Tests
1st tests to order
synovial fluid Gram stain and culture
Test
It is recommended that synovial fluid for Gram stain and culture be drawn before starting antibiotic therapy.
There is some evidence that the yield of culture is improved by inoculating synovial fluid into blood culture bottles at the bedside.[25][26]
Positive in approximately 70% of cases.
Microscopic analysis and culture may reveal the causative organism and its sensitivities.
Polarizing microscopy may reveal the presence of urate or pyrophosphate crystals (gout or pseudogout).
A negative result does not exclude the diagnosis of septic arthritis.
Crystal arthritis and septic arthritis can coexist.
In the case of suspected sepsis in a prosthetic joint, referral should always be made to an orthopedic surgeon, since arthrocentesis should not be performed outside of a sterile operating room environment.
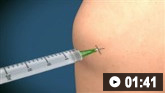
How to aspirate synovial fluid from the knee and administer intra-articular medication using a medial approach.
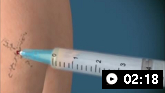
How to aspirate synovial fluid from the shoulder and administer intra-articular medication. Video demonstrates a posterior approach to the glenohumeral joint and a lateral approach to the subacromial space.
Result
presence of microorganisms; subsequent culture revealing organism type and sensitivities to antibiotic therapy
synovial fluid white cell count
Test
It is recommended that synovial fluid for white cell count be drawn before starting antibiotic therapy. The synovial fluid white cell count is neither 100% sensitive nor 100% specific, although a count of >100,000 cells/microliter significantly increases the likelihood of the diagnosis of sepsis.[33]
In the case of suspected sepsis in a prosthetic joint, referral should always be made to an orthopedic surgeon, since arthrocentesis should not be performed outside of a sterile operating room environment.
How to aspirate synovial fluid from the knee and administer intra-articular medication using a medial approach.
How to aspirate synovial fluid from the shoulder and administer intra-articular medication. Video demonstrates a posterior approach to the glenohumeral joint and a lateral approach to the subacromial space.
Result
quantity of white cells
blood culture
Test
It is recommended that blood for cultures should always be taken before starting antibiotic therapy.
Positive in approximately 25% of cases. In some cases the blood culture may be positive in the absence of a positive synovial culture. A negative result does not exclude the diagnosis of septic arthritis.
Result
presence of microorganisms; subsequent culture revealing organism type and sensitivities to antibiotic therapy
white cell count
Test
Not diagnostic.
Elevated in approximately 50% of cases.
Useful in monitoring the response to treatment.
Result
may be elevated
erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Test
Not diagnostic.
May be only moderately elevated, or normal.
Useful in monitoring the response to treatment.
Result
may be elevated
CRP
Test
Not diagnostic.
Useful in monitoring the response to treatment.
Result
elevated
plain radiograph
Test
No benefit in making the diagnosis but may reveal underlying joint disease.
Recommended as a baseline investigation.
Result
may reveal degenerative changes or chondrocalcinosis
ultrasound
Test
If hip sepsis is suspected, it is recommended that aspiration be performed under ultrasound guidance.
Result
may show the presence of an effusion to guide aspiration
Tests to consider
procalcitonin
MRI
Test
Not specific enough to be diagnostic.
Appropriate if suspecting associated osteomyelitis that may require a surgical approach.
Result
may show evidence of associated osteomyelitis
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer