Last reviewed: 19 Mar 2025
Last updated: 01 Oct 2024
Summary
Definition
History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
- presence of risk factors
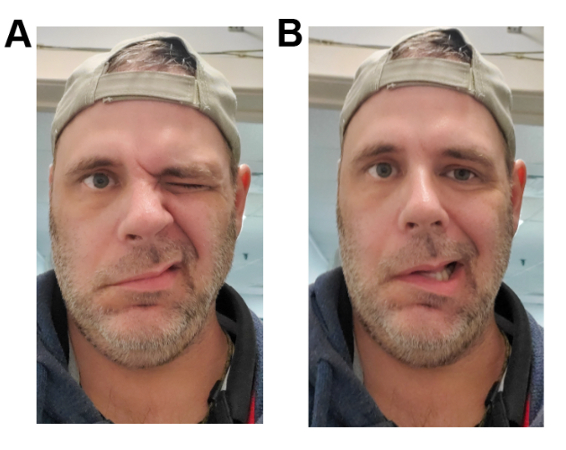
- sudden-onset (<72 hours) unilateral facial weakness
- ipsilateral severe ear/facial pain
- ipsilateral vesicular rash
- absence of constitutional symptoms
Other diagnostic factors
- dry eye
- vertigo
- hearing loss
- tinnitus
- epiphora
- altered taste
- oral lesions
- keratitis
Risk factors
- prior exposure to varicella zoster virus (VZV)
- age >50 years
- immunosuppression
- recent physiological stressor
- female sex
Diagnostic investigations
1st investigations to order
- clinical diagnosis
- varicella zoster virus (VZV) polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Investigations to consider
- electroneurography (evoked electromyography)
- MRI head and neck with contrast
- serology for Borrelia burgdorferi
Treatment algorithm
Contributors
Authors
Jonas R. Miller, MD
Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Fellow Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery
UNC Facial Nerve Center
University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill
Chapel Hill
NC
Disclosures
JRM declares that he has no competing interests.
Matthew Q. Miller, MD
Assistant Professor Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
Director UNC Facial Nerve Center
University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill
Chapel Hill
NC
Disclosures
MQM is a paid consultant for Checkpoint Surgical, Inc.
Peer reviewers
Douglas J. Lanska, MD, MS, MSPH
Honorary Fellow
Department of Neurology
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
Madison
WI
Disclosures
DJL declares that he has no competing interests.
Mervi Kanerva, MD, PhD
Associate Professor
Senior ENT Consultant
Helsinki University Hospital
Helsinki
Finland
Disclosures
MK declares that she has no competing interests.
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer