Last reviewed: 18 Mar 2025
Last updated: 19 Jan 2024
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- noisy breathing during sleep
- apnoeas
- choking or gasping
Other diagnostic factors
- waking up tired
- daytime somnolence
- hyperactivity
- behavioural problems
- night terrors
- enuresis
Risk factors
- increasing age
- male sex
- obesity (BMI >30)
- cranio-facial abnormalities
- endocrine disorders
- neck circumference above 40 cm
- sedating medications
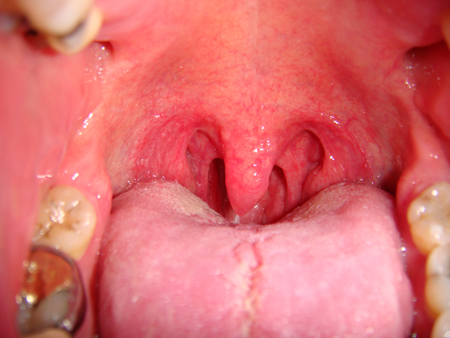
- adenotonsillar hypertrophy
- long soft palate and uvula
- alcohol consumption
- Down's syndrome
- gastro-oesophageal reflux
- active or passive smoking
- abnormal epiglottis
- hypo-pharyngeal cysts or tumours
- rhinitis/nasal obstruction
- asthma
Diagnostic investigations
Investigations to consider
- snoring scale score
- TFTs
- growth hormone level
- skin-prick tests/serum allergen-specific IgE tests
- sleep study
- acoustic analysis
- pharyngeal manometry
- sleep nasendoscopy
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Nadia Ashraf, BMBS, BMedSci(Hon), DA, DOHNS, FRCS(ORL-HNS)
Specialty Registrar in Otorhinolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery
Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
Sheffield
UK
Disclosures
NA declares that she has no competing interests.
Showkat Mirza, BM, BS, BMedSci, FRCS(ORL-HNS)
Consultant in Otorhinolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery
Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
Sheffield
UK
Disclosures
SM declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Jayant Pinto, MD
Assistant Professor of Surgery
Section of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
University of Chicago
Chicago
IL
Disclosures
JP declares that he has no competing interests.
Michael J. Hensley, MBBS, PhD, FRACP
Director
Department of Respiratory and Sleep Medicine
John Hunter Hospital
Professor and Head
School of Medicine and Public Health
Faculty of Health
The University of Newcastle
NSW
Australia
Disclosures
MJH declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer