Tests
1st tests to order
CBC
CRP
Test
C-reactive protein is likely to be elevated.[9]
CRP level on admission ≥10 mg/L and leukocytosis ≥16,000/microliter are strong predictive factors for appendicitis in children
Result
there is no clear cut-off value for a raised CRP in children, CRP likely to be elevated
abdominal and pelvic CT scan
Test
Wall thickening, wall enhancement, and inflammatory changes in the surrounding tissues are additional findings seen in a CT scan of abdomen and pelvis.[69]
Appendiceal CT scan is increasingly used as the initial diagnostic test for acute appendicitis, and it is routine practice in the US to request a CT for patients presenting to the emergency room with features of acute appendicitis.[29] The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) offers a conditional recommendation for abdominal CT as the initial imaging modality to diagnose acute appendicitis.[53] A CT is also indicated in atypical presentations.[33][54]
Intravenous contrast is usually appropriate whenever a CT is obtained in adults with suspected acute appendicitis; however, CT without intravenous contrast also has high diagnostic accuracy in detecting acute appendicitis and may be appropriate.[33][53] Intravenous contrast-enhanced CT scan with or without oral contrast has up to 100% sensitivity compared with 92% sensitivity in nonintravenous, contrast-enhanced CT scan.[56][57][58] The IDSA recommends to consider observation and supportive care, with or without antibiotics, if CT is negative but clinical suspicion for acute appendicitis persists.[53] If clinical suspicion is high, consider surgical intervention.[53] Laparoscopy may also be reasonable if there is diagnostic uncertainty.
In pregnant women presenting with features of appendicitis, an abdominal sonogram should be performed to identify the appendix.[53] If the sonogram examination is inconclusive, abdominal MRI (particularly in early pregnancy) may be appropriate.[33][53][54]
In children where there is diagnostic doubt, and inconclusive ultrasound results, a second-line imaging technique (CT or MRI) should be used based on local availability and expertize.[7][Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: CT abdomen - thickened appendix.Nasim Ahmed, MBBS, FACS; used with permission [Citation ends].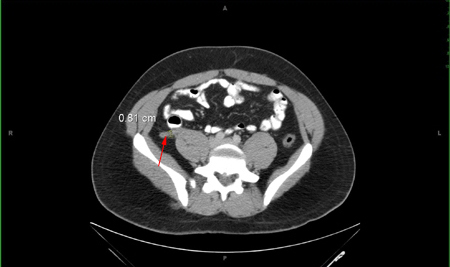
Result
abnormal appendix (diameter >6 mm) identified or calcified appendicolith seen in association with periappendiceal inflammation, fat stranding
Tests to consider
abdominal ultrasound
Test
Although CT scan has greater sensitivity and specificity than ultrasound in diagnosing appendicitis, the latter is readily available, rapid, and able to be performed at the bedside.[7][48][49][50] Ultrasound has a sensitivity of 71% to 94% and specificity of 60% to 98% for acute appendicitis; if ultrasound is unequivocally positive for appendicitis, ultrasound has comparable accuracy to a positive CT or MRI for ruling in appendicitis.[51][52] If, on ultrasound, a normal appendix is visualized in its full length, then acute appendicitis can be excluded. However, this is rarely the case, and the greatest utility for ultrasound is to detect an alternative cause of abdominal pain that excludes appendicitis.[7]
In pregnant women presenting with features of appendicitis, an abdominal sonogram should be performed to identify the appendix.[53] If the sonogram exam is inconclusive, an abdominal MRI (particularly in early pregnancy) may be appropriate.[33][35][53][54]
In children, point-of-care ultrasound is the most appropriate first-line diagnostic tool, if an imaging investigation is indicated based on clinical assessment.[52][53]
Sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound may be higher in children compared with adults.[48][70][71]
In children with inconclusive ultrasound results, a second-line imaging technique (CT or MRI) can be chosen based on local availability and expertize.[7][53] Low dose CT is preferred if ultrasound is negative.[7]
Result
aperistaltic or noncompressible structure with outer diameter >6 mm, fluid collection if perforated, fat stranding, appendicolith
urinalysis
Test
If positive for red cells, white cells, or nitrates, an alternative diagnosis such as renal colic or urinary tract infection should be considered.
Result
negative
urinary pregnancy test
Test
If positive, the possibility of ectopic pregnancy should be considered.
Result
negative
abdominal and pelvic MRI in pregnancy
Test
In pregnant women presenting with features of appendicitis, an abdominal sonogram should be performed to identify the appendix. If the sonogram examination is inconclusive, abdominal MRI (particularly in early pregnancy) may be appropriate.[33][54] MRI has been proven to be a highly accurate diagnostic test for acute appendicitis, with a sensitivity of 0.96 and specificity of 0.97 in pregnant women.[59]
A negative or inconclusive MRI does not exclude appendicitis and surgery should still be considered if clinical suspicion is high.[7]
Result
abnormal appendix (diameter >6 mm) identified and evidence of periappendicial inflammatory changes, appendicolith, fat stranding
Emerging tests
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
serum sodium
pentraxin-3
Test
Pentraxin-3 is an acute phase protein, which may be elevated in acute appendicitis.[64]
Result
elevated pentraxin-3
serum amyloid A
Test
A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that serum amyloid A has a sensitivity and specificity for acute appendicitis of 0.87 and 0.74 respectively.[65]
Result
elevated serum amyloid A
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer