Images and videos
Images
Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
Transthoracic echocardiogram: apical 4-chamber view showing significant right atrial and right ventricular dilation
From the personal collection of the author, Gustavo A. Heresi, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
Comprehensive risk assessment in pulmonary arterial hypertension (three-strata model). 6MWD, 6-minute walking distance; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; CI, cardiac index; cMRI, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; CPET, cardiopulmonary exercise testing; HF, heart failure; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; PAH, pulmonary arterial hypertension; pred., predicted; RA, right atrium; RAP, right atrial pressure; sPAP, systolic pulmonary arterial pressure; SvO2, mixed venous oxygen saturation; RVESVI, right ventricular end-systolic volume index; RVEF, right ventricular ejection fraction; SVI, stroke volume index; TAPSE, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion; VE/VCO2, ventilatory equivalents for carbon dioxide; VO2, oxygen uptake; WHO-FC, World Health Organization functional class. a: Occasional syncope during heavy exercise or occasional orthostatic syncope in a stable patient. b: Repeated episodes of syncope even with little or regular physical activity. c: Observe that 6MWD is dependent upon age, height, and burden of comorbidities.
European Heart Journal. 2022 Oct 7;43(38):3618-731; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
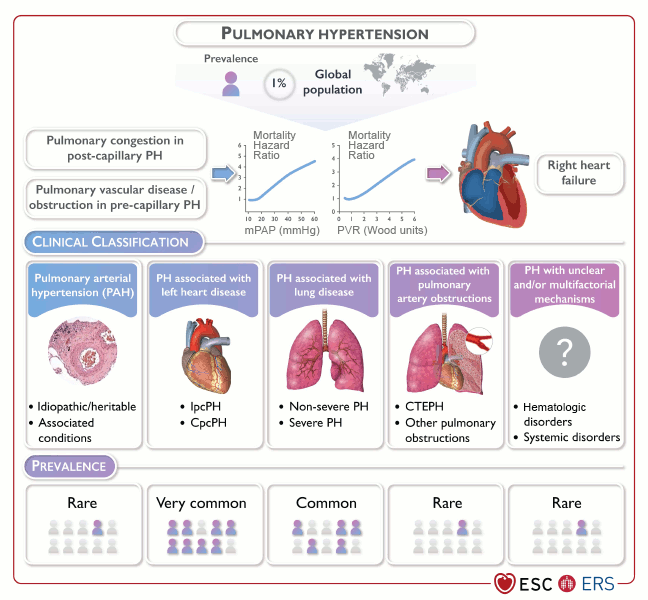
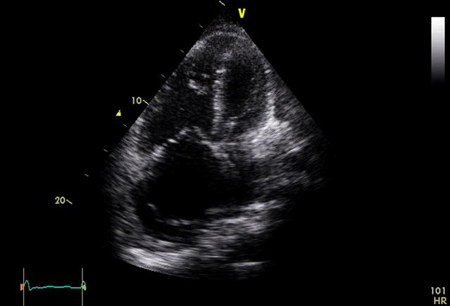
Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
Clinical classification and prevalence of pulmonary hypertension. CTEPH, chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; CpCPH, combined post- and pre-capillary pulmonary hypertension; IpcPH, isolated post-capillary pulmonary hypertension; mPAP, mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PH, pulmonary hypertension; PVR, pulmonary vascular resistance.
Adapted from Eur Heart J, Volume 43, Issue 38, 7 October 2022, 3618–731; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
ECG showing a tall R wave and small S wave (R/S ratio >1) in lead V1, qR complex in V1, right axis deviation, and right atrial enlargement (P wave ≥2.5 mm in lead II)
From the personal collection of the author, Gustavo A. Heresi, MD
See this image in context in the following section/s:

Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
Variables used to calculate the simplified four-strata risk-assessment tool
European Heart Journal. 2022 Oct 7;43(38):3618-731; used with permission
See this image in context in the following section/s:
Use of this content is subject to our disclaimer