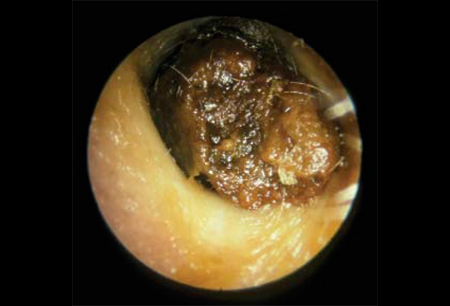
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
- visualisation of cerumen
- hearing loss
- fullness in the ear
Risk factors
- age >50 or <5 years
- male sex
- stenotic ear canal
- Down's syndrome
- cotton-tipped applicator use
- hearing aid use
- living in a nursing home
Diagnostic investigations
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Stephen Wetmore, MD, MBA, FACS

Professor Emeritus
Department of Otolaryngology
West Virginia University School of Medicine
Morgantown
WV
Disclosures
SW declares that he has no competing interests.
Peer reviewers
Rahul K. Shah, MD, FAAP
Associate Professor of Otolaryngology and Pediatrics
Division of Otolaryngology
Children's National Medical Center
Assistant Professor
Otolaryngology and Pediatrics
George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences
Washington
DC
Disclosures
RKS declares that he has no competing interests.
Seth R. Schwartz, MD, MPH
Director of Research
The Listen For Life Center At Virginia Mason
Otology/Otolaryngology
Department of Otolaryngology
Virginia Mason Medical Center
Seattle
WA
Disclosures
SRS is an author of a reference cited in this topic.
Robin Youngs, MD, FRCS
Consultant Otologist
Gloucestershire Royal Hospital
Gloucester
UK
Disclosures
RY declares that he has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer