Tests
1st tests to order
x-rays
Test
Radiographs should be obtained in the presence of trauma or if there is concern that a tumor or infection may be present.
X-rays are typically normal in an acute, nontraumatic rotator cuff injury.
In a post-traumatic shoulder, the surgeon must exclude emergent or urgent shoulder pathology early. Other trauma from high-energy mechanisms can include glenoid fracture, greater tuberosity humerus fracture, and glenohumeral dislocation.
A standard x-ray series consisting of a true anteroposterior, axillary lateral, and outlet/scapular Y views is key to excluding these associated pathologies.
Result
usually normal; may show opacities if calcific tendonitis present; may show superior migration of the humeral head relative to the glenoid (large or massive tears); may show pseudosubluxation of the humeral head inferior to the glenoid (acute massive tears)
Tests to consider
diagnostic injection
Test
To distinguish true weakness from weakness caused by pain, a pain-relieving injection of 1% lidocaine into the subacromial bursa should be followed by retesting of rotator cuff strength. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Subacromial injection. Insert needle just inferior to posterior edge of acromion (x), aiming parallel to the undersurface of the acromionFrom the collection of Daniel J. Solomon, MD; used with permission [Citation ends].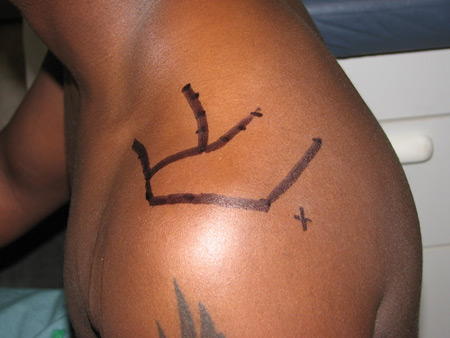
If strength does not improve, the test suggests rotator cuff tear.
Result
weakness despite pain relief
MRI
Test
Advanced imaging may be recommended if surgery is being contemplated or if the patient continues to have pain and decreased motion after at least 6 weeks of therapy.
MRI and ultrasound are usually the advanced imaging modalities of choice.[15][16] MRI is often preferred, as ultrasound is highly operator-dependent.
Sensitivity and specificity of MRI utilized to detect full-thickness rotator cuff tears are 91% and 97%, respectively.[26]
Sagittal oblique images provide excellent information regarding muscle quality and infiltrate.
Result
full-/partial-thickness tears, intrasubstance signal change, fatty infiltration, retraction, fluid within subacromial bursa, effusion
ultrasound
Test
Advanced imaging may be recommended if surgery is being contemplated or if the patient continues to have pain and decreased motion after at least 6 weeks of therapy.
Ultrasound is a better modality than MRI if there is prior metal hardware, such as suture anchors, present in the humeral head or glenoid. It also allows a dynamic evaluation of the shoulder, whereas other imaging modalities are static. However, the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound is operator-dependent.
One meta-analysis found 95% sensitivity and 96% specificity for full-thickness rotator cuff tears, and 72% sensitivity and 93% specificity for partial-thickness tears.[29]
Result
full-/partial-thickness tears, intrasubstance signal change, fatty infiltration, retraction, fluid within subacromial bursa, effusion
magnetic resonance arthrography
Test
Advanced imaging may be recommended if surgery is being contemplated or if the patient continues to have pain and decreased motion after at least 6 weeks of therapy.
In a meta-analysis, magnetic resonance arthrography was found to be more sensitive and specific than MRI and ultrasound (which are equivalent) in the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears.[24]
Result
full-/partial-thickness tears, intrasubstance signal change, fatty infiltration, retraction, fluid within subacromial bursa, effusion
CT arthrography
Test
Rarely used. Soft-tissue detail is superior with MRI and ultrasound.
CT arthrograms have been shown to be comparable to MR arthrography in diagnosing full-thickness rotator cuff tears, but inferior to MR arthrography for diagnosing partial-thickness rotator cuff tears.[25]
Result
in full-thickness tears, fluid within subacromial bursa connecting to fluid within the glenohumeral joint
CT scan
Test
Rarely used. Soft-tissue detail is superior with MRI and ultrasound. It can show healing of cuff tears after rotator cuff repair and is good to evaluate muscle quality.
Result
in full-thickness tears, fatty infiltration, retraction, fluid within subacromial bursa
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer