Tests
1st tests to order
anti-Toxoplasma IgG (serum)
Test
Can be ordered when screening for previous exposure, such as in a potential organ transplant recipient, an HIV-infected patient, or a woman being seen for preconception planning.
Detectable IgG indicates prior infection (in rare cases, patients with toxoplasmosis who are immunocompromised can have no detectable anti-Toxoplasma IgG).
Titer does not correlate with severity of illness.[17]
Result
detectable anti-Toxoplasma IgG, with titer
anti-Toxoplasma IgM (serum)
Test
Can be ordered when evaluating for acute infection.
A negative test rules out acute infection.
A positive test does not signify acute infection. Many commercially available tests have high false positive rates (up to 60%) and IgM can remain detectable for many months after initial infection.
The IgM immunosorbent agglutination assay is available through reference labs for testing of newborns, and is more sensitive and specific than commercially available tests. Demonstration of IgM in the serum of the newborn at or after 5 days of age is diagnostic of congenital disease.[11]
Part of a panel of tests used by reference labs to diagnose infection during pregnancy and in the newborn.
Result
detectable anti-Toxoplasma IgM, with titer
CT (with intravenous contrast) or MRI of brain
Test
Should be ordered for any patient who is immunocompromised with a decreased level of consciousness or with focal neurologic deficits.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Computed tomography: brain of central nervous system toxoplasmosisFrom the collection of Louis M. Weiss, MD, MPH; used with permission [Citation ends].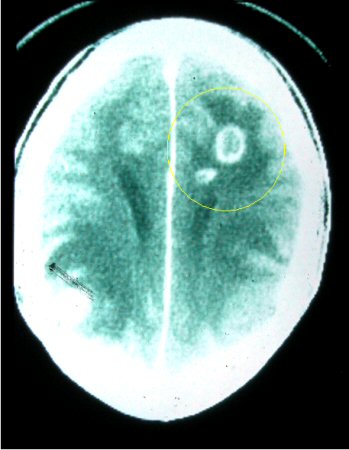
Result
ring-enhancing brain lesion(s), usually multiple, often involving the basal ganglia
Tests to consider
anti-Toxoplasma IgA (serum)
Test
Most helpful for diagnosing congenital disease. IgA does not cross the placenta, therefore its presence reflects the newborn’s own immune response to Toxoplasma infection.[11]
Demonstration of IgA in the serum from the newborn at or after 10 days is diagnostic of congenital disease.[11]
IgA detection in the adult patient is of little value in diagnosing recent infection (can remain positive for over a year after acute infection).
Result
detectable anti-Toxoplasma IgA
Toxoplasma-specific IgG avidity index (serum)
Test
Useful in pregnant women who have detectable IgG and IgM as it identifies recent versus chronic infection.
A high avidity result in the first 12 to 16 weeks of pregnancy rules out infection acquired during pregnancy.
A low IgG avidity result should not be interpreted as an indication of recent infection because the IgG response can mature slowly over several months in some people.[39]
Result
high avidity index indicates a mature IgG response to Toxoplasma gondii and presumes infection is not acute
differential agglutination test (AC/HS)
Test
Used as part of a panel of tests by reference labs to diagnose infection during pregnancy.
Uses 2 antigen preparations found early during acute infection (AC) and in the later stages of infection (HS)
Ratios of AC and HS titers are interpreted as acute, equivocal, nonacute, or nonreactive.
The acute pattern may persist for 1 or more years following infection.
Result
ratio of AC/HS titer interpreted as acute
polymerase chain reaction (body fluids and tissue)
Test
Perform on amniotic fluid if the mother has serologic evidence of recent toxoplasmosis, in order to diagnose spread of infection to the fetus.
Diagnostic sensitivity is around 70% and specificity is around 90%.[10] Amniotic fluid PCR assay should be done at ≥4 weeks after acute primary maternal infection and at ≥18 weeks of gestation to reduce the risk of false negative results.[11]
Consider polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and urine in newborns with potential congenital disease.[11]
Perform on aqueous or vitreous fluid in patients with atypical retinal lesions who have a suboptimal response to anti-Toxoplasma treatment.[17]
In patients who are immunocompromised and suspected to have localized or disseminated disease, PCR can be performed on blood (buffy coat), other body fluids, bone marrow aspirate or tissue as a diagnostic aid.
In patients with AIDS, PCR of CSF has high specificity (97% to 100%) but low sensitivity (50% to 60%). Sensitivity is even lower after treatment is started.[40]
Consideration should be given to performing a PCR at regular intervals for screening purposes in patients who are at high risk of disseminated disease (e.g., heart or allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients).[41]
Result
detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in amniotic fluid indicates fetal infection. Detection of T gondii DNA in body fluids in an individual who is immunocompromised establishes infection. Detection of T gondii in vitreous fluid indicates ophthalmic infection
biopsy
Test
The immunoperoxidase method, which uses antisera to Toxoplasma gondii, is used on tissue sections, and Wright-Giemsa staining is used for specimens on slides.
Biopsy of brain lesions should be performed for patients with suspected toxoplasmosis who do not have improvement in lesions on brain imaging after 2 weeks of medical treatment. This is done to rule out other potential causes of such lesions.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Brain pathology: while this is pathology from mouse tissue, it is quite similar to the appearance in human tissueFrom the collection of Louis M. Weiss, MD, MPH; used with permission [Citation ends].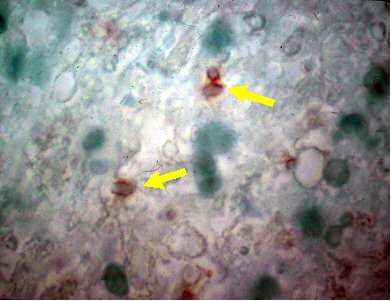
Result
cysts, free tachyzoites, inflammatory cells, necrotizing abscesses
Emerging tests
IgG or IgM Immunoblot (serum)
Test
Used in diagnosis of congenital disease.
Most useful in newborns with no demonstrable IgM and/or IgA by conventional serologic methods, born to mothers with confirmed or highly suspected acute infection.[39]
Differentiates between maternal IgG transferred through the placenta and IgG synthesized by the neonate.
For the newborn, Immunoblot has a sensitivity of around 70%. This sensitivity increases to 85% within the first 3 months after birth.[10]
Result
detectable anti-Toxoplasma IgG/IgM synthesized by the neonate indicates congenital infection
enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay
Test
Measures interferon-gamma production from a patient’s peripheral blood mononuclear cells in response to Toxoplasma gondii antigens.[34]
May be helpful in stratifying risk of recurrence of toxoplasmic encephalitis in T gondii IgG+ HIV-infected patients: a higher number of spots, indicating a greater amount of interferon-gamma production and thus a stronger immune response to T gondii, may correlate with reduced risk of recurrence of toxoplasmic encephalitis.
Not used by reference laboratories because cut-off values to discriminate among patients with adequate or insufficient T gondii-specific immune responses have not been determined.
Result
number of spots correlates with amount of interferon-gamma production; a higher number indicates a stronger immune response to T gondii
interferon-gamma release assay
Test
Measures interferon-gamma production from whole blood stimulated with Toxoplasma gondii antigen. Sensitivity and specificity of the test in infants suspected of having congenital disease were 94% and 98%, respectively.[33]
Absence of production of interferon-gamma in response to T gondii antigen may be used to rule out congenital infection in newborns and thus avoid the need for serologic follow-up. Production of interferon-gamma in response to T gondii antigen may rule in a diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis.
Requires only 1 mL of whole blood, which may be an important consideration in newborn testing. May help to interpret an ambiguous serologic status during pregnancy. Not commercially available or routinely performed by reference laboratories.
Result
presence of interferon-gamma
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer