Tests
1st tests to order
CBC
Test
Suggests inflammatory process.
Result
elevated WBC
C-reactive protein
Test
Suggests inflammatory process.
Result
>3 mg/dL
LFTs
Test
Show a cholestatic picture, though they should not be the only method to identify common bile duct stones.[36]
Result
elevated alkaline phosphatase, gamma glutamyl transferase, and bilirubin
right upper quadrant ultrasound scan
Test
A rapid, noninvasive, affordable, and sensitive technique. Detection of gallstones alone does not definitively diagnose the condition. To make an accurate diagnosis, the findings of stones and a sonographic Murphy sign are required. About 92% of patients with a positive sonographic Murphy sign in the presence of gallstones have the condition.[39] [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Ultrasound of acute cholecystitis and presence of gallstonesFrom the collection of Dr Charles Bellows; used with permission [Citation ends].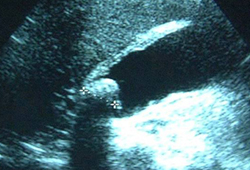
Pericholecystic fluid is a sign of actual or impending perforation in severe cases.[35][42]
A preoperative gallbladder ultrasound evaluation for symptomatic cholecystitis that documents a thick gallbladder wall (≥3 mm) with calculi is a clinical warning, for laparoscopic surgeons, of the potential for a difficult laparoscopic cholecystectomy procedure that may require conversion to an open cholecystectomy procedure.
Result
gallstones, pericholecystic fluid, distended gallbladder, thickened gallbladder wall, positive sonographic Murphy sign
Tests to consider
cholescintigraphy (hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid [HIDA] scan)
Test
Directly shows cystic duct obstruction.
The absence of gallbladder filling within 60 minutes after the administration of tracer indicates obstruction of the cystic duct and has a sensitivity of >90% for acute cholecystitis.[45][46] The "rim sign" is a blush of increased pericholecystic radioactivity, which is present in about 30% of patients with acute cholecystitis and in about 60% with acute gangrenous cholecystitis.[45]
Used if the diagnosis remains in doubt after ultrasound scanning.[42]
HIDA scan has the highest sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of acute calculus cholecystitis (ACC) as compared with other imaging modalities.[36] Disadvantages include radiation exposure, lack of widespread availability, and no evaluation of an alternative abdominal diagnosis.
Result
failure of gallbladder filling with normal hepatic uptake and biliary excretion; normal in acalculous cholecystitis
abdominal CT
Test
Inferior to ultrasound in assessment of acute biliary disease, but helps exclude concomitant pathologies.
Result
gallbladder wall inflammation; linear high-density areas in pericholecystic fat tissue
abdominal MRI
Test
Appropriate for pregnant patients with abdominal pain.[41] Helpful for evaluating the presence of stones in the bile duct (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography sequences).
Result
enlarged gallbladder with thickened wall; pericholecystic high signal
abdominal x-ray
Test
Radiographic demonstration of gas in the gallbladder wall, lumen, or pericholecystic tissues indicates emphysematous cholecystitis (severe variant of cholecystitis). This is more common in diabetes mellitus and in older patients.[47]
Result
may see gallstones
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer