History and exam
Key diagnostic factors
common
nodules on shins
Abrupt-onset, red, tender subcutaneous swellings on the legs.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema nodosum on the shin of a patient.From the personal collection of Dr Om P. Sharma, MD, FRCP, DTM&H; used with permission [Citation ends].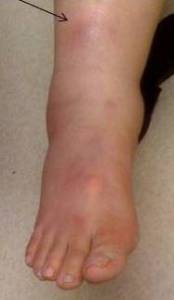 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema nodosum on a patient's legFrom the collection of Henry W. Lim, MD, Dept of Dermatology, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, MI; used with permission [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema nodosum on a patient's legFrom the collection of Henry W. Lim, MD, Dept of Dermatology, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, MI; used with permission [Citation ends].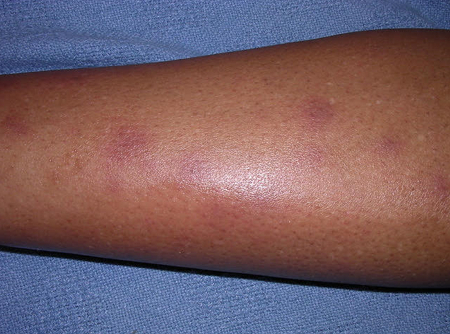
uveitis, red eyes, retinal nodules, or candle-wax drippings
Seen with sarcoidosis. Candle-wax drippings are waxy deposits on the sides of retinal veins.
nodules on other skin areas
Lesions can occur less commonly in areas other than the shins.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema nodosum on a patient's arms and handsCDC Public Health Image Library [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema nodosum lesions on skin of back due to hypersensitivity to antigens of Coccidioides immitisCDC Public Health Image Library [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema nodosum lesions on skin of back due to hypersensitivity to antigens of Coccidioides immitisCDC Public Health Image Library [Citation ends].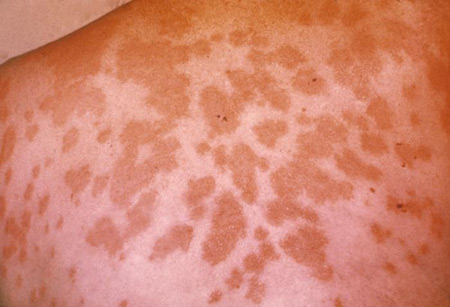
uncommon
anesthetic skin lesions
Raised skin lesions that are typically pale or slightly red, dry, hairless, and numb to touch. May indicate leprosy.
Other diagnostic factors
common
joint pains
Generalized joint pain with erythema and swelling can occur with erythema nodosum; can also suggest underlying rheumatologic disease.
fever
Fever and cough are common in bacterial and viral pneumonia.
uncommon
diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, hematochezia
Gastrointestinal symptoms may suggest possible underlying inflammatory bowel disease, Behcet disease, or Yersinia colitis infection.
enlarged spleen
May indicate histoplasmosis, brucellosis, bacterial endocarditis, or sarcoidosis as underlying cause.
miliary nodules on the retina
Seen in brucellosis and tuberculosis.
Risk factors
strong
streptococcal infection
sarcoidosis
EN may be a presenting feature in patients with sarcoidosis.[18]
Seen with bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, most commonly in northern Europe.
tuberculosis
Various risk factors, including exposure, institutionalization (in the US), concurrent HIV infection.
Tuberculosis is the most common etiology in developing countries.
coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis predominates in the western and southwestern regions of the US.[11][12]
Common in the San Joaquin Valley region of California, and in patients with a history of desert camping or digging.[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Erythema nodosum lesions on skin of back due to hypersensitivity to antigens of Coccidioides immitisCDC Public Health Image Library [Citation ends].
histoplasmosis
EN is one of the most common skin manifestations of histoplasmosis, which is seen mainly in the southern and midwestern US, the Mississippi valley, Central America, and parts of South America.[10]
blastomycosis
Endemic areas include the Mississippi and Ohio River basins, the midwestern US, and areas of Canada along the St Lawrence River and the Great Lakes. Also reported in Africa.
EN is rarely described in blastomycosis, but may be the cause in these regions.[13]
Behcet disease
oral contraceptives
Less common cause now that hormone concentrations are lower.
leprosy
More common in tropical countries and India.
weak
brucellosis
More common in the Middle East, tropical countries, and in dairy workers and farmers.
EN-like lesions are the most frequently encountered cutaneous lesions in brucellosis.[17]
sulfonamides
Uncommon cause.
Drugs such as sulfonamides, bromides, and oral contraceptives have been identified as the cause of EN in 3% to 5% of patients.[3]
iodides and antiepileptic drugs
Can also be associated with lesions.
psittacosis
Usually associated with exposure to birds.
inflammatory bowel disease
EN is the most common cutaneous manifestation of inflammatory bowel disease.[19][20][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Singular erythema nodosum mimicking cellulitis, the most common lesion associated with inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn disease (4-6% of patients, most often women ages 10-30 years)From the collection of Dr Daniela Kroshinsky, MD, MPH; used with permission [Citation ends].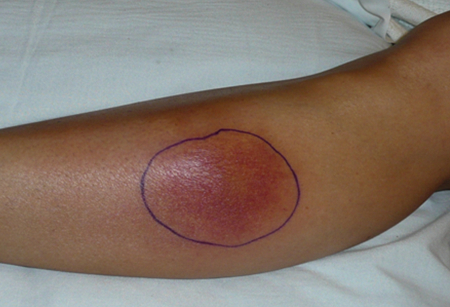
pregnancy
The cause in 2% to 6% of patients.[3]
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer