign’); reduced contractility of the RV free wall compared with the RV apex ‘McConnell's sign’); RV dilatation and hypokinesis; RV diameter/LV diameter >0.9; interventricular septal flattening and paradoxical leftward septal motion; tricuspid regurgitation; pulmonary hypertension
More - D-dimer:
positive
More
Mitral valve stenosis
History
chronic dyspnoea, dyspnoea on exertion, orthopnoea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea, palpitations; may become clinically apparent with pregnancy-induced haemodynamic changes; history of recurrent respiratory infections (group A haemolytic streptococci) during childhood, rheumatic fever, rheumatic heart disease, living in endemic areas for mitral stenosis, atherosclerotic heart disease, and/or mitral annular calcification
Exam
reduced pulse pressure, elevated jugular venous distension, plethoric cheeks, right ventricular lift, atrial fibrillation, diastolic rumble, opening snap, loud S1, loud P2, hoarseness (recurrent laryngeal nerve impingement by the left atrium)
1st investigation
- CXR:
dilated left atrium, variable cardiomegaly, calcified mitral valve, increased interstitial markings with Kerley-B lines
- ECG:
atrial fibrillation with right ventricular hypertrophy, left atrial enlargement with long P wave (>120 milliseconds), broad notched P waves in lead II
- transthoracic echocardiogram:
leaflet thickening, commissural fusion, chordal shortening, chordal fusion
Other investigations
Left ventricular failure
History
history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidaemia, or tobacco use; coronary, valvular, or peripheral vascular disease; dyspnoea, palpitations, chest discomfort, orthopnoea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea, fatigue
Exam
neck vein distension, hepatojugular reflux, rales, S3 gallop, cardiomegaly, tachycardia
1st investigation
- transthoracic echocardiogram:
systolic heart failure: depressed and dilated left and/or right ventricle with low ejection fraction; diastolic heart failure: left ventricular ejection fraction normal but left ventricular hypertrophy and abnormal diastolic filling patterns
- ECG:
evidence of previous infarct, left ventricular hypertrophy, or atrial enlargement; may be conduction abnormalities and abnormal QRS duration
- CXR:
cardiomegaly, pulmonary vascular congestion, Kerley B lines, pleural effusions
- Urea and creatinine:
normal to elevated
- blood glucose:
elevated in diabetes
- thyroid function tests:
hypothyroidism: elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), decreased free triiodothyronine (FT3), decreased free thyroxine (FT4); hyperthyroidism: decreased TSH, elevated FT4
- blood lipids:
elevated in dyslipidaemia
- B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)/N-terminal pro BNP levels:
elevated
Other investigations
Coagulopathy
History
association with advanced liver and kidney disease, haematological malignancy, recent cytotoxic chemotherapy, specific disorders of coagulation cascade (factor deficiency); menorrhagia
Exam
petechiae, small capillary haemorrhages, ecchymoses, haematomas, haemarthrosis
1st investigation
- INR and PTT:
elevated
- urea and creatinine:
may be elevated
Other investigations
- specific coagulation factor deficiency:
decreased or absent
- thrombin time:
elevated
Thrombocytopenia
History
may present with purpura or be associated with gestation, HIV, liver disease, myelodysplastic syndrome; may be drug-induced
Exam
purpura, mucosal bleeding, epistaxis, signs of liver disease
1st investigation
- peripheral blood smear:
thrombotic microangiopathy (schistocytes)
- FBC with differential:
low platelet count
More
Other investigations
- LFTs:
may be normal; elevated in HELLP syndrome
- lactate dehydrogenase:
elevated in haemolysis
- haptoglobin:
low level with haemolysis
- INR/PTT:
elevated in disseminated intravascular coagulation
- fibrinogen:
low in disseminated intravascular coagulation
- D-dimer:
elevated in disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
History
fever, cough, dyspnoea, confusion, epistaxis, bleeding gums; possible history of sepsis, obstetric complications such as placental abruption, snake bite, malignancy (e.g., acute promyelocytic leukaemia), or tissue trauma (e.g., surgery)
Exam
petechiae, gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract bleeding, hypotension, tachycardia, pleural friction rub
1st investigation
- FBC with differential:
pancytopenia
- peripheral blood smear:
thrombotic microangiopathy (schistocytes)
- serum INR and activated PTT:
elevated
- serum fibrinogen:
low
- D-dimer:
elevated
Other investigations
Uncommon
Aspergilloma
History
mostly asymptomatic, commonly secondary to underlying chronic lung disease; weight loss, chronic cough, malaise
Exam
cough, variable haemoptysis
1st investigation
- CXR:
upper lobe mobile intracavitary mass with an air crescent in the periphery
- high-resolution chest CT scan:
upper lobe cavitary mass with intracavitary contents and adjacent pleural thickening
More
Other investigations
Endobronchial and pulmonary mucormycosis
History
underlying diabetes mellitus, immunosuppressed state, haematological disorder or transplant, chronic renal failure, chronic steroid use; fever, cough, dyspnoea, haemoptysis
Exam
sinusitis if upper airway is involved, wheezing if lower airway is involved, normal exam if only lung parenchyma is involved
1st investigation
- CXR:
pulmonary infiltrates
- high-resolution chest CT scan:
unilateral or bilateral infiltrates, cavity, endobronchial mass may mimic tumour
- CT guided needle biopsy:
non-septate or minimally septate broad, ribbon-like hyphae
More
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage:
non-septate or minimally septate broad, ribbon-like hyphae
More
Endobronchial neuroendocrine tumour (carcinoid)
History
asymptomatic; may cause cough, dyspnoea, wheezing if nodule is endobronchial
Exam
often normal examination, unilateral wheezing may be present
1st investigation
Other investigations
Aspiration of foreign body
History
may be asymptomatic, cough paroxysms, localised wheezing, choking crisis; most common in children <15 years of age; associated with alcohol misuse, sedative use, poor dentition, neurological disease, loss of consciousness, seizure in older adults
Exam
focal wheezing, choking crisis, focal decrease in breath sounds
1st investigation
Other investigations
- chest CT scan:
associated air trapping, atelectasis
More
Aspiration of gastric contents
History
history of GORD, age >70 years, general anaesthesia, cerebrovascular disease; fever, intractable cough, dyspnoea, alcohol misuse
Exam
fever, crackles, wheezing, dyspnoea
1st investigation
- CXR:
patchy airspace consolidations
Other investigations
- chest CT scan:
opacities in dependent segments
More
Broncholithiasis
History
chronic cough, occasional chest pain, may be asymptomatic, history of recurrent pneumonias in same location
Exam
rarely wheezing due to airway obstruction
1st investigation
- chest CT scan:
calcified mediastinal adenopathy or bronchial obstruction
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy:
splayed or irregular carinas
More
Tracheo-oesophageal fistula
History
feeding difficulties, recurrent aspiration pneumonia, cough
Exam
laboured breathing, coughing, choking, and cyanosis are non-specific findings
1st investigation
- CXR:
mediastinal air, gas-filled gastrointestinal tract, dependent infiltrates; insertion of a nasogastric tube may show coiling in the upper pouch
- upper gastrointestinal series:
spilling of contrast into the trachea
More
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy:
presence of a fistula
Bronchial telangiectasia
History
sometimes associated with hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia, recurrent epistaxis
Exam
mucocutaneous telangiectasia, pulmonary bruit, stigmata of right-to-left shunting such as cyanosis and clubbing
1st investigation
- CT angiography:
presence of arteriovenous malformations
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy:
non-specific network of submucosal dilated vessels
Airway trauma
History
recent history of high-velocity accident, blunt trauma to neck or chest, or exposure to explosive blast; iatrogenic haemoptysis may occur with traumatic intubation, bronchoscopy, and endobronchial therapeutic manoeuvres
Exam
tachypnoea, wheezing, chest or neck pain; external signs may or may not indicate magnitude of trauma
1st investigation
- CXR:
presence of widened mediastinum
More - chest CT scan:
fractures, haematomas, patchy or diffuse infiltrates in the lung parenchyma that do not conform to segmental or lobar anatomy
Other investigations
- bronchoscopy:
distal haemorrhage, pulmonary contusion, aspirated material
More
Dieulafoy's disease
History
congenital origin; history of comorbidities: cardiovascular disease, hypertension, chronic renal failure, diabetes, or alcohol misuse
Exam
Dieulafoy's disease is a vascular anomaly characterised by the presence of a tortuous dysplastic artery in the submucosa; cases involving a sub-epithelial bronchial artery have caused haemoptysis; most cases involve the gastrointestinal tract
1st investigation
- bronchoscopy:
arterial bleeding in area of ulcer or nodule; raised nipple or visible vessel without an ulcer, in absence of bleeding
- endoscopy:
arterial bleeding in area of ulcer or nodule; raised nipple or visible vessel without an ulcer, in absence of bleeding
Other investigations
Thoracic endometriosis
History
catamenial symptoms (within 24-48 hours of onset of menstruation); may have dysmenorrhoea, dyspareunia; chest pain, shortness of breath
Exam
no physical findings; pelvic tenderness, cul-de-sac nodularity may be present
1st investigation
- no test required:
diagnosis is clinical
Other investigations
- chest CT scan:
may be negative; pulmonary or pleural nodules seen during menses
Pulmonary artery aneurysm
History
congenital or related to pulmonary artery catheter complication
Exam
non-specific; chest pain may be present
1st investigation
- CT angiography:
presence of pulmonary artery aneurysm
Other investigations
Fat embolism
History
dyspnoea, fever, changes in mental status; usually 24-72 hours after long-bone fracture or liposuction
Exam
hypoxaemia, tachypnoea, changes in mental status; petechiae in the head, neck, anterior chest, and axillae
1st investigation
- no test required:
diagnosis is clinical
Other investigations
Tumour thromboembolism
History
history of mucin-secreting adenocarcinomas (breast, lung, stomach, colon), hepatoma, prostate cancer, choriocarcinoma, or renal cell carcinoma
Exam
tachypnoea, hypoxaemia, tachycardia
1st investigation
- CT angiography:
diagnosis is made in conjunction with high clinical suspicion; isolated vascular filling defect may be difficult to distinguish from blood clot
Other investigations
- ECG:
right-heart strain
- surgery:
histopathological demonstration of tumour cells in the pulmonary vasculature
Arteriovenous malformation
History
dyspnoea; history of stroke, brain abscess, cirrhosis (hepatopulmonary syndrome); personal or family history of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia
Exam
pulmonary bruit; arteriovenous communications or telangiectasia in skin, mucous membranes, and other organs; cyanosis, clubbing; neurological signs from cerebral aneurysms, cerebral emboli, or metastatic abscess; stigmata of advanced liver disease (jaundice, small liver, ascites, skin spider angiomata)
1st investigation
- chest CT with contrast:
round or oval nodule(s) with feeding artery and draining vein; pulmonary arteriole enlargement in dependent portions of the lungs
More
Other investigations
- pulmonary angiography:
confirms presence and location of malformations, identifies feeding arterial and venous structures
More - transthoracic contrast echocardiography:
delayed shunting suggests transpulmonary shunting
- radionuclide perfusion scanning:
does not typically define a pulmonary arteriovenous malformation anatomically, but can confirm or identify the presence of a right-to-left shunt
More - ABG analysis:
decreased partial pressure of oxygen, decreased oxygen saturation when arteriovenous flow is severe
More
Pulmonary haemorrhagic syndromes
History
cough, fever, dyspnoea; history of bone marrow transplant; history of connective tissue disease or vasculitis
Exam
usually negative; presence of leukocytoclastic vasculitis, arthritis, or synovitis, indicative of connective tissue disease
1st investigation
- CXR:
alveolar infiltrates, usually patchy or diffuse
- FBC:
decreased haemoglobin level
- bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage and/or lung biopsies:
sequential lavage yields progressively more haemorrhagic fluid; cytology shows haemosiderin-laden macrophages; lung biopsies may show capillaritis, vasculitis or immune complex deposition.
Other investigations
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate:
usually elevated
- urinary sediment:
may be present
More - ANA, C-ANCA, anti-GBM, and anti-DNA antibodies:
may be positive
More - pulmonary function test with diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide:
usually restrictive pattern with elevated diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (formerly Wegener's granulomatosis)
History
cough, chest pain, dyspnoea, rhinorrhoea, epistaxis, ear/sinus pain, hoarseness, fever, fatigue, anorexia, weight loss
Exam
palpable purpura, painful ulcers, uveitis, wheezing, sinus tenderness
1st investigation
- chest CT scan:
solitary or multiple lung nodules; airways are frequently affected
- anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody:
usually positive
More
Systemic vasculitis
History
complaints of arthralgias, myalgias, malaise, fatigue for several months before more specific signs or symptoms develop
Exam
specific organ involvement, which may demonstrate a pattern of disease (e.g., eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangitis is associated with poorly controlled asthma)
1st investigation
Other investigations
- biopsy of affected tissue:
vessel wall necrosis, fibrinoid necrosis, karyorrhexis (destructive fragmentation of the nucleus of a dying cell), red blood cell extravasation
More
Congenital heart disease
History
from asymptomatic to disabling symptoms: progressive heart disease, dyspnoea, fatigue, orthopnoea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea
Exam
frothy pink sputum, stigmata of right-to-left shunting (cyanosis, clubbing), heart murmur
1st investigation
- echocardiogram:
reflects the congenital cardiac defect
More
Other investigations
Tricuspid endocarditis
History
history of intravenous drug use, mitral valve prolapse, or congenital heart disease; fever, malaise, fatigue, chest pains, weakness, night sweats, palpitations
Exam
fever, Janeway lesions, Osler's nodes, splinter haemorrhages, cardiac murmur
1st investigation
- FBC:
elevated white blood cells
- blood cultures:
bacteraemia, fungaemia
- ECG:
prolonged PR interval; non-specific ST/T wave abnormalities; atrioventricular block
- echocardiogram:
mobile valvular vegetations
Other investigations
- urinalysis:
red blood cell casts, white blood cell casts, proteinuria, pyuria
Bronchogenic cyst
History
usually asymptomatic unless infected or results in airway obstruction; incidental finding
Exam
asymptomatic; cough, dyspnoea
1st investigation
Other investigations
Factitious haemoptysis
History
frequently young patients, healthcare workers; evidence of self-inflicted wounds or interventions capable of causing haemoptysis supports the diagnosis
Exam
absence of an alternative aetiology on work-up
1st investigation
- clinical history and examination:
diagnosis is clinical with a high index of suspicion; tests may not be indicated
Other investigations
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer
 ]
]