Images and videos
Images
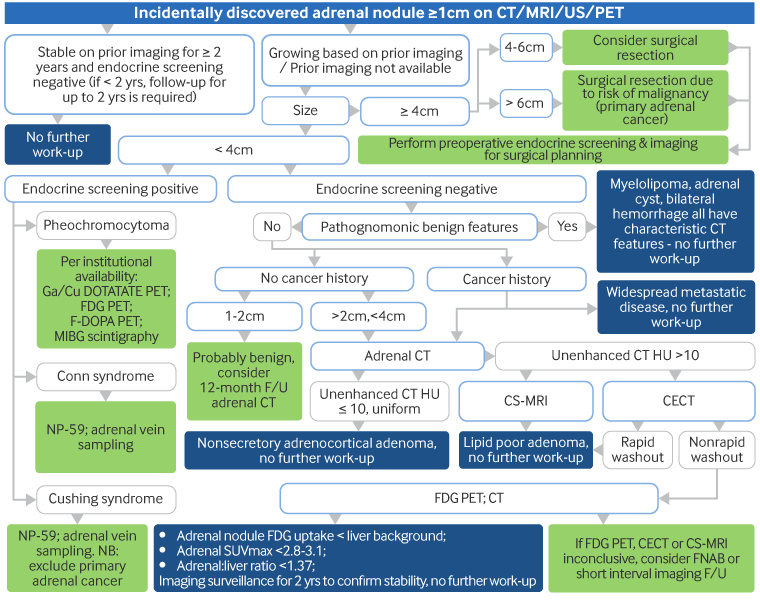
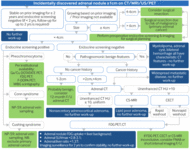
Evaluation of incidental adrenal mass
Workup of an adrenal mass incidentally found on imaging [Abbreviations: CT: computed tomography; CECT: contrast-enhanced CT; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; CS-MRI: compressed sensing MRI; F-DOPA: 3,4-dihydroxy-6-(18)F-fluoro-l-phenylalanine; FDG: 18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose; Ga/Cu DOTATATE: ⁶⁸Ga- or ⁶⁴Cu-DOTA-(Tyr3)-octreotate; FNAB: fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy; HU: Hounsfield unit; MIBG: meta-iodobenzylguanidine; NP-59: iodine-131-6-beta-iodomethylnorcholesterol (or radio-iodine-labeled norcholesterol); PET: positron emission tomography; SUVmax: maximum standardized uptake value; US: ultrasound]
Adapted by Dr Ka Kit Wong from Mayo-Smith WW et al. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017 Aug;14(8):1038-44; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
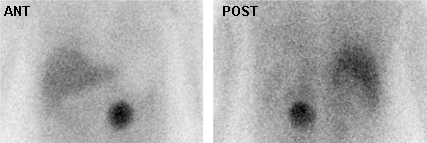
Evaluation of incidental adrenal mass
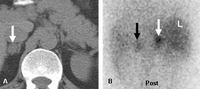
Meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scan demonstrating intensely focal tracer activity in the left adrenal gland consistent with pheochromocytoma in a 56-year-old woman with HTN, elevated plasma norepinephrine levels, and a 3 cm left adrenal mass seen on cross-sectional anatomic imaging
Avram A, Fig LM, Gross MD. Semin Nucl Med. 2006 Jul;36(3):212-27; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
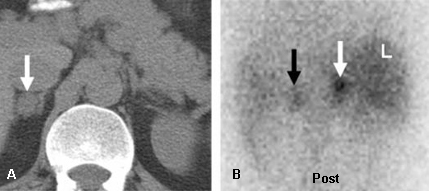
Evaluation of incidental adrenal mass
Incidentally discovered, 1.8 cm diameter, right adrenal mass in a 37-year-old man. Abdominal CT (A) depicts the mass as lipid-poor with atypical contrast enhancement; NP-59 scintigraphy done without dexamethasone suppression; (B) demonstrates a concordant pattern of imaging with right > left adrenal accumulation of iodocholesterol on the fifth and sixth days postinjection, compatible with a benign etiology
DeGroot LJ, Jameson JL, eds. Endocrinology, 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2006; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
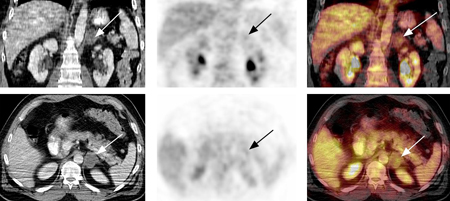
Evaluation of incidental adrenal mass
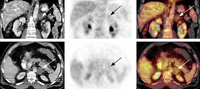
18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (FDG) PET-CT: adrenal adenoma. 46-year-old man with squamous cell carcinoma of the neck (TxN1 tumor) status post-external beam radiation therapy; restaging PET-CT demonstrates low-attenuation, non-FDG avid, 3.7 cm left adrenal nodule consistent with adrenal adenoma; FDG PET study excluded distant metastasis to the adrenal gland
Gross MD, Avram A, Fig LM, et al. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007 Apr;34(4):547-57; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Evaluation of incidental adrenal mass
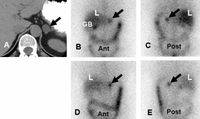
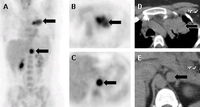
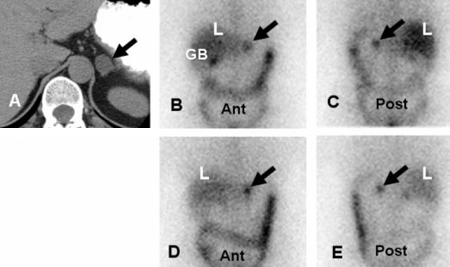
Left adrenal aldosteronoma depicted with dexamethasone suppression NP-59 imaging: 57-year-old woman with biochemical evidence of hyperaldosteronism and a left adrenal mass. Abdominal CT (A) demonstrates a 2 cm left adrenal mass (black arrow), anterior and posterior abdominal NP-59 scans (B and C) on the third day postinjection; anterior and posterior abdominal NP-59 scans (D and E) on the fifth day postinjection; abnormal left adrenal uptake (black arrows) occurs early, before day 5 postinjection (B and C); normal uptake in liver (L), bowel (B), and gallbladder (GB)
Rubello D, Bui C, Casara D, et al., Eur J Endocrinol. 2002 Jul;147(1):13-28; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Evaluation of incidental adrenal mass
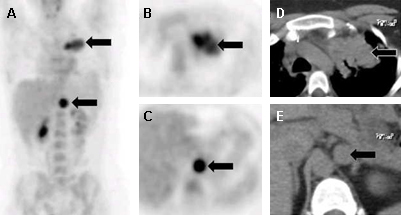
Left adrenal metastasis (arrow) depicted by 18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (FDG) PET-CT (A-C) in a patient with a non-small cell lung cancer (arrow); corresponding chest (D) and abdominal (E) CT scans identify the lung primary and the adrenal metastasis (arrow)
Avram A, Fig LM, Gross MD. Semin Nucl Med. 2006 Jul;36(3):212-27; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Evaluation of incidental adrenal mass
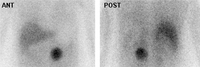
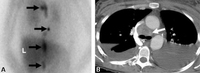
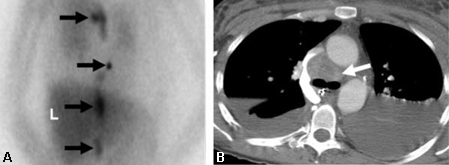
Malignant, metastatic pheochromocytoma demonstrated by 123-I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) and CT in a 31-year-old woman after bilateral adrenalectomy and persistent HTN complicated by renal insufficiency and recent development of superior vena cava (SVC) obstruction; (A) anterior chest and abdomen scan. L = normal liver uptake while arrows depict multiple, abnormal foci of 123-1-MIBG in metastatic pheochromocytoma deposits in the mediastinum and para-aortic regions; (B) chest CT identifies the superior mediastinal mass responsible for SVC obstruction (white arrow)
Rubello D, Bui C, Casara D, et al. Eur J Endocrinol. 2002 Jul;147(1):13-28; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Evaluation of incidental adrenal mass
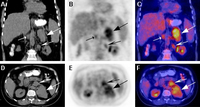
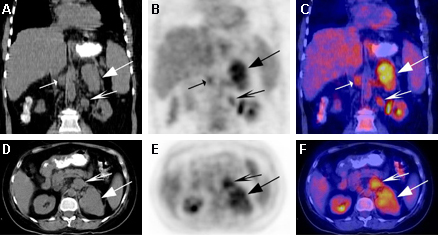
18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (FDG) PET-CT: adrenocortical carcinoma. 51-year-old woman with Cushing syndrome and large, multilobulated and intensely 18-F-FDG avid left adrenal mass and metastatic aortocaval and left para-aortic lymph nodes
Gross MD, Avram A, Fig LM, et al. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007 Sep;51(3):272-83; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer