Tests
1st tests to order
abdominal x-ray
Test
Should be obtained as baseline evidence of fecal retention, and can be used for subsequent evaluations to note progress or recurrence of fecal retention.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Abdominal radiograph showing severe stool retention in child with fecal soilingFrom the personal collections of Dr Linda S. Nield and Dr Uwe Blecker; used with permission [Citation ends].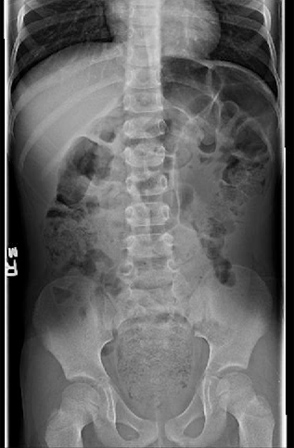
Result
severe stool retention in fecal incontinence associated with chronic constipation; large, distended bowel loops (bottleneck appearance) may be noted in Hirschsprung disease
Tests to consider
unprepared barium enema
Test
Should be obtained in suspected cases of Hirschsprung disease (i.e., the child did not stool within the first 72 hours of life, empty rectal vault).
Result
narrowed distal colon transitioning to a dilated proximal colon is the classic finding in Hirschsprung disease
spinal x-ray
Test
Should be obtained only if abnormal neurological examination (i.e., lower-extremity motor or sensory deficits, abnormal reflexes).
Result
rule out spinal defects
MRI spine
Test
Obtained only if abnormal neurological examination (i.e., lower-extremity motor or sensory deficits, abnormal reflexes); may have to be obtained at a tertiary care facility.[17]
Result
rule out spinal defects
radiopaque marker transit radiograph
Test
May be obtained in a tertiary care/motility specialty clinic but is typically unavailable to the primary care clinician.
Result
delayed passage and excretion of marker
colonic and rectal manometry studies
Test
Would not be ordered by a primary care provider; the pediatric gastroenterologist determines the need for this test. Assesses resting and squeeze anal pressures.[17]
Result
abnormal functioning of the anal sphincter indicates organic etiology of fecal incontinence
rectal biopsy
Test
Would not be ordered by a primary care provider; the pediatric gastroenterologist determines the need for this test.
Result
absence of ganglionic cells and presence of excess nonmyelinated nerves
serum thyroid-stimulating hormone level
Test
Should be obtained when signs and symptoms of thyroid disease are present.
Result
high in hypothyroidism, suggestive of organic cause for chronic constipation
serum free thyroxine (T4) level
Test
Should be obtained when signs and symptoms of thyroid disease are present.
Result
low in hypothyroidism, suggestive of organic cause for chronic constipation
sweat chloride test
Test
Obtained when signs and symptoms of cystic fibrosis are present, especially if rectal prolapse is a feature.
Result
abnormally high levels indicate cystic fibrosis
tissue transglutaminase IgA
Test
Celiac studies can also be ordered if celiac disease is suspected, as this disease may present with constipation.
Result
elevated in celiac disease
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer